- The paper presents a novel benchmark that increases task difficulty by expanding distractor options and integrating complex reasoning questions.
- It leverages expert-reviewed dataset construction across 14 domains, ensuring balanced and discriminative evaluation of language models.
- Experimental results reveal marked performance gaps and validate the effectiveness of Chain-of-Thought reasoning in addressing model limitations.
MMLU-Pro: A More Robust and Challenging Multi-Task Language Understanding Benchmark
Introduction
In the continuous evolution of LLMs, benchmarks serve as crucial touchstones for assessing and guiding advancements in artificial intelligence capabilities. The Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) dataset has stood as the standard for evaluating these models across a broad set of domains. However, as models have improved, they have saturated performance metrics on MMLU, prompting a need for more rigorous evaluations. To address this, the paper introduces MMLU-Pro, a fundamentally enhanced dataset aimed at challenging LLMs with reasoning-focused questions and an expanded choice set from four to ten options.
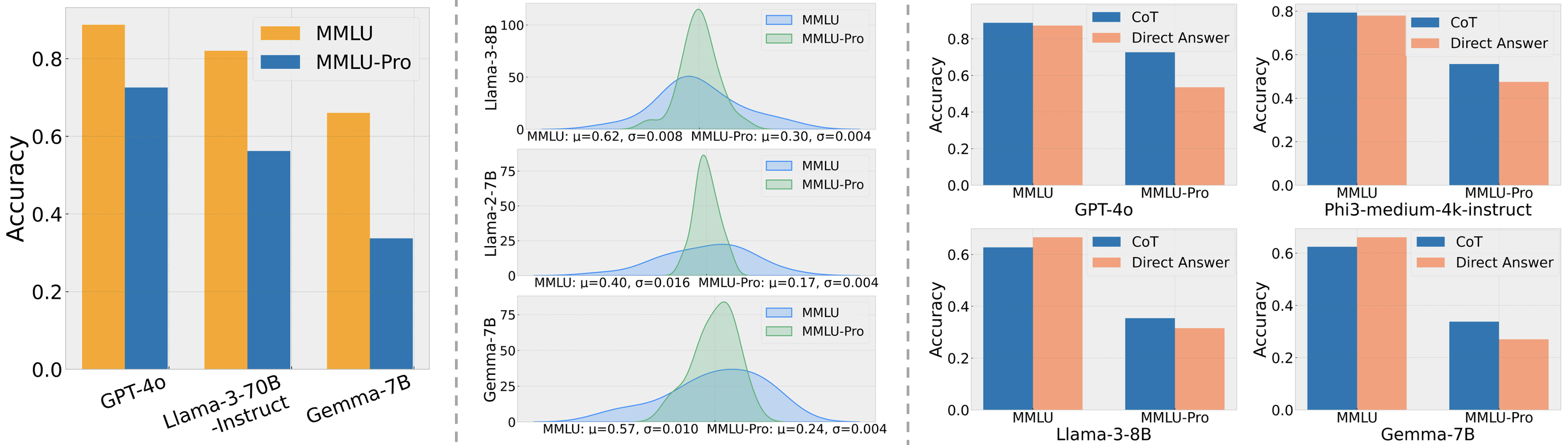
Figure 1: Comparing between MMLU and MMLU-Pro: (Left) Performance gap; (Center) Accuracy distributions affected by 24 prompts, with taller and thinner profiles indicating more stability and shorter and wider profiles indicating greater fluctuations; (Right) Performance using CoT vs. Direct.
Benchmark Limitations and MMLU-Pro Design
The MMLU dataset has faced issues with its limited number of distractors and predominantly knowledge-driven questions, especially in STEM subjects. This format enables LLMs to leverage shortcuts, potentially overestimating their reasoning capabilities. MMLU-Pro addresses these concerns by integrating more complex reasoning questions, expanding the choice set, and eliminating trivial queries.
Dataset Construction
The MMLU-Pro dataset spans 14 diverse domains including mathematics, engineering, and psychology, with over 12,000 questions sourced from refined MMLU sets and newly gathered data from specialized science and theorem-based resources.
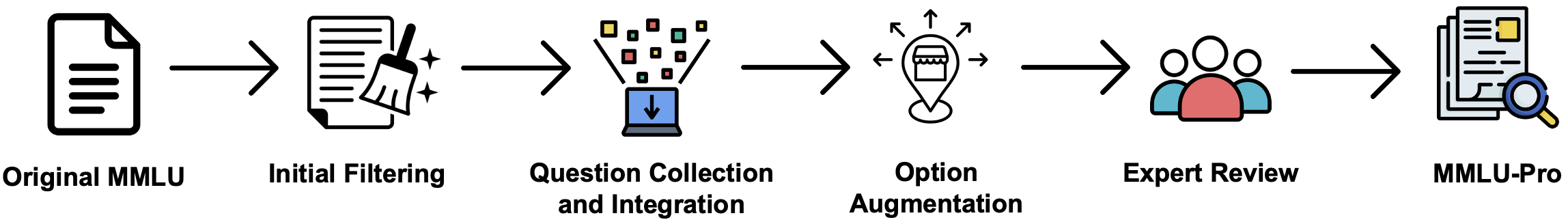
Figure 2: MMLU-Pro Dataset Construction Pipeline.
To ensure robustness, MMLU-Pro underwent multiple expert reviews and modifications, incorporating advanced distractor generation processes and error reduction techniques, resulting in a more discriminative and reliable benchmark.
Experimental Evaluation and Findings
Evaluating over 50 LLMs showed MMLU-Pro significantly heightens difficulty, with leading models like GPT-4o scoring 72.6%, leaving ample room for improvements compared to MMLU’s near-saturation.
Discriminative Power
MMLU-Pro exhibits enhanced discriminative power, evidenced by an increased accuracy gap between models, such as the 9% difference between GPT-4o and GPT-4-Turbo, compared to MMLU’s 1% gap.
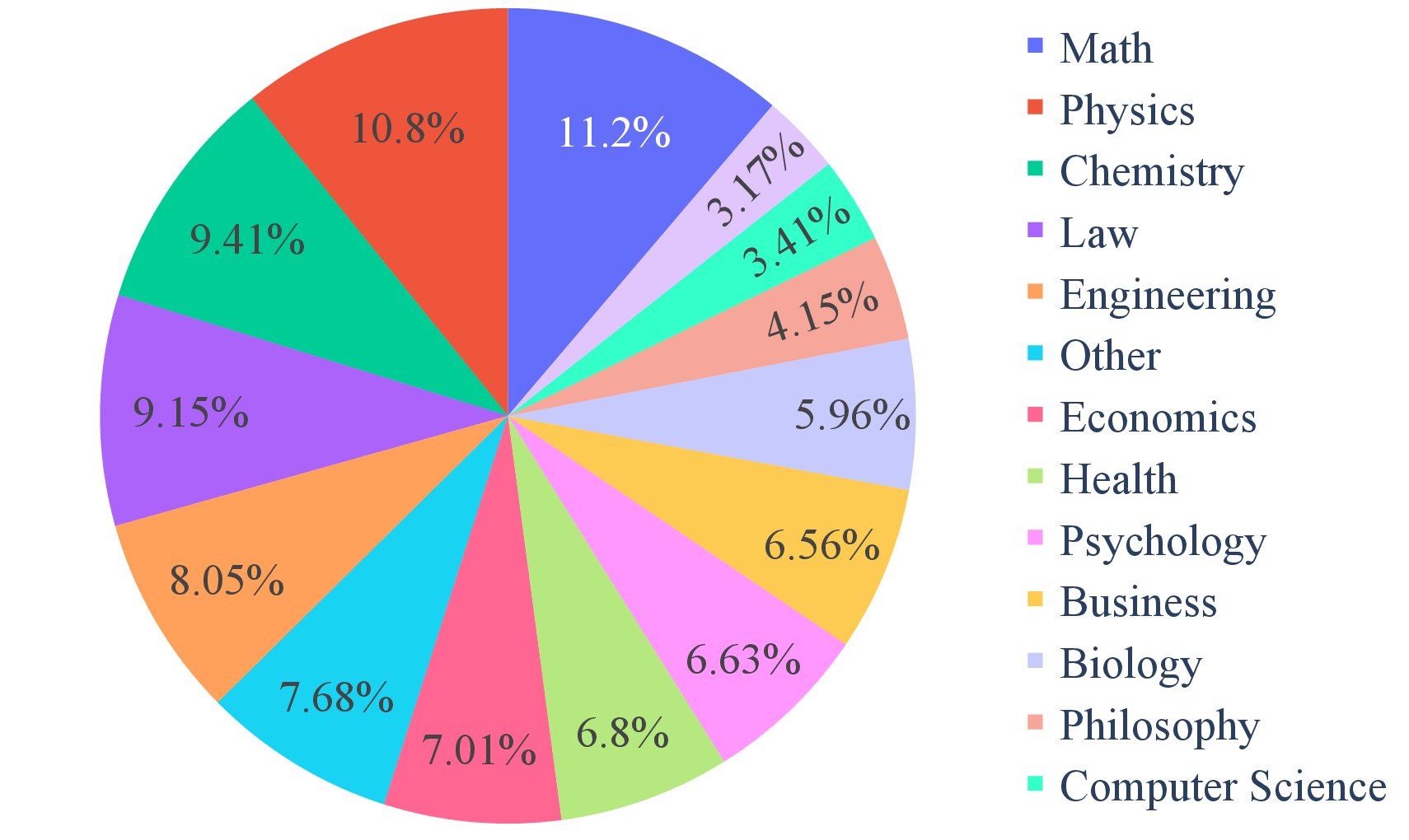
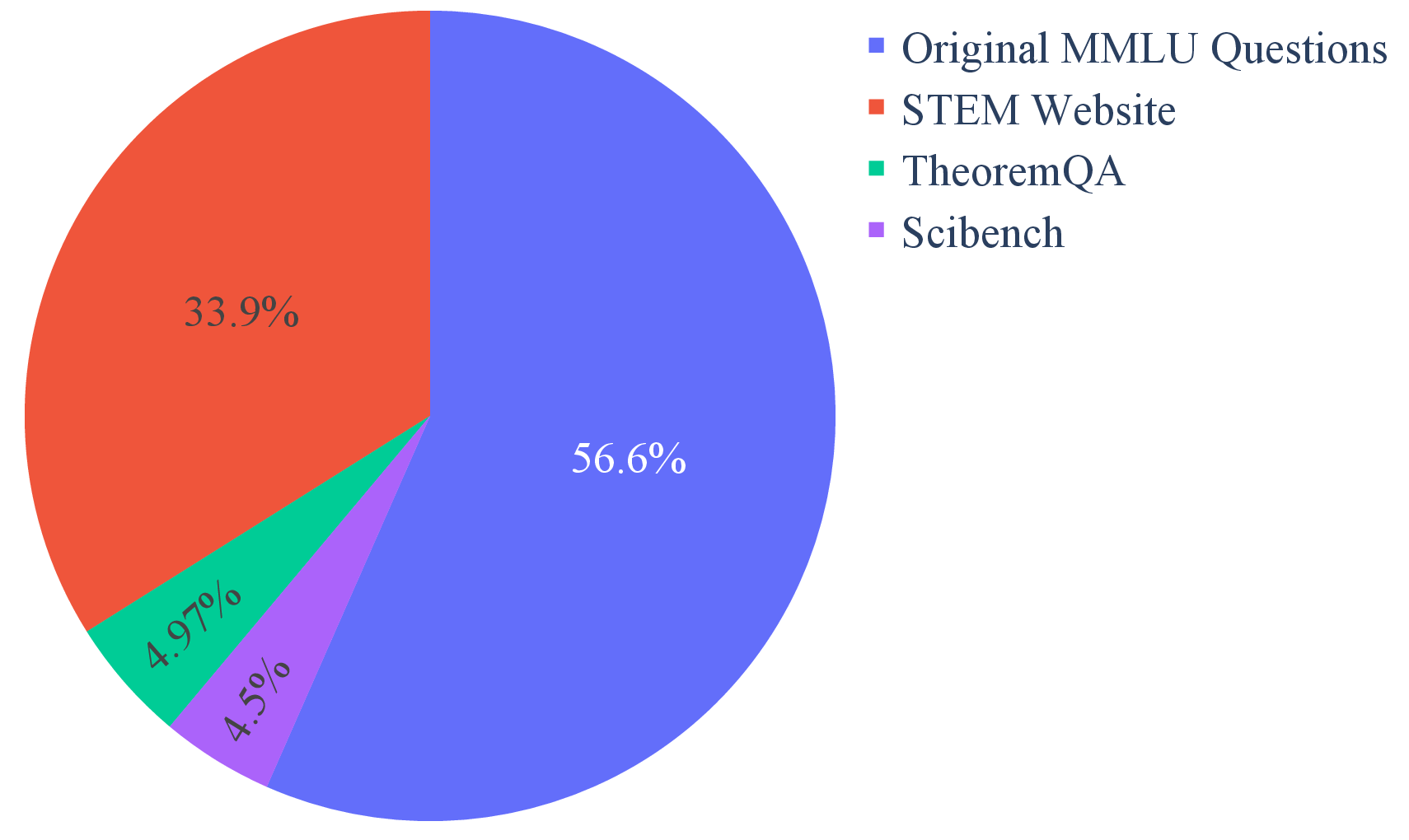
Figure 3: Distribution of Disciplines in MMLU-Pro.
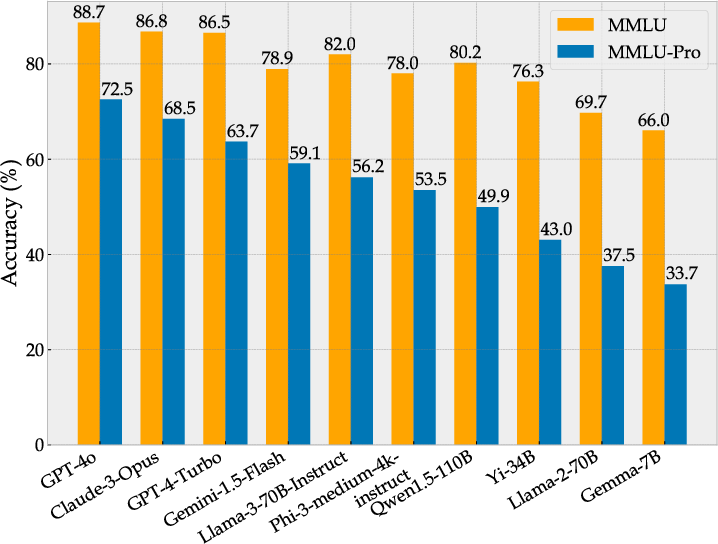
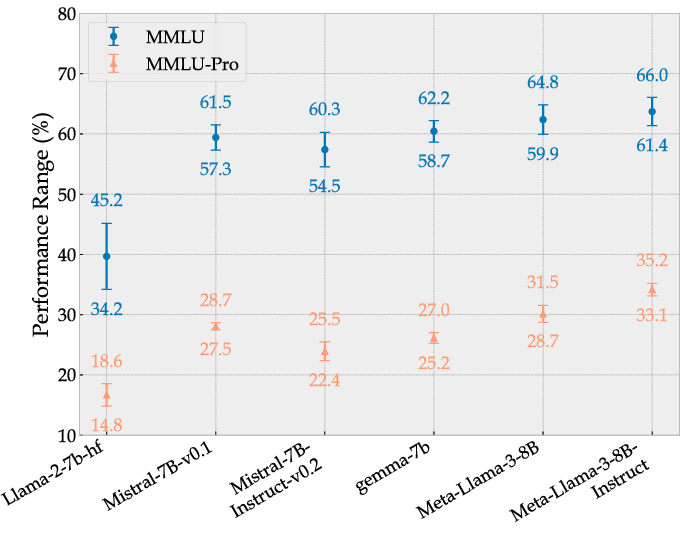
Figure 4: Performance Comparison: MMLU vs. MMLU-Pro.
Reasoning Capabilities
Models that employed Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning showed significant performance gains on MMLU-Pro, unlike on MMLU, emphasizing that MMLU-Pro's structure demands deliberate reasoning to achieve optimal results.
Error Analysis
A detailed examination of errors by models like GPT-4o identified major failure points, including reasoning flaws (39%), domain-specific knowledge gaps (35%), and computational errors (12%). These insights reflect MMLU-Pro’s capacity to pinpoint areas for model enhancement and guide future research directions.
Conclusion
MMLU-Pro emerges as a robust tool for tracking progress in AI by challenging models with complex reasoning tasks, effectively differentiating their capabilities, and providing valuable insights into AI's limitations and potential. This benchmark is poised to drive advancements in achieving expert-level AI across diverse domains and scenarios. Moving forward, MMLU-Pro sets a higher standard for evaluating multi-task language understanding in LLMs, crucial for navigating the trajectory toward advanced AI systems.





