- The paper presents a novel method that uses evolutionary algorithms to automatically generate and optimize multi-agent systems.
- It integrates crossover and mutation with an LLM-based quality check to iteratively refine agent configurations.
- Experimental results on NLP and real-world planning tasks demonstrate enhanced scalability and performance compared to traditional frameworks.
EvoAgent: Automatic Multi-Agent Generation using Evolutionary Algorithms
The paper "EvoAgent: Towards Automatic Multi-Agent Generation via Evolutionary Algorithms" introduces a generic method for automatically extending expert agents into multi-agent systems using evolutionary algorithms. This paper addresses the limitations of existing LLM-based agent frameworks that rely heavily on human-designed settings. By leveraging evolutionary algorithms, EvoAgent enhances the scalability and effectiveness of multi-agent systems, allowing them to tackle more complex tasks.
Introduction and Background
The advent of LLMs, such as GPT-4 and Gemini, has driven advancements in autonomous agents capable of solving diverse tasks. Multi-agent systems combine the expertise of various agents to emulate human-like collaboration in addressing complex scenarios. Traditionally, these systems require extensive human intervention to design agent roles, task scopes, and framework settings. EvoAgent aims to alleviate these constraints by introducing a process analogous to biological evolution.
Evolutionary algorithms simulate the natural processes of mutation, crossover, and selection to optimize and generate diverse individuals. EvoAgent applies these principles to evolve agent settings automatically, creating specialized agents that collectively enhance task-solving capabilities. This approach transforms agent generation into an iterative procedure that begins with existing frameworks and evolves them without additional human labor.
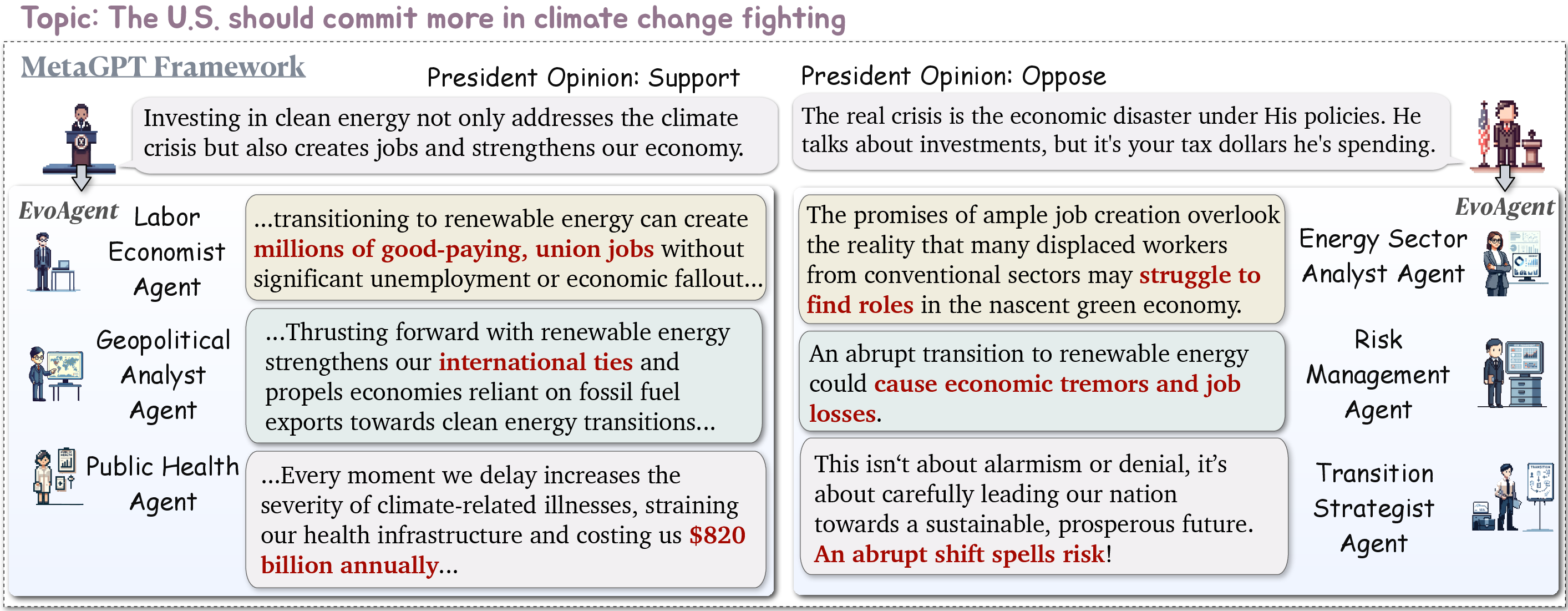
Figure 1: The adaption of EvoAgent on MetaGPT framework. With the EA, we can extend the original role in the debate scenario to different expert agents to enrich the opinions.
Methodology
EvoAgent's methodology consists of several steps:
- Initialization: EvoAgent commences with existing agent frameworks as the initial generation of agents. The framework design serves as the initial "individual" in evolutionary terms.
- Evolutionary Operations: EvoAgent uses crossover and mutation operators to derive new agents from the existing ones. During crossover, EvoAgent combines settings from successful agents to generate offspring agents. Mutation introduces variability by altering specific aspects of an agent's settings to discover optimal configurations.
- Selection Process: The system includes a quality-check module employing LLMs to validate the fitness of generated agents. The module ensures diversity among agents and the effectiveness of generated solutions, mimicking natural selection.
- Iterative Process: Agents undergo multiple evolutionary cycles, iteratively refining their settings through newly generated agents until high-quality, specialized agents are consistently produced.
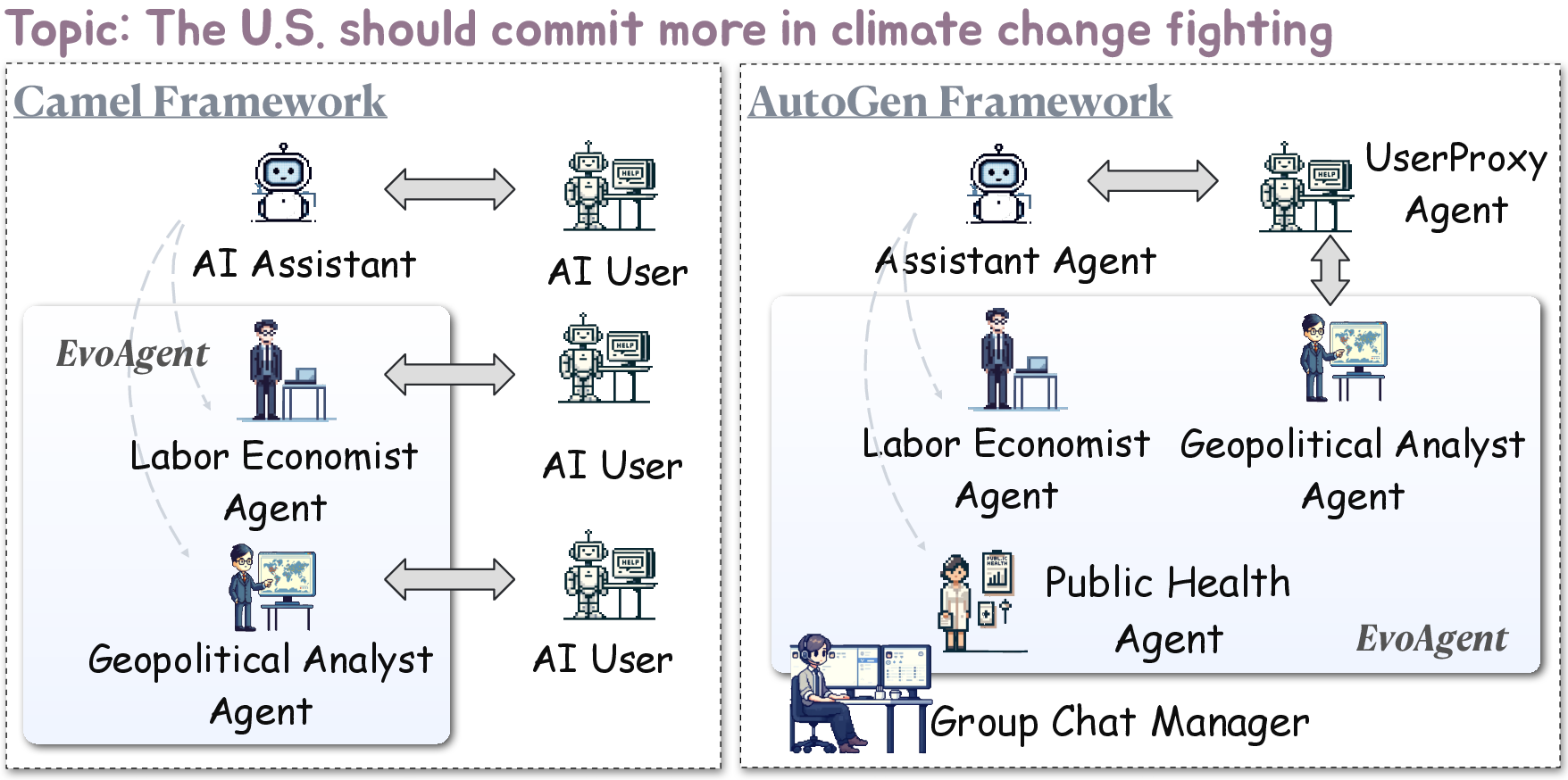
Figure 2: The adaption of EvoAgent on Camel and AutoGen frameworks.
Experimental Evaluation
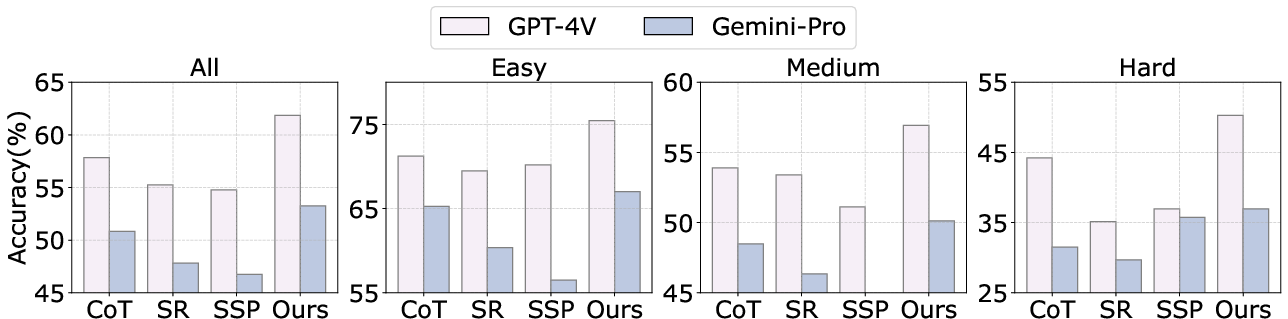
Experiments conducted on various NLP and multi-modal benchmarks demonstrate EvoAgent's ability to improve LLM-based agents:
Conclusion
EvoAgent represents a pioneering approach in automating the generation of multi-agent systems using evolutionary algorithms. By dispensing with human-designed frameworks and settings, EvoAgent enhances scalability and effectiveness, optimizing LLM-based agents for diverse real-world applications. The research establishes EvoAgent as a versatile method capable of extending any agent framework, highlighting its broad potential for future developments in AI.