- The paper presents a novel multimodal LLM, V-Zen, that overcomes GUI automation challenges with dual-resolution processing and precise spatial grounding.
- It integrates specialized modules like LRVFE, HRCVM, and HPGM to effectively capture both global interface context and fine-grained component details.
- Empirical results on the GUIDE dataset show 93.2% next-task prediction accuracy and 89.7% bounding box accuracy, setting new benchmarks for agentive AI.
V-Zen: Efficient GUI Understanding and Precise Grounding with a Novel Multimodal LLM
Motivation and Challenges in GUI Automation
Graphical User Interface (GUI) automation is a critical bottleneck for agentive AI systems. Standard Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in visual reasoning tasks but struggle with the precision required to interact with GUIs, where components like icons, buttons, and text fields must be detected and localized with high fidelity. Existing approaches typically rely on coarse textual grounding or low-resolution images, limiting the granularity and actionable accuracy of predicted interactions.
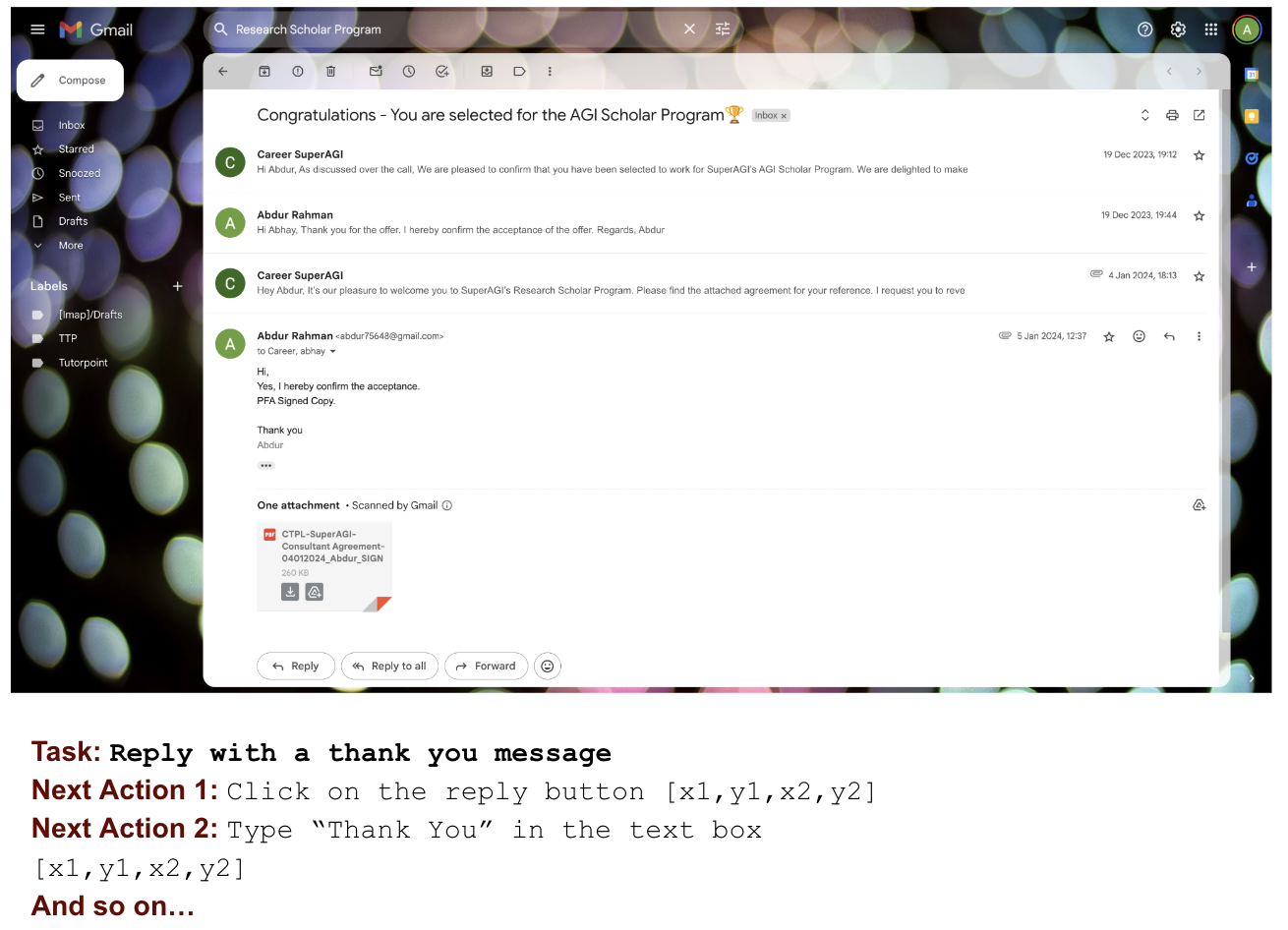


Figure 1: A sample Gmail GUI case illustrating the challenges of precise component identification, next-action prediction, and grounding required for automation.
This research introduces V-Zen: a new MLLM architecture designed to address these deficiencies, specializing in efficient GUI component understanding and precise grounding. The model is complemented by GUIDE—a large-scale GUI interaction dataset with bounding box annotations and chain-of-thought traces for realistic agentive workflows.
Contextualizing V-Zen within MLLM Evolution
The paradigm shift towards MLLMs has brought advances in integrating multimodal inputs, particularly text and images, but most SOTA models have focused on generic visual reasoning rather than GUI-specific automation. A survey of recent landmark models (GPT-4V, Gemini-Pro, Chatterbox, CogAgent) highlights two principal limitations for GUI automation: (1) precise bounding box output is typically text-based and not spatially accurate; (2) most models operate at low image resolutions, missing fine GUI details crucial for interaction.
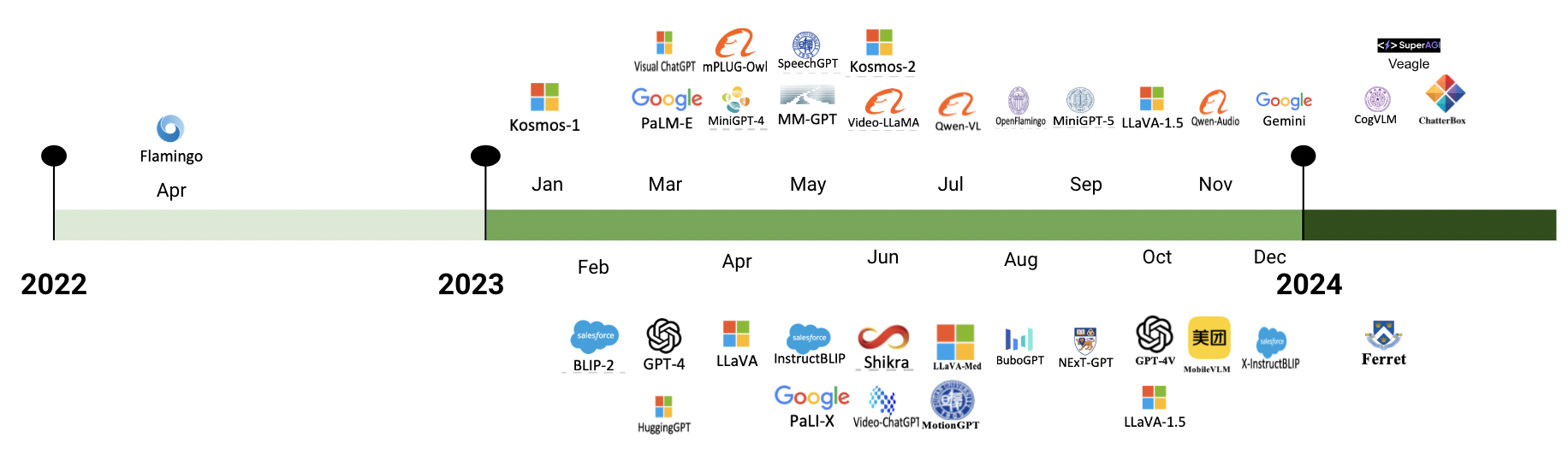


Figure 2: Timeline of SOTA MLLMs, positioning V-Zen as a next-generation model focused on GUI-centric tasks.
V-Zen is explicitly constructed to overcome these limitations via dual-resolution visual processing and direct spatial grounding output, setting a new operational baseline for agentive AI.
Architectural Advances: V-Zen Modules
The V-Zen architecture consists of five specialized modules designed for holistic multimodal GUI understanding and grounding:
- Low-Resolution Visual Feature Extractor (LRVFE): Utilizes EVA-2-CLIP to encode images at 224x224 resolution, extracting global visual features.
- Multimodal Projection Adapter (MPA): Transforms image features for compatibility with the LLM backbone, facilitating modality alignment.
- Pretrained LLM with Visual Expert (PLMVE): Employs Vicuna-7B base LLM augmented with visual expert layers for parallel text/image reasoning.
- High-Resolution Cross Visual Module (HRCVM): Processes images at 1120x1120 resolution with cross-attention (inspired by CogAgent) to capture fine-grained component structure and embedded UI text.
- High-Precision Grounding Module (HPGM): Leverages an enhanced DINO detector to output spatially precise bounding boxes directly, driven by LLM-generated queries and multiscale visual features from a Swin Transformer backbone.
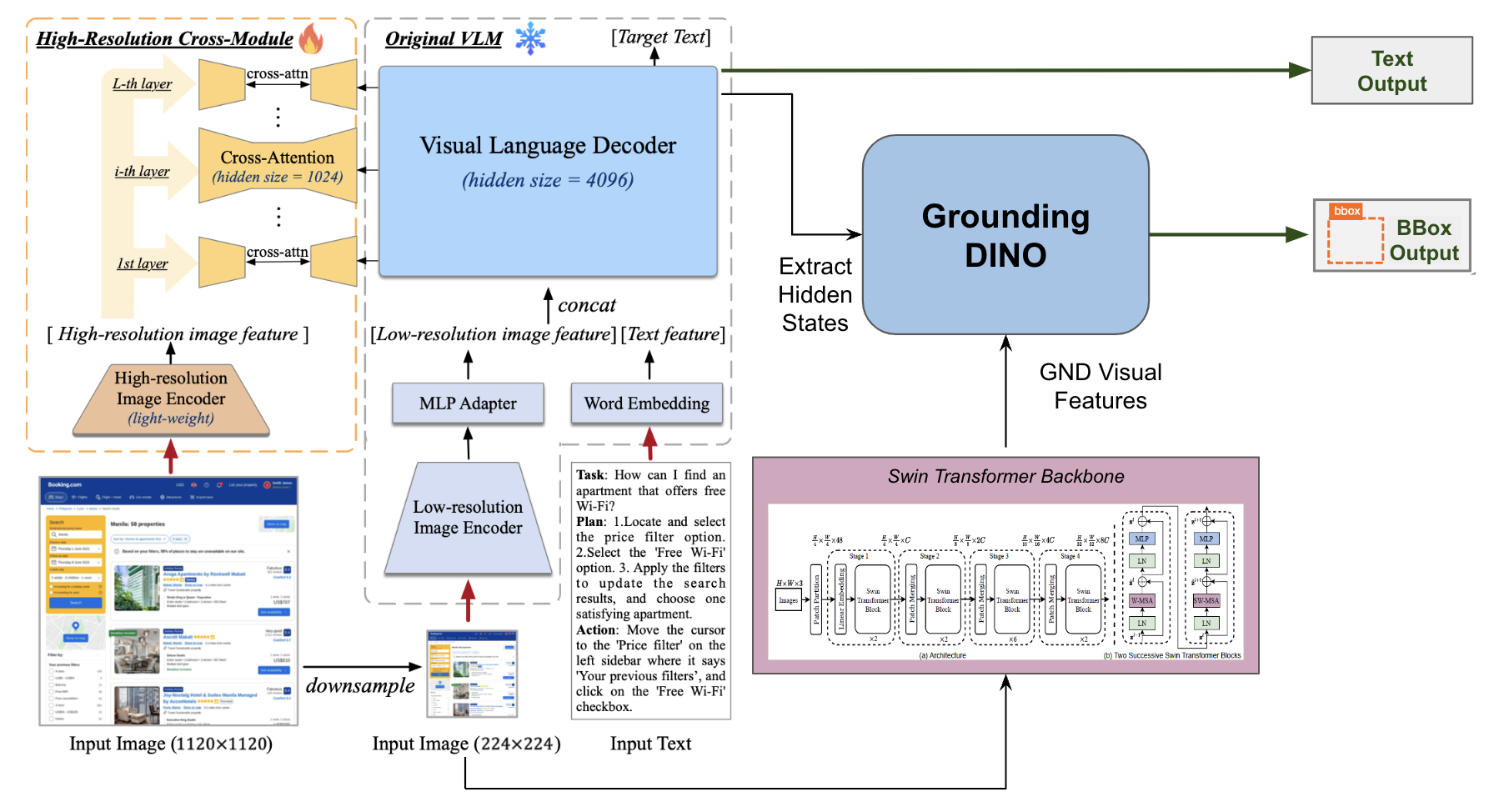


Figure 3: Schematic representation of the V-Zen architecture, including its dual resolution path, multimodal adapters, and grounding module.
This design enables V-Zen to process both global interface context and fine subcomponent details, achieving precise element localization and next-action prediction.
GUIDE: A Specialized Dataset for GUI Automation
V-Zen's performance is grounded in the GUIDE dataset, a domain-optimized corpus capturing realistic GUI interactions across a wide variety of platforms (Apollo.io, Gmail, Google Calendar, Canva, etc.). GUIDE contains 124,000 annotated samples, with each record providing: GUI screenshot, textual task description, last and next actions, action grounding coordinates, and a chain-of-thought history for context-aware reasoning. The annotation process employed the NEXTAG tool to ensure diversity and context depth.
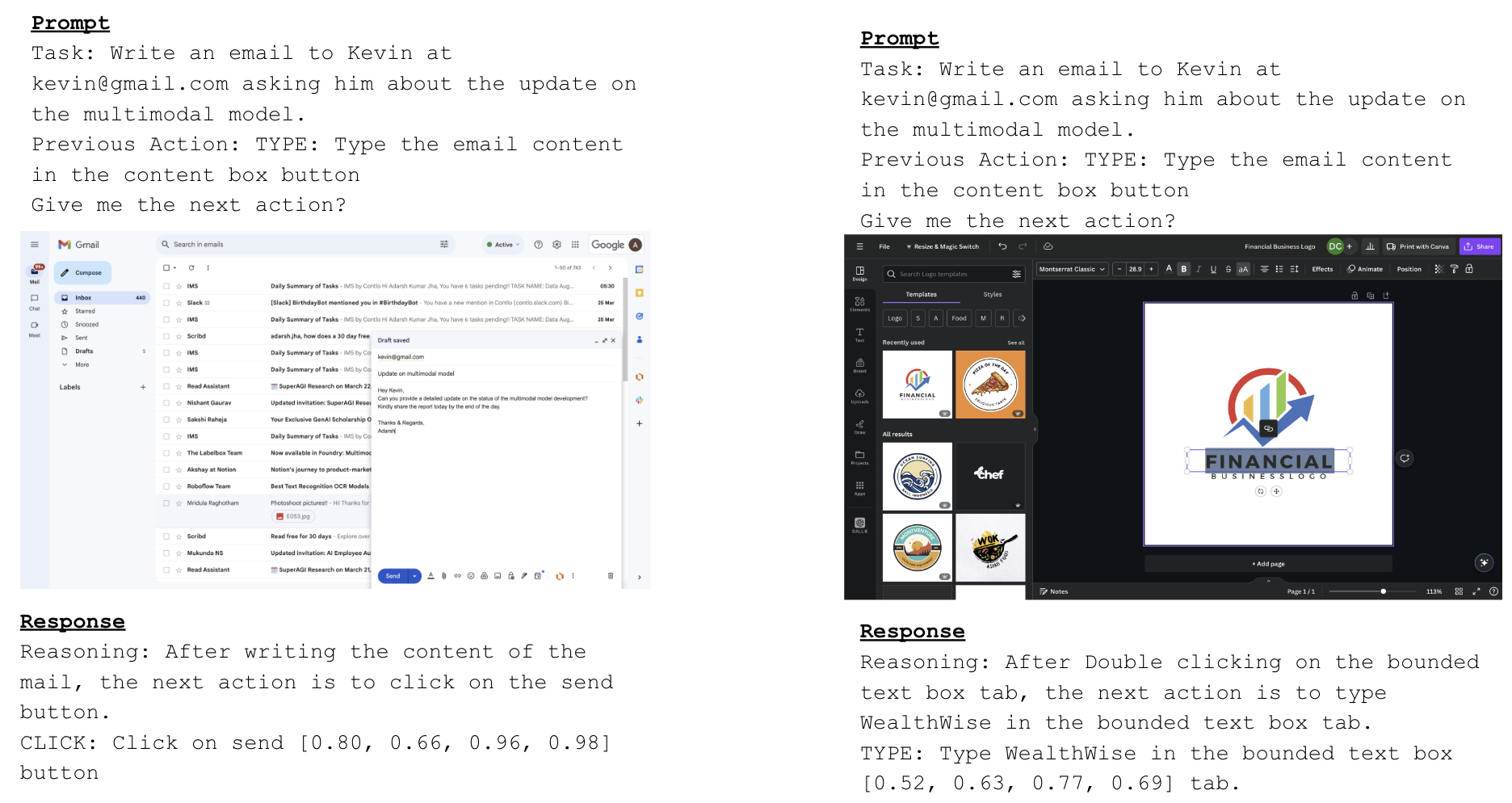


Figure 4: Representative GUIDE samples showing next-action prediction and bounding box annotation for GUI automation.
GUIDE’s coverage of cross-platform workflows and its incorporation of historical context make it uniquely suited for model training targeting agentive automation, rather than generic visual reasoning.
Training Protocol and Evaluation Metrics
V-Zen’s training protocol combines CogAgent-style multimodal pre-training (synthetic renderings, academic documents, OCR images) with specialized fine-tuning on GUIDE. The model is optimized using DeepSpeed and Adam with strong computational resources (8×A100 GPUs).
Evaluation focuses on two axes:
- Next-Task Prediction Accuracy: Semantic match between predicted and ground-truth actions for sequential workflow progression.
- Grounding Accuracy: F1 score for bounding box localization in object detection settings.
Comparison benchmarks include CogAgent, GPT-4V, Gemini-Pro, and Chatterbox. Ablation studies isolate the contribution of each architectural module.
Empirical Results & Analysis
V-Zen achieves notable performance metrics:
- Next-Task Prediction: 93.2% accuracy (vs. 94% GPT-4V, 92.4% CogAgent, 91.3% Chatterbox)
- Grounding Accuracy: 89.7% (vs. 87.9% Chatterbox, 86.3% CogAgent, 28% GPT-4V, 21% Gemini-Pro)
The introduction of high-resolution cross-attention and direct bounding box output leads to substantial gains over baseline and SOTA models, especially in spatially fine-grained grounding tasks.
Figure 5 presents qualitative samples underscoring V-Zen’s superior next-action prediction and bounding box localization, demonstrating utility for complex automation scenarios.
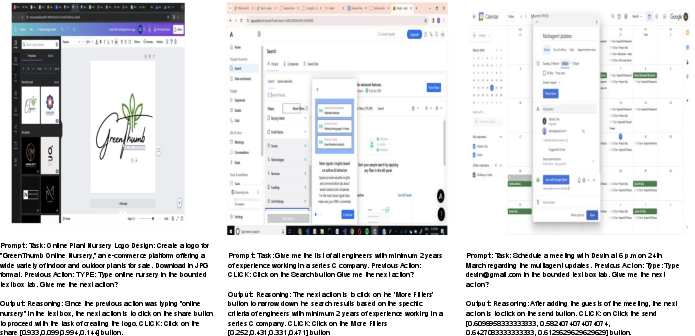


Figure 5: Qualitative results on GUIDE samples using V-Zen, highlighting accurate sequential action prediction and bounding box localization.
Practical/Theoretical Implications and Future Prospects
The explicit module separation and dual-resolution processing in V-Zen establish a foundation for high-fidelity GUI automation agents capable of navigating visually complex interfaces. Moving beyond textual grounding enables reliable robotic process automation (RPA) and integration with real-world computer systems, reducing error rates and manual script interventions.
The GUIDE dataset catalyzes further advancements in agentive multimodal modeling, opening paths for:
- Transfer learning across interface platforms
- Context-dependent reasoning via chain-of-thought records
- Robust cross-device and cross-browser generalization
Future research may extend V-Zen’s architectural principles to support dynamic GUI modification handling, real-time interface adaptation, and integration with broader executable agent frameworks.
Conclusion
V-Zen provides a significant methodological advance for GUI understanding and grounding tasks in agentive AI. Through its carefully engineered multimodal architecture and training on the GUIDE dataset, V-Zen demonstrates high accuracy in both action prediction and spatial grounding, outperforming prior SOTA models in GUI automation. The modular design and dual-resolution encoding set a new technical standard, with practical implications across RPA, computer vision, and interactive AI research. The open release of V-Zen and GUIDE will serve as an accelerator for the next generation of multimodal agentive systems and GUI-centric AI applications.




