- The paper presents a human-AI collaborative approach that constructs structured taxonomies for enhancing profession-specific writing tools.
- It employs a three-step methodology—taxonomy generation, validation, and merging—to address limitations in clarity, coherence, and content accuracy from LLM outputs.
- The study demonstrates that integrating expert feedback with iterative LLM refinements leads to more precise and contextually relevant writing assistance.
Human-AI Collaborative Taxonomy Construction: A Case Study in Profession-Specific Writing Assistants
Introduction
The evolution of LLMs has significantly impacted the landscape of text revision and creative writing tasks. While LLMs like GPT-4 have demonstrated proficiency in generalized writing assistance, their deployment in specialized sectors such as business, law, or marketing—a domain-specific writing context—remains limited. This paper investigates the integration of Human-AI collaboration in constructing taxonomies that bolster the efficiency of profession-specific writing assistants powered by LLMs (2406.18675).

Figure 1: An end-to-end pipeline of our three-step Human-AI collaborative taxonomy construction process. For each step, we portray several design implications for better human-AI interaction strategies.
Challenges in Domain-Specific Writing
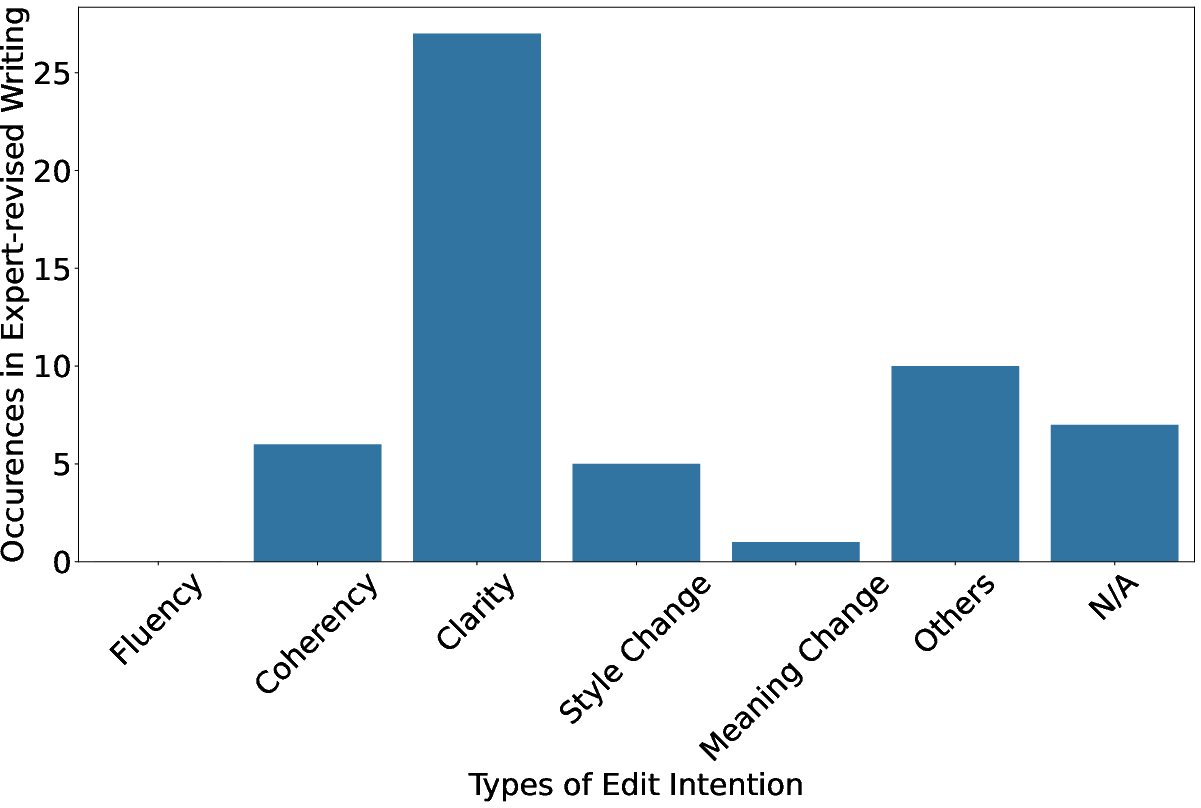
A formative paper involved professionals from marketing and human resources to assess LLM capabilities in domain-specific writing tasks. Participants provided inputs for generating writing templates using GPT-4, revised those templates, and annotated their modifications based on revision taxonomies (2406.18675). The results highlighted significant limitations in GPT-4's capacity to meet domain-specific expectations.
The paper identified multiple deficiencies in LLM-generated content:
These insights underscore the necessity for a refined taxonomy to guide LLMs in generating contextually appropriate content.
Proposed Taxonomy Construction Methodology
The paper proposes a collaborative approach involving iterative feedback between domain experts and LLMs, aimed at developing structured taxonomies tailored for specific professions (2406.18675).
Step 1: Taxonomy Generation
This phase employs LLMs to autonomously generate components of the taxonomy in the absence of pre-existing structured data. Using hierarchical prompts that leverage advanced designs in output specifications, LLMs create initial taxonomy drafts. Importantly, they provide explanations for each element to enhance the transparency and trustworthiness of the generated information.
Step 2: Taxonomy Validation
Experts validate and refine the generated taxonomy through an interactive dialogue process facilitated by LLMs acting as mediators. Multiple LLMs operate distinct roles: an 'Interviewer LLM' gathers expert feedback while a 'Creator LLM' integrates revisions based on these interactions. This dual-layer LLM usage aims to bolster the reliability of the taxonomy by integrating human insights into AI outputs.
Step 3: Taxonomy Merging and Testing
The final phase focuses on synthesizing validated taxonomies from different experts into a unified structure, mitigating individual biases. Further evaluations ensure that elements are exhaustive and comprehensive, drawing on standardized taxonomy evaluation practices and inter-coder reliability measurements.
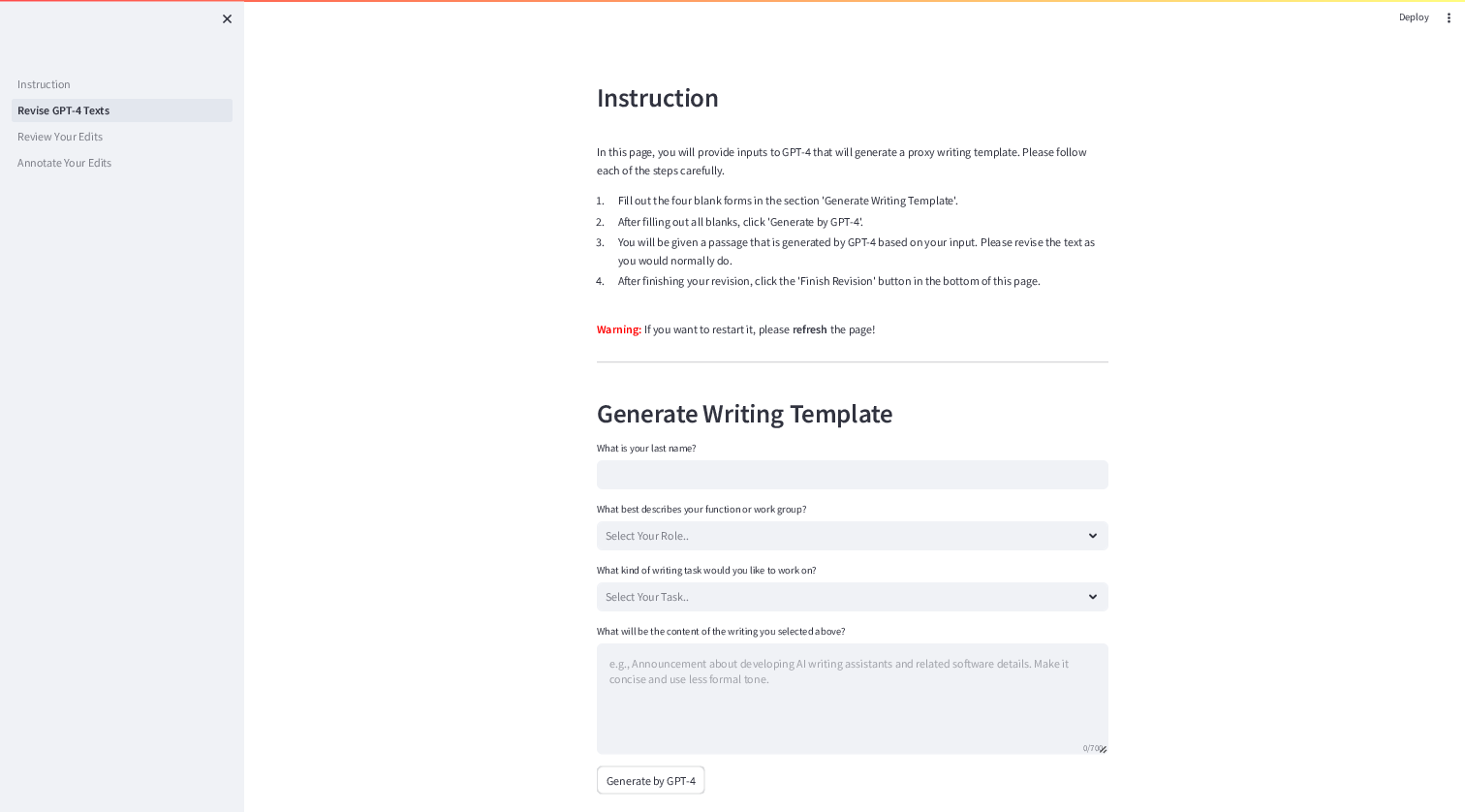
Figure 3: The interface for the first step, where a participant provided their background information that GPT-4 then used to generate a writing template.
Future Directions
Building on the initial successes of the formative paper, the research envisages a user-friendly web application supporting taxonomy development through structured user dialogues. Experimentation will extend to open-source models, enhancing accessibility and broad applicability across domains. This adaptive approach promises robust integration into profession-specific writing assistants (2406.18675).
Conclusion
This paper presents a comprehensive framework for leveraging Human-AI collaboration to construct domain-specific taxonomies for writing assistance tools. Through detailed interaction between experts and LLMs, the research aims to overcome current limitations in LLM applications, paving the way for more precise and relevant writing support tools tailored to professional needs.
The implementation of this structured taxonomy approach in profession-specific contexts offers significant prospects for enhancing the reliability and applicability of AI-driven writing assistance tools.