- The paper presents QOQA, a framework that leverages LLM-driven query rephrasing and alignment scoring to reduce hallucinations in RAG systems.
- It employs BM25, dense, and hybrid scores to evaluate query-document alignment, achieving a notable nDCG@10 score improvement on the SciFact dataset.
- The approach integrates query expansion and optimization to generate precise queries, thereby enhancing document retrieval and factual grounding in generated responses.
Optimizing Query Generation for Enhanced Document Retrieval in RAG
The research introduces an innovative approach to addressing hallucinations in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems by optimizing query generation. RAG combines document retrieval with language generation to improve the factual accuracy of responses by grounding them in external documents. However, existing RAG systems often suffer from vague or ambiguous queries, leading to hallucinations in the generated output. This study proposes Query Optimization using Query expAnsion (QOQA) to generate precise queries that enhance document retrieval.
Introduction
LLMs have excelled in various NLP tasks, but their susceptibility to generating incorrect information, known as hallucinations, remains a significant challenge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) partially mitigates this issue by providing factual grounding through document retrieval. However, inaccurate queries can still result in hallucinations, highlighting a critical limitation in current RAG implementations. The paper addresses this limitation by introducing QOQA, which employs query expansion and optimization to improve the precision of document retrieval in RAG systems by utilizing a query-document alignment score to guide the refinement process.
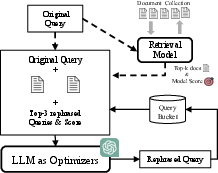
Figure 1: Concept figure of QOQA. Given expansion query with top-k docs, we add top-3 rephrased queries and scores to LLM. We optimize the query based on the scores and generate the rephrased query.
Query Optimization using Query Expansion
Query Optimization with LLM
The QOQA method begins by generating multiple rephrased versions of an original query using a LLM. These rephrased queries are evaluated for their alignment with retrieved documents using a scoring function, and the best-performing rephrased queries are retained. The process involves creating an expanded query that includes information from the top retrieved documents, which helps in generating more precise reformulations. The rephrased queries undergo an optimization process, whereby high-score queries expand the query bucket, improving the overall retrieval precision. Prompt templates (Figure 2) are utilized to dynamically adjust the information provided to the LLM, ensuring the most effective query generation.

Figure 2: Prompt template used in QOQA. The black texts describe instructions of the optimizing task. The blue texts show the original query with top-N retrieved documents.
Query-Document Alignment Score
To evaluate the effectiveness of generated queries, the study employs three types of alignment scores: BM25 for sparse retrieval, dense retrieval scores based on embedding similarity, and hybrid scores which combine both approaches. The BM25 score utilizes term frequencies and inverse document frequencies to assess query relevance, whereas dense scores leverage vector representation alignment for a more semantic evaluation. Hybrid scores integrate these methodologies, offering a balanced approach to measuring query effectiveness.
Results and Analysis
The research evaluates QOQA on several datasets including SciFact, Trec-Covid, and FiQA, demonstrating that the system improves document retrieval accuracy. In experiments, the QOQA-enhanced retrieval model shows a notable increase in nDCG@10 scores compared to baseline methods, indicating more relevant document retrieval across different domains. For example, using the BM25 score, QOQA achieved an nDCG@10 score of 75.4 on the SciFact dataset, outperforming baseline models.
Case analyses further highlight the effectiveness of QOQA in generating rephrased queries that include precise and relevant keywords (Table 2), resulting in retrieval of documents that align closely with the users' information needs. The ablation studies (Table 3) validate the significance of both the expansion and optimization components, with notable performance drops when either is removed.
Conclusion
The paper presents a robust framework for optimizing query generation in RAG systems through the novel application of query expansion and refinement techniques. By leveraging the power of LLMs to generate and score query rephrasings, QOQA substantially reduces hallucination occurrences by enhancing document retrieval precision. The study establishes that precise query generation is crucial for improving RAG system reliability. Future work may explore the integration of more sophisticated query refinement techniques and expand the applicability across different RAG use cases.



