- The paper introduces Knowledge Graph Tuning (KGT) that personalizes LLM responses by refining knowledge graphs using human feedback.
- It employs an ELBO optimization framework to retrieve personalized knowledge triples and adjust the KG in real-time without modifying LLM parameters.
- Experimental results show significant improvements in latency, GPU memory usage, and response accuracy compared to traditional parameter-based approaches.
Knowledge Graph Tuning: Real-time LLM Personalization
Knowledge Graph Tuning (KGT) presents a novel approach to personalize LLMs leveraging knowledge graphs (KGs), addressing the computational inefficiency and lack of interpretability inherent in parameter-based personalization methods. This essay outlines the paper's methodology and performance, focusing on practical implementation aspects and implications for real-time personalization.
Introduction
LLMs have demonstrated proficiency across various natural language processing tasks. Traditional methods of personalizing LLMs through mechanisms like Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning and Knowledge Editing often incur significant computational and memory costs due to back-propagation. These techniques can also compromise model interpretability and performance across extended interaction periods. KGT proposes a paradigm shift where personalization is achieved by optimizing KGs, maintaining computational efficiency and enhancing interpretability without modifying LLM parameters.
The proposed method extracts personalized knowledge triples from user-LLM interactions and refines the KG based on these insights. This approach ensures the LLM retrieves relevant personalized knowledge and generates responses with high confidence, significantly reducing latency and GPU memory usage.
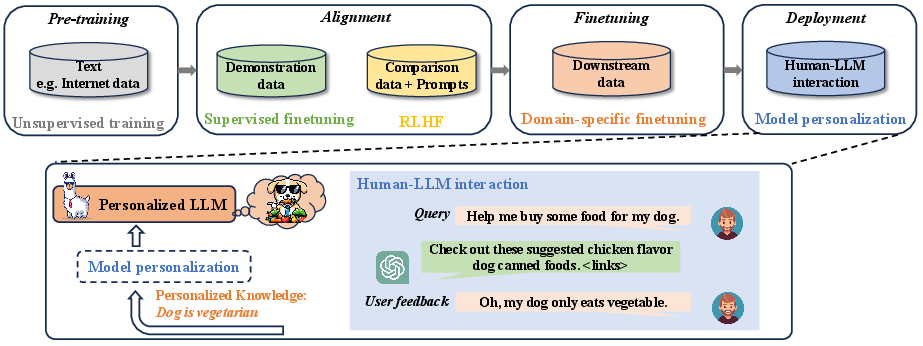
Figure 1: Pipeline of the development of an LLM. In the deployment phase, the model is personalized based on human feedback during the human-LLM interactions.
Methodology
KGT optimizes the knowledge graph by adding and removing knowledge triples based on user feedback without adjusting the LLM's parameters. The process is divided into knowledge retrieval and knowledge-enhanced reasoning, formulated using an ELBO optimization objective. The core aim is to finetune the KG such that the LLM retrieves personalized triples and generates responses that align with user feedback.
Knowledge Retrieval
The retrieval process estimates the posterior distribution of personalized triples (Q(z∣q,a)), ensuring the LLM predominantly retrieves pertinent triples, thereby optimizing computational efficiency. By emulating user feedback through specially designed query templates, KGT enables efficient relation extraction, contributing to real-time personalization without extensive human intervention.
Knowledge-enhanced Reasoning
The reasoning component maximizes the probability that the LLM generates accurate responses based on retrieved knowledge. In this setup, heuristic algorithms iteratively refine the KG, adding triples that promote correct answer generation and removing those decreasing response accuracy, significantly improving computational effectiveness and interpretation clarity.
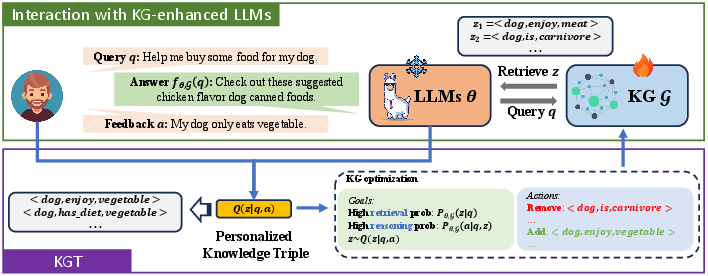
Figure 2: The overview of KGT. The LLM extracts the posterior distribution of personalized knowledge triples from human-LLM interaction.
Experimental Results
The experimentation evaluates KGT's efficacy on datasets where user feedback conflicts with LLM's pre-trained knowledge. It demonstrated a marked improvement in personalization performance compared to traditional parameter-based methods such as fine-tuning, MEND, and ROME.
KGT achieved a remarkable increase in both the efficacy and paraphrase scores across multiple LLMs, notably outperforming baselines by substantial margins on tested datasets like CounterFact. The personalization gains illustrate KGT's scalability and its ability to cater to extensive personalized knowledge, highlighting its viability for long-term application scenarios.
Efficiency Comparison
A critical component of KGT is its efficiency in terms of computational resource utilization. Experiments showcased significant reductions in latency and GPU memory usage compared to parameter-based approaches, underscoring KGT's suitability for on-device applications and resource-constrained environments.
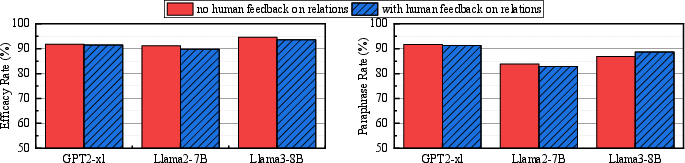
Figure 3: Compared results on CounterFact dataset with and without user feedback on relations.
Implications and Future Directions
KGT offers a compelling solution for real-time model personalization, with the potential to be extended to various domains needing scalable, interpretable personalization capabilities. Future work could explore variations of KG structures and retrieval mechanisms to further enhance performance across diverse LLM model architectures.
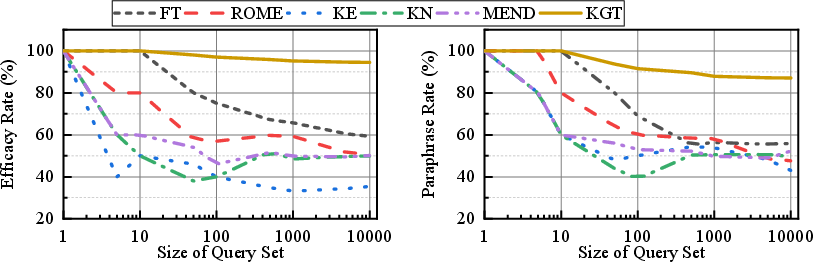
Figure 4: Compared results on CounterFact dataset using Llama3-8B with different query set sizes.
Conclusion
Knowledge Graph Tuning introduces a promising personalization framework that enhances computational efficiency and interpretability for LLMs during deployment, demonstrating superior numerical performance and scalability compared to existing dedication techniques. By shifting personalization from parameter tuning to KG optimization, KGT advocates a paradigm conducive to real-time interaction enhancements with profound implications for future LLM applications.





