- The paper presents using LLMs to generate synthetic queries that closely mirror real user interactions for voice assistants.
- It compares LLM-based methods with traditional template-based approaches using metrics like negative log-likelihood and reciprocal rank.
- It highlights the complementary benefits of both methods in addressing common and emerging query scenarios to improve VA responsiveness.
Synthetic Query Generation using LLMs for Virtual Assistants
This paper explores the integration of LLMs into synthetic query generation for Virtual Assistants (VAs), emphasizing the generation of queries that mirror user interactions and improve ASR systems' robustness, especially for emerging or infrequent use-cases.
Introduction
Virtual Assistants rely heavily on voice commands, where speech-to-text systems convert spoken queries into processable text. This system faces challenges, especially with phonetically similar terms, necessitating a robust query prior. Synthetic queries, traditionally generated using template-based methods, serve to reinforce these priors but often lack specificity and flexibility. The advent of LLMs offers a promising alternative to create more contextually rich and specific queries that might better capture the nuances of user intent.
Methodology
Approach
The paper proposes a method using LLMs for generating queries from textual descriptions sourced from Wikipedia. Entity-specific prompts are crafted for the LLM to simulate potential user queries. The approach is depicted in a structured pipeline (Figure 1).
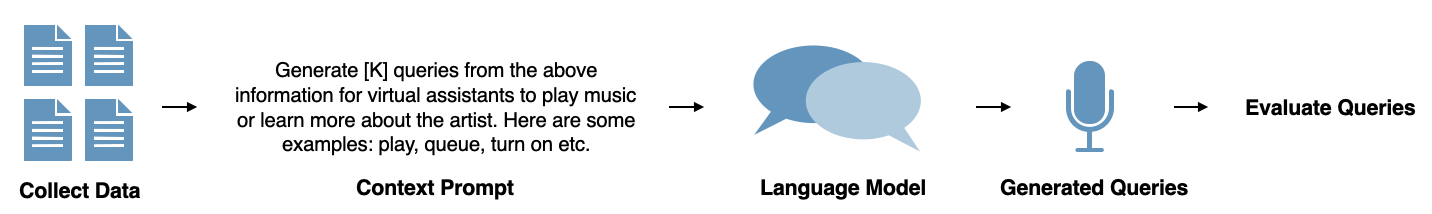
Figure 1: Proposed pipeline to generate queries for a VA via an LLM.
Knowledge Base and Prompt Engineering
A comprehensive knowledge base is constructed by linking metadata from popular music platforms to Wikipedia entries via SPARQL queries. This ensures detailed context for each artist, which is processed into prompts that guide the LLM in query generation. The prompts are finely tuned to reflect commands typical of VA interactions, such as playing specific songs or learning more about an artist.
Experimental Setup
Methods
The paper contrasts traditional template-based query generation with four variants of OpenAI's LLMs. Key evaluation measures include:
- Negative Log-Likelihood (NLL): This metric assesses how well the generated queries align with real-world VA query logs.
- Reciprocal Rank (RR): This measures how effectively the generated queries can retrieve the correct artist from a constructed index.
Query Generation
Queries are generated for over 14,161 music artists using both the entity name and synthetic methods, yielding diverse query structures. The LLM-based methods, particularly the GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 series, exhibit the capacity to generate semantically rich queries.
Results and Discussion
Query Length and Diversity
LLM-generated queries tend to be longer and more complex than those generated by templates (Figure 2), often incorporating specific details from the artist's biography. This verbosity, while potentially advantageous for detailed requests, can introduce retrieval challenges due to increased specificity.
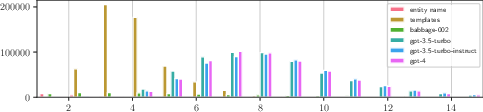
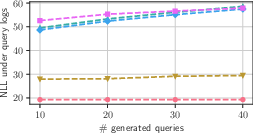
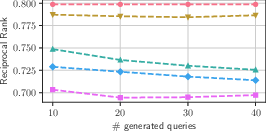
Figure 2: Distribution of generated query lengths across the approaches under consideration.
Domain Match and Specificity
The paper finds that LLM-generated queries correlate well with actual user behavior, albeit exhibiting higher specificity. This specificity, while sometimes reducing retrieval performance, highlights the LLM's ability to generate queries that better reflect nuanced user intents versus the more generic template-based queries.
Complementarity of Methods
The paper concludes that template-based and LLM-based queries together offer a comprehensive solution, with templates ensuring common usage scenarios coverage and LLMs addressing rare or emerging entity-specific scenarios efficiently.
Conclusions
The integration of LLMs into query generation for VAs demonstrates complementary strengths to traditional template-based methods. Future work should focus on optimizing this synthesis to dynamically adjust query generation in response to evolving user behavior and entity prominence. Additionally, refining prompt strategies and further fine-tuning LLMs may enhance the specificity and relevance of generated queries, potentially improving the overall VA-user interaction experience.





