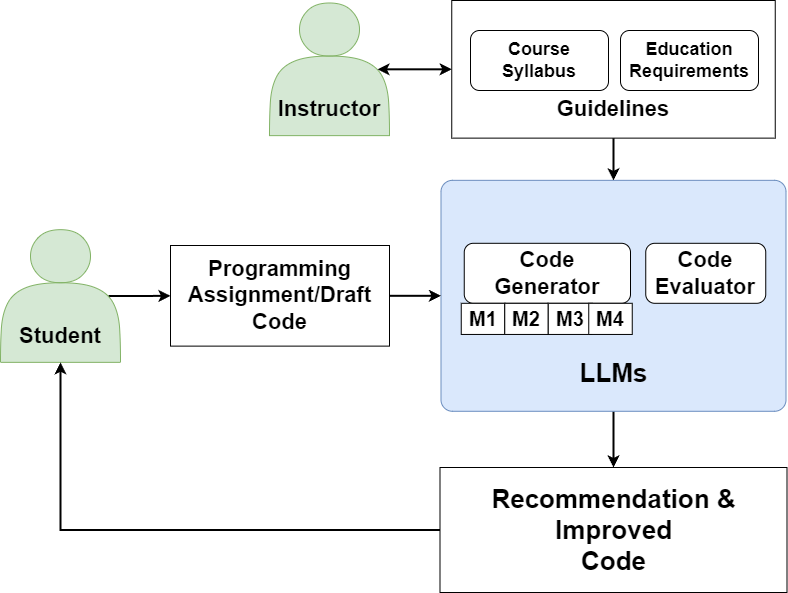
- The paper introduces a framework to categorize prompt engineering strategies for various coding education contexts.
- It demonstrates that multi-step prompts, especially with GPT-4 and GPT-4o, boost accuracy, speed, and adherence to coding standards.
- The study offers actionable guidelines for educators and highlights ongoing challenges in addressing complex, multi-stage programming problems.
Enhancing Computer Programming Education with LLMs: A Study on Effective Prompt Engineering for Python Code Generation
Introduction
The paper "Enhancing Computer Programming Education with LLMs: A Study on Effective Prompt Engineering for Python Code Generation" investigates the transformative potential of LLMs in the field of computer programming education. The research focuses on how tailored prompt engineering strategies can enhance the educational utility of LLMs, particularly in generating Python code. The paper leverages models like GPT-4, GPT-4o, Llama3-8b, and Mixtral-8x7b, employing datasets from LeetCode and USACO to evaluate model efficacy.
Research Contributions
The paper addresses three primary research questions:
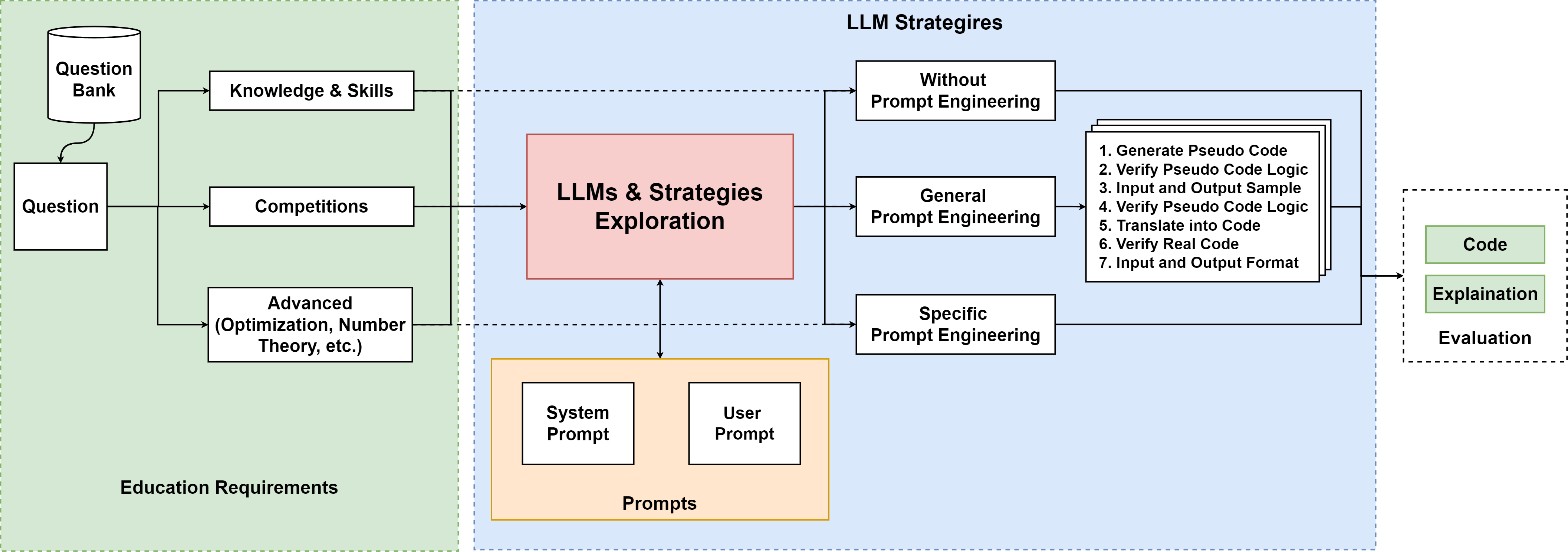
- Categorization of Prompt Strategies: The paper proposes a framework to systematically categorize prompt engineering strategies based on educational needs. This categorization helps optimize learning experiences across foundational, competitive, and advanced problem-solving contexts.
- Empowerment of LLMs: It examines how specific prompts can enhance the problem-solving capacity of LLMs beyond their native capabilities, especially when engaged with complex coding challenges.
- Evaluation Framework: The research establishes a robust framework for testing different prompt strategies, providing educators with actionable guidelines to implement LLMs effectively in programming education.
Methodology
The methodology involves a structured approach where programming questions are categorized, various prompt engineering strategies are applied, and the generated responses are evaluated. Key methodological steps include:
Experimental Results
LeetCode Dataset
The analysis on LeetCode datasets demonstrated that GPT-4 and GPT-4o substantially outperformed other models. Performance metrics indicated:
- Accuracy: Both models achieved near-perfect accuracy, with GPT-4o showing a slight edge in multi-step prompts.
- Time Efficiency: GPT-4 was the most time-efficient across all prompt types, supporting its use in time-sensitive educational scenarios.
- Code Quality: High Pylint scores underscored sound adherence to coding standards, vital for educational integrity and maintainability.
USACO Dataset
The USACO analysis provided deeper insights into the use of advanced and specific prompts:
Discussion
The research suggests that prompt engineering can dramatically enhance LLM efficacy in educational contexts, with tailored strategies recommended for various learning objectives. For instance:
- Basic Instruction: Direct problem statements suffice for basic coding skills due to pre-existing exposure in LLM training data.
- Competitive Programming: Multi-step conversational prompts excel in competitions, offering iterative refinement and contextual understanding.
- Advanced Problems: Highly specific, detailed prompts are essential for tackling sophisticated algorithms and mathematical challenges.
The paper's findings support the use of GPT-4o, emphasizing its adaptability and superior performance across scenarios requiring iterative and complex problem-solving approaches.
Conclusion
This paper underscores the potential of LLMs in redefining computer programming education through strategically engineered prompts. By systematically categorizing and testing prompts, educators can deploy LLMs to effectively enhance learning outcomes, from fundamental skill acquisition to addressing formidable cognitive challenges. Future research could extend these findings by developing more sophisticated prompt strategies to further improve LLM robustness and functionality in educational settings, addressing intricacies in logic, numerical complexity, and multi-stage contextual reasoning.
Figure 3: A screenshot of the USACO evaluation system displaying user submission results (all pass).