- The paper introduces an automated pipeline that builds a 30,000-hour ASR corpus from unlabeled YouTube audio to support low-resource languages.
- It employs Whisper for transcription, TorchAudio for alignment, and iterative Noisy Student Training to improve label accuracy and reduce WER by up to 40%.
- The work demonstrates significant performance improvements over existing systems, paving the way for scalable multilingual ASR research.
GigaSpeech 2: An Evolving, Large-Scale ASR Corpus
The paper "GigaSpeech 2: An Evolving, Large-Scale and Multi-domain ASR Corpus for Low-Resource Languages with Automated Crawling, Transcription and Refinement" presents a comprehensive approach to developing a massive Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) dataset tailored specifically for low-resource languages. Unlike traditional methods reliant on expensive human labeling, GigaSpeech 2 uses innovative techniques to construct a large-scale corpus without paired speech and text data.
Introduction and Motivation
GigaSpeech 2 is motivated by the limitations faced in ASR for low-resource languages, where labeled training data is scarce and costly to produce. Traditional datasets cater predominantly to high-resource languages such as English and Mandarin, leaving a gap for languages like Thai, Indonesian, and Vietnamese. This corpus aims to bridge the gap by leveraging unlabeled YouTube audio to create a dataset with approximately 30,000 hours of speech data. This is achieved via a robust, automated pipeline without dependency on labeled data.
This approach includes initial transcription using Whisper, forced alignment with TorchAudio, and iterative label refinement through a modified Noisy Student Training (NST) method. The NST method iteratively refines pseudo labels, enhancing model performance significantly and reducing Word Error Rate (WER) by up to 40% compared to existing models.
Methodology
Automated Pipeline
The automated pipeline for constructing GigaSpeech 2 is designed to handle large volumes of audio data efficiently:
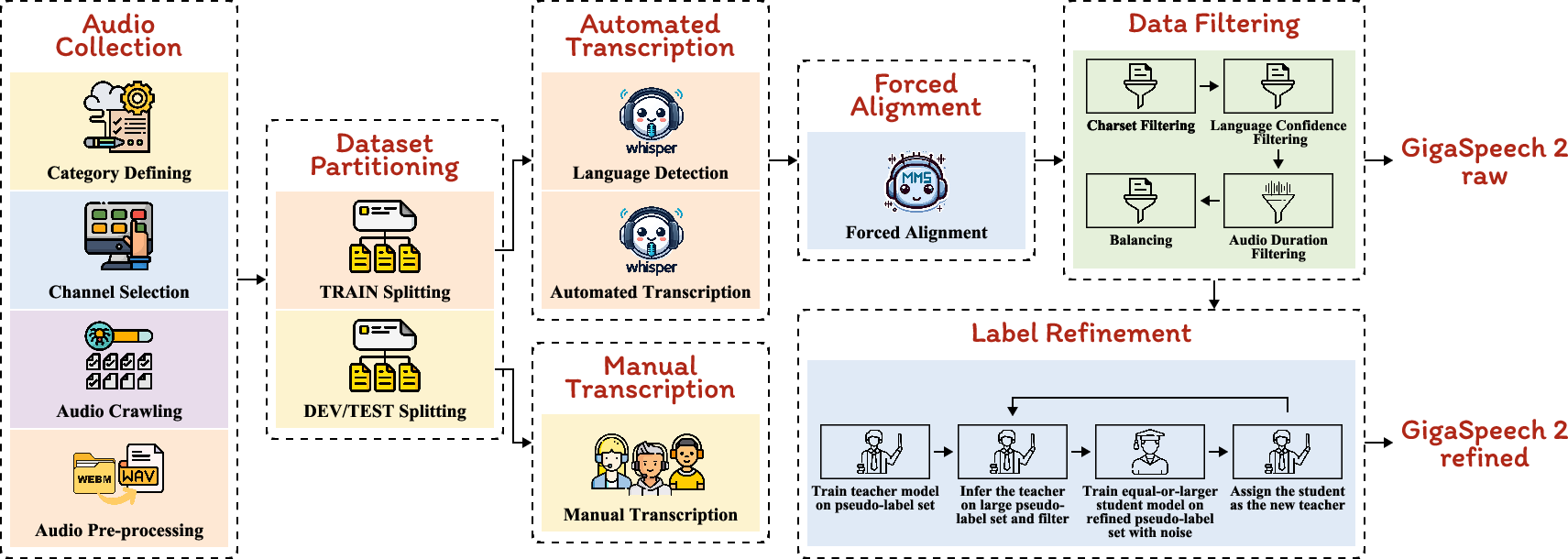
Figure 1: Automated construction pipeline of GigaSpeech 2, comprising (1) audio collection, (2) dataset partitioning, (3) automated transcription with Whisper, (4) forced alignment with TorchAudio, (5) transcription normalization, (6) data filtering, and (7) label refinement.
- Audio Collection: Audio files are collected from diverse YouTube channels, ensuring comprehensive domain coverage without speaker overlap.
- Transcription: Utilizing Whisper for language detection and transcription.
- Alignment and Filtering: Testing alignment accuracy with TorchAudio and applying multi-dimensional filters to enhance transcription quality.
- Label Refinement: The NST model iteratively refines labels, significantly improving transcription quality using techniques like SpecAugment and Bypass.
Label Refinement Process
The iterative Noisy Student Training involves training a teacher model on flawed labels and using it to generate new labels for a student model with added noise to improve robustness. Each iteration refines the label set, thus progressively enhancing model performance. This method employs stochastic depth (as feature masks) to introduce noise, facilitating robust learning patterns and reducing error rates over iterations.
Evaluation
GigaSpeech 2's ASR models demonstrate notable improvements across various benchmarks:
- Strong performance compared to both open-source and commercial systems, with superior results obtained for low-resource languages.
- Effective WER reduction compared to Whisper large-v3 models, highlighting computational efficiency and model robustness.
Quantitative analysis reveals performance improvements across multiple evaluation datasets (e.g., Common Voice, FLEURS), confirming the effectiveness of the iterative NST approach.
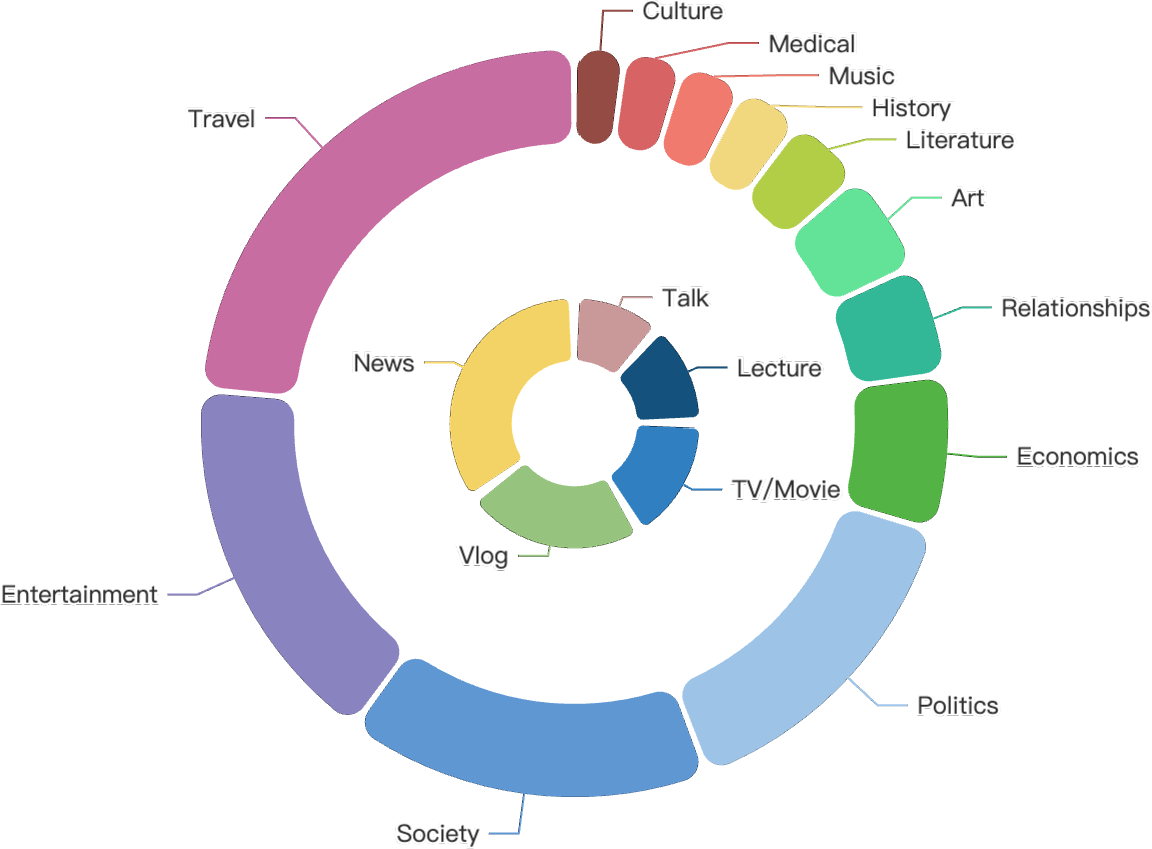
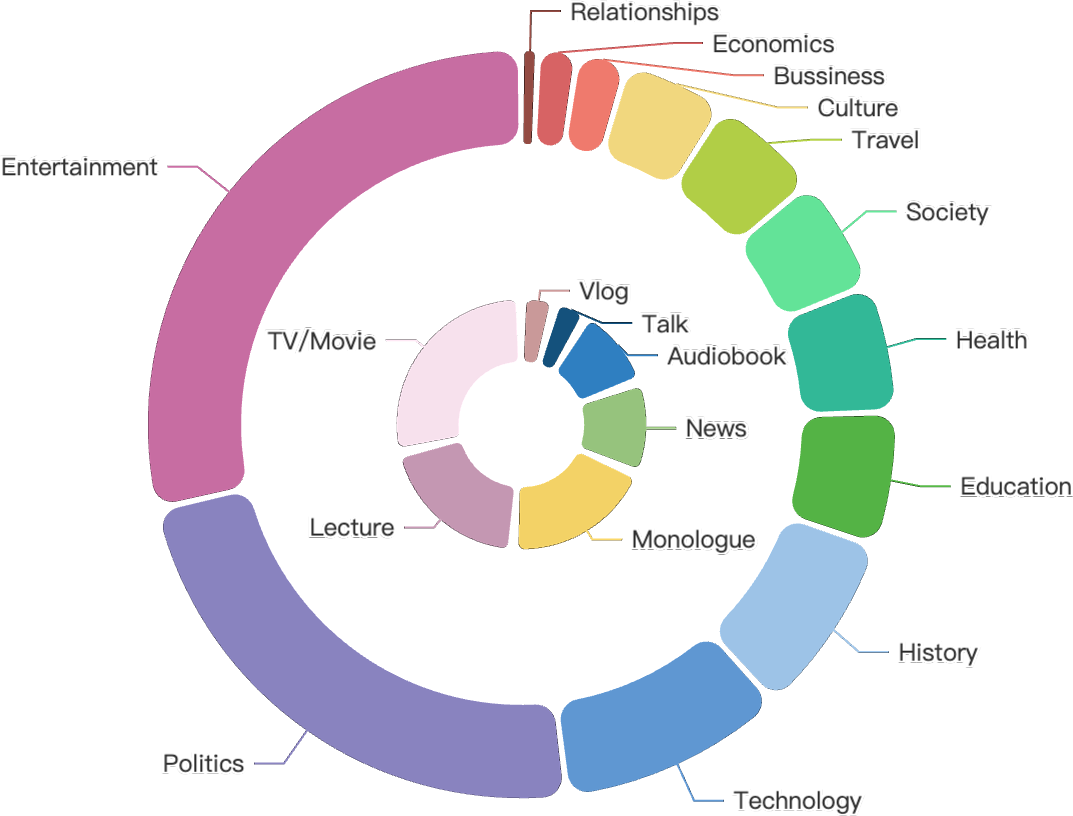
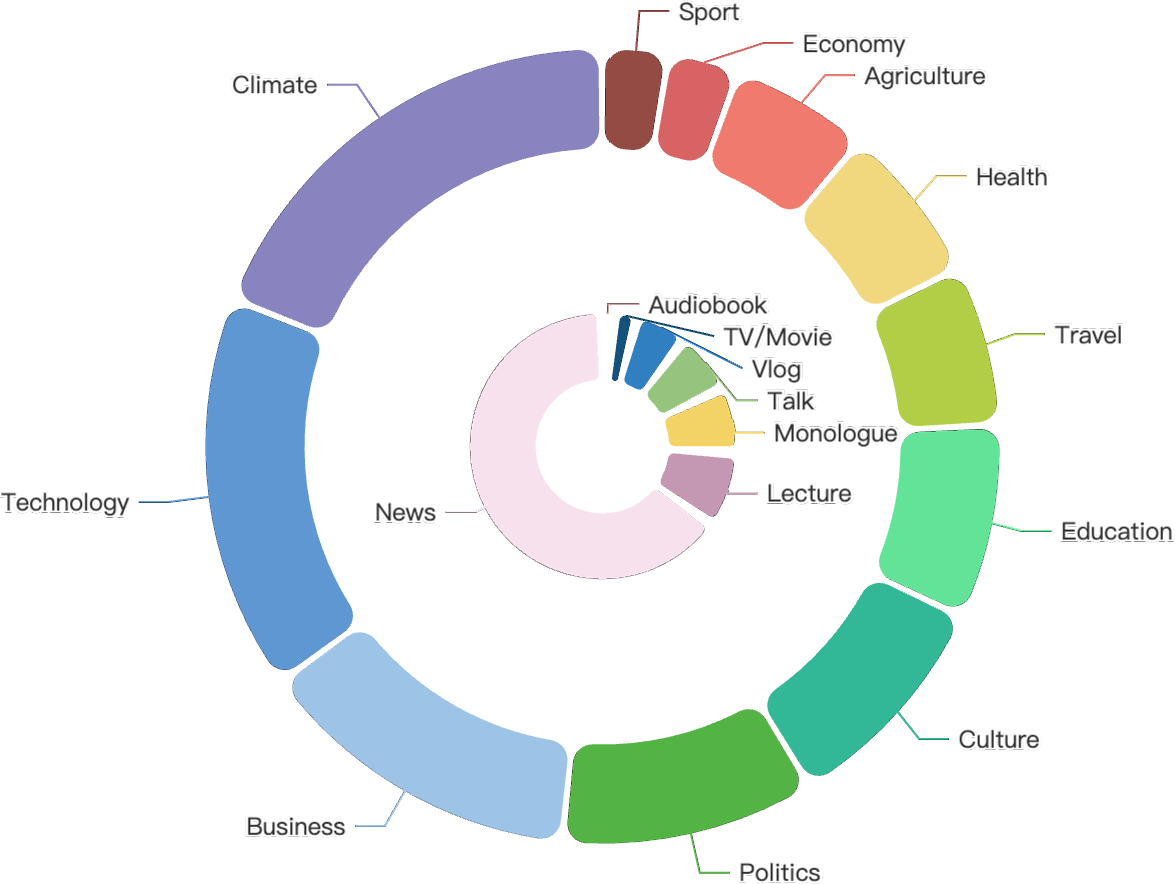
Figure 2: Hours distribution of manual evaluation sets for Thai, Indonesian, and Vietnamese.
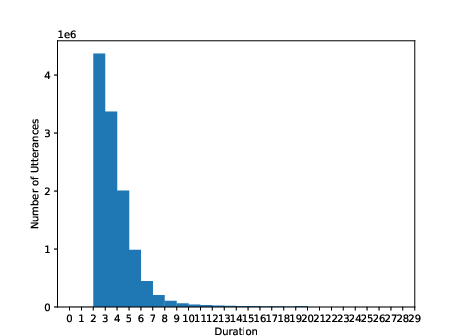
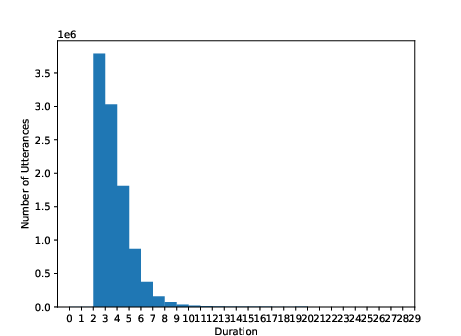
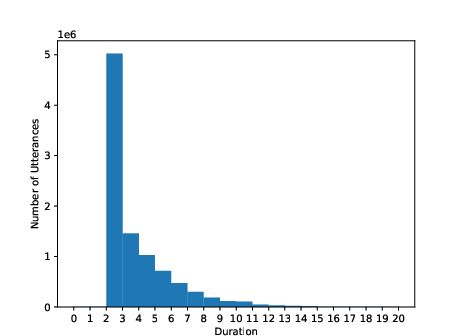
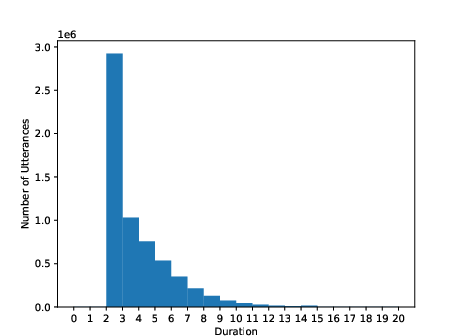
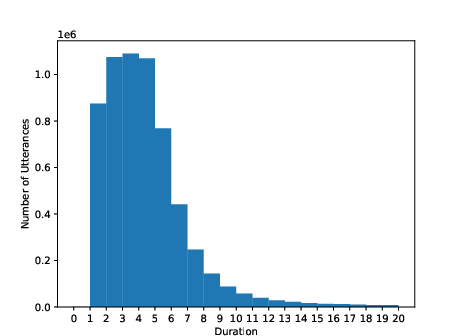
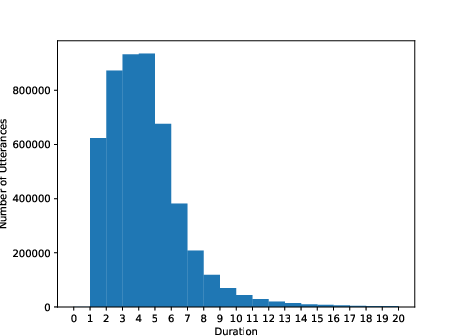
Figure 3: Utterance-level duration (second) distribution of training sets for Thai, Indonesian, and Vietnamese.
Implications and Future Work
The development of GigaSpeech 2 has substantial implications for ASR research, especially in low-resource languages. Reducing dependency on labeled data opens new avenues for multilingual speech recognition systems, enabling rapid adaptation to new languages and domains.
Future work includes scaling the number of NST iterations and expanding the dataset to cover additional Southeast Asian languages. Additionally, combining data from other sources may further refine LLM integration and boost model performance.
Conclusion
GigaSpeech 2 stands as a pivotal contribution to speech technology for low-resource languages, offering an innovative approach to large-scale dataset construction. By leveraging unlabeled data through efficient, automated processes, it provides a robust foundation for future ASR systems, facilitating research and development across diverse linguistic backgrounds. The dataset not only democratizes access to ASR technology but also underscores the potential of using large-scale unlabeled data effectively.











