- The paper presents a novel system X that integrates a dynamic PCG management protocol with a multi-agent framework to generate realistic urban scenes.
- It leverages multimodal inputs such as OSM, semantic maps, and satellite images to optimize asset selection and ensure scene consistency.
- Experiments demonstrate that X outperforms previous methods in geometric regularity and aesthetic evaluation for unbounded 3D city generation.
Controllable Procedural Content Generation for Unbounded 3D Cities
Introduction
Procedural Content Generation (PCG) for large-scale 3D urban environments presents a complex challenge due to the diverse 3D assets involved and the necessity for strict, varied layout constraints. Existing methodologies have attempted to address these issues using generative models or NeRF-based approaches but often fall short in scaling and fine-grained control. "CityX: Controllable Procedural Content Generation for Unbounded 3D Cities" (2407.17572) introduces a novel multi-modal controlled PCG method, named X, designed to enhance the generation of realistic 3D cities guided by multimodal inputs such as OpenStreetMap (OSM), semantic maps, and satellite images.
Methodology
The proposed system, X, integrates a PCG management protocol with a multi-agent framework to generate and manage urban scenes effectively.
PCG Management Protocol
X introduces a dynamic protocol to integrate various PCG plugins, managing the complex interaction between these plugins and Blender’s action functions. This protocol comprises:
- Dynamic API Conversion Interface: Facilitates the integration and communication among diverse PCG APIs, enabling seamless adaptation of different plugin formats.
- Structured Encapsulation: Lowers the technical barriers for beginners by employing a consistent structure for action functions, making it easier to utilize complex PCG functionalities within the Blender environment.
- Infinite Asset Libraries: Utilizes a continually expanding library of assets coupled with an innovative asset-retrieval system through pre-trained CLIP models, optimizing the asset selection process to fit city layout demands.
Multi-Agent Framework
This framework orchestrates the procedural generation process through multiple specialized agents:
- Annotator: Labels action functions for easy access by other agents.
- Planner: Devises a flexible, open-loop workflow that dynamically adjusts to user inputs and system feedback, ensuring coherent task execution.
- Executor: Operates within Blender to execute tasks using structured encapsulation, thereby enhancing system interactivity and accuracy.
- Evaluator: Employs visual feedback to assess task completion, guiding the system towards more precise urban scene generation.

Figure 1: The proposed X, under the guidance of multimodal inputs including OSM data, semantic maps, and satellite images, facilitates the automatic creation of realistic large-scale 3D urban scenes.
Experiments and Results
Experiments demonstrate the efficacy of X in producing realistic urban environments from various multimodal inputs. The framework not only supports diverse inputs but also improves scene realism and consistency when compared to existing methods.
Comparative Study
X outperforms prior city generation methodologies like CityDreamer and SceneDreamer under different input conditions by addressing issues such as asset overlap and repetitive structures. The system's ability to maintain geometric regularity while ensuring high-quality output sets it apart.

Figure 2: Comparative results on city generation. Issues with unreasonable geometry are observed in previous works, while our method performs well in generating realistic large-scale city scenes.
Aesthetic Evaluation
In collaborative aesthetic evaluations involving both experts and volunteers, X achieved higher scores across both aesthetic and rationality dimensions, marking a significant improvement in urban scene generation quality.
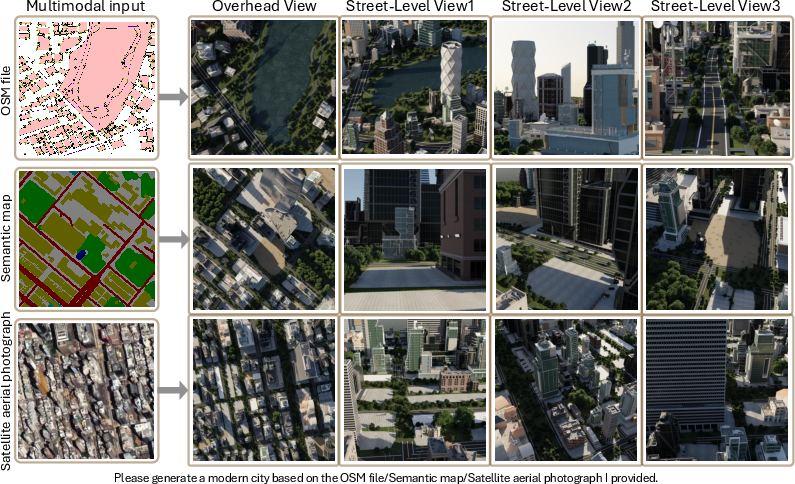
Figure 3: Urban scene generation with multimodal inputs, where we present an overhead view aligned with the multimodal input perspective, along with three street-level views.
Conclusions
X represents a significant advancement in procedural content generation for urban environments, effectively bridging the gap between generated assets and industrial requirements. Its capacity for handling multimodal inputs and delivering scalable, high-resolution 3D city scenes highlights its potential contributions to the PCG community and its applications in gaming, virtual reality, and animation industries.
The multi-agent framework is particularly noteworthy for its innovative handling of complex interactions within urban generation tasks, providing a versatile and scalable solution that could inform future developments in procedural generation systems. While promising, future research may focus on enhancing parameter extraction efficiency and broadening the diversity of generation techniques beyond existing procedural constraints.




