Automating the Enterprise with Foundation Models
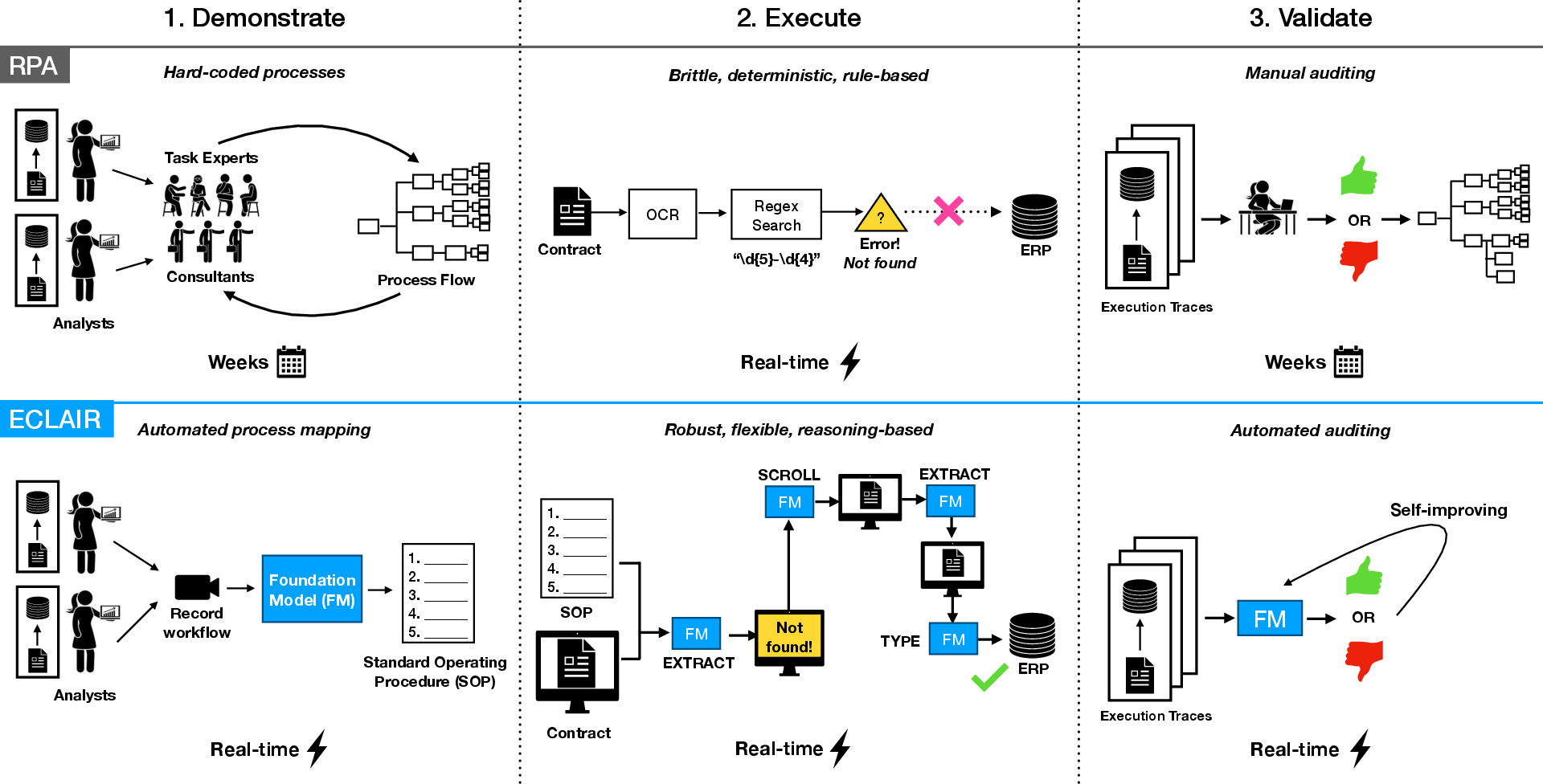
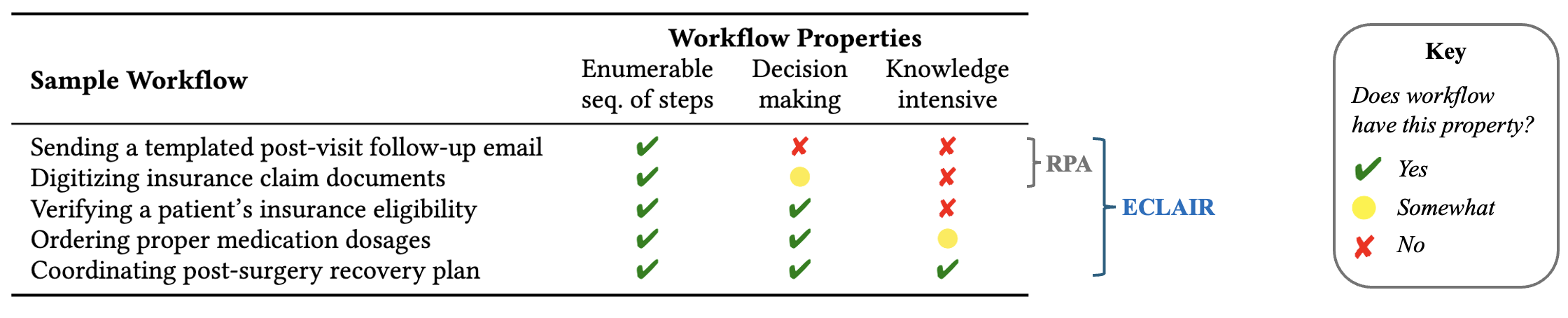
Abstract: Automating enterprise workflows could unlock $4 trillion/year in productivity gains. Despite being of interest to the data management community for decades, the ultimate vision of end-to-end workflow automation has remained elusive. Current solutions rely on process mining and robotic process automation (RPA), in which a bot is hard-coded to follow a set of predefined rules for completing a workflow. Through case studies of a hospital and large B2B enterprise, we find that the adoption of RPA has been inhibited by high set-up costs (12-18 months), unreliable execution (60% initial accuracy), and burdensome maintenance (requiring multiple FTEs). Multimodal foundation models (FMs) such as GPT-4 offer a promising new approach for end-to-end workflow automation given their generalized reasoning and planning abilities. To study these capabilities we propose ECLAIR, a system to automate enterprise workflows with minimal human supervision. We conduct initial experiments showing that multimodal FMs can address the limitations of traditional RPA with (1) near-human-level understanding of workflows (93% accuracy on a workflow understanding task) and (2) instant set-up with minimal technical barrier (based solely on a natural language description of a workflow, ECLAIR achieves end-to-end completion rates of 40%). We identify human-AI collaboration, validation, and self-improvement as open challenges, and suggest ways they can be solved with data management techniques. Code is available at: https://github.com/HazyResearch/eclair-agents
- Do as i can, not as i say: Grounding language in robotic affordances. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.01691 (2022).
- Automation Anywhere. 2020. https://www.automationanywhere.com/company/press-room/global-research-reveals-worlds-most-hated-office-tasks
- The Unsolved Challenges of LLMs as Generalist Web Agents: A Case Study. In NeurIPS 2023 Foundation Models for Decision Making Workshop.
- Automated discovery of process models from event logs: Review and benchmark. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering 31, 4 (2018), 686–705.
- David Autor. 2014. Polanyi’s paradox and the shape of employment growth. Technical Report. National Bureau of Economic Research.
- Maintaining database integrity with refinement types. In European Conference on Object-Oriented Programming. Springer, 484–509.
- Introducing our Multimodal Models. https://www.adept.ai/blog/fuyu-8b
- Matthew Bayley and Ed Levine. 2013. Hospital revenue cycle operations: opportunities created by the ACA. Management (2013).
- Querying with access patterns and integrity constraints. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment 8, 6 (2015), 690–701.
- Amanda Bergson-Shilcock and Roderick Taylor. 2023. Closing the Digital” Skill” Divide: The Payoff for Workers, Business, and the Economy. National Skills Coalition (2023).
- Alessandro Berti and Mahnaz Sadat Qafari. 2023. Leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Process Mining (Technical Report). arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12701 (2023).
- Collaborative data analytics with DataHub. In Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Vol. 8. NIH Public Access, 1916.
- On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07258 (2021).
- Generative AI at work. Technical Report. National Bureau of Economic Research.
- Fabio Casati and Ming-Chien Shan. 2000. Process automation as the foundation for e-business. In VLDB. Citeseer, 688–691.
- From Robotic Process Automation to Intelligent Process Automation: –Emerging Trends–. In Business Process Management: Blockchain and Robotic Process Automation Forum: BPM 2020 Blockchain and RPA Forum, Seville, Spain, September 13–18, 2020, Proceedings 18. Springer, 215–228.
- The economic potential of generative AI The next productivity frontier The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier.
- Intelligent methods for business rule processing: State-of-the-art. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.11775 (2023).
- Laila Dahabiyeh and Omar Mowafi. 2023. Challenges of using RPA in auditing: A socio-technical systems approach. Intelligent Systems in Accounting, Finance and Management (2023).
- Mind2Web: Towards a Generalist Agent for the Web. arXiv:2306.06070 [cs.CL]
- Towards a unified agent with foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09668 (2023).
- AI-augmented business process management systems: a research manifesto. ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems 14, 1 (2023), 1–19.
- How well can large language models explain business processes? arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.12846 (2024).
- Dahlia Fernandez and Aini Aman. 2021. The challenges of implementing robotic process automation in global business services. International Journal of Business and Society 22, 3 (2021), 1269–1282.
- Drive like a human: Rethinking autonomous driving with large language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. 910–919.
- Multimodal Web Navigation with Instruction-Finetuned Foundation Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11854 (2023).
- An overview of workflow management: From process modeling to workflow automation infrastructure. Distributed and parallel Databases 3 (1995), 119–153.
- Large Language Models can accomplish Business Process Management Tasks. In International Conference on Business Process Management. Springer, 453–465.
- A real-world webagent with planning, long context understanding, and program synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12856 (2023).
- WebVoyager: Building an End-to-End Web Agent with Large Multimodal Models. arXiv:2401.13919 [cs.CL]
- From revenue cycle management to revenue excellence.
- Metagpt: Meta programming for multi-agent collaborative framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00352 (2023).
- CogAgent: A Visual Language Model for GUI Agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.08914 (2023).
- Data management perspectives on business process management: tutorial overview. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. 943–948.
- A data-driven approach for learning to control computers. In International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 9466–9482.
- Robotic process automation: systematic literature review. In Business Process Management: Blockchain and Central and Eastern Europe Forum: BPM 2019 Blockchain and CEE Forum, Vienna, Austria, September 1–6, 2019, Proceedings 17. Springer, 280–295.
- ADEPT: An agent-based approach to business process management. ACM Sigmod Record 27, 4 (1998), 32–39.
- How can we know what language models know? Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics 8 (2020), 423–438.
- CHORUS: Foundation Models for Unified Data Discovery and Exploration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09610 (2023).
- Victor Kilanko. 2023. Leveraging Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Revenue Cycle Management in the United States. International Journal of Scientific Advances 4, 4 (2023), 505–14.
- Robotic process mining: vision and challenges. Business & Information Systems Engineering 63 (2021), 301–314.
- Xavier Lhuer. 2016. The next acronym you need to know about: RPA (robotic process automation). (2016).
- More agents is all you need. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.05120 (2024).
- Interactive task and concept learning from natural language instructions and gui demonstrations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.00031 (2019).
- Encouraging divergent thinking in large language models through multi-agent debate. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.19118 (2023).
- Demonstration of collaborative and interactive workflow-based data analytics in texera. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment 15, 12 (2022), 3738–3741.
- Bolaa: Benchmarking and orchestrating llm-augmented autonomous agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05960 (2023).
- Query-based workload forecasting for self-driving database management systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Management of Data. 631–645.
- Interrupt Handling Schemes in Operating Systems. Springer.
- Process automation using RPA–a literature review. Procedia Computer Science 219 (2023), 244–254.
- Towards large language model-based personal agents in the enterprise: Current trends and open problems. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023. 6909–6921.
- Can Foundation Models Wrangle Your Data? Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment 16, 4 (2022), 738–746.
- R OpenAI. 2023. GPT-4 technical report. arXiv (2023), 2303–08774.
- Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Advances in neural information processing systems 35 (2022), 27730–27744.
- Generative agents: Interactive simulacra of human behavior. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology. 1–22.
- Self-Driving Database Management Systems.. In CIDR, Vol. 4. 1.
- Make your database system dream of electric sheep: towards self-driving operation. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment 14, 12 (2021), 3211–3221.
- Prototyping and implementing Robotic Process Automation in accounting firms: Benefits, challenges and opportunities to audit automation. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems 51 (2023), 100641.
- R1. 2022. Healthcare Financial Trends Report. https://www.r1rcm.com/news/healthcare-trends-and-data-show-clinical-shortage-tip-of-the-iceberg
- Worker skill estimation in team-based tasks. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment 8, 11 (2015), 1142–1153.
- Lars Reinkemeyer. 2020. Process mining in action. Process Mining in Action Principles, Use Cases and Outloook (2020).
- A Case for Business Process-Specific Foundation Models. In International Conference on Business Process Management. Springer, 44–56.
- Tara Safavi and Danai Koutra. 2021. Relational world knowledge representation in contextual language models: A review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.05837 (2021).
- Invoice processing using robotic process automation. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol 6, 2 (2020), 216–223.
- Henriika Sarilo-Kankaanranta and Lauri Frank. 2021. The Slow Adoption Rate of Software Robotics in Accounting and Payroll Services and the Role of Resistance to Change in Innovation-Decision Process. In Conference of the Italian Chapter of AIS. Springer, 201–216.
- Business process cockpit. In VLDB’02: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Very Large Databases. Elsevier, 880–883.
- Fred Schulte and Erika Fry. 2019. Death by 1,000 clicks: Where electronic health records went wrong. Kaiser Health News 18 (2019).
- From Pixels to UI Actions: Learning to Follow Instructions via Graphical User Interfaces. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.00245 (2023).
- HuggingGPT: Solving AI Tasks with ChatGPT and its Friends in Hugging Face. arXiv:2303.17580 [cs.CL]
- Reflexion: Language Agents with Verbal Reinforcement Learning.(2023). arXiv preprint cs.AI/2303.11366 (2023).
- Just ask for calibration: Strategies for eliciting calibrated confidence scores from language models fine-tuned with human feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14975 (2023).
- UIPath. 2022. UiPath Certified RPA Associate v1.0 - EXAM Description.pdf. https://start.uipath.com/rs/995-XLT-886/images/UiPath%20Certified%20RPA%20Associate%20v1.0%20-%20EXAM%20Description.pdf
- Wil MP Van der Aalst. 2014. Process mining in the large: a tutorial. Business Intelligence: Third European Summer School, eBISS 2013, Dagstuhl Castle, Germany, July 7-12, 2013, Tutorial Lectures 3 (2014), 33–76.
- Large Language Models for Business Process Management: Opportunities and Challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.04309 (2023).
- Voyager: An open-ended embodied agent with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16291 (2023).
- Cogvlm: Visual expert for pretrained language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.03079 (2023).
- Jarvis-1: Open-world multi-task agents with memory-augmented multimodal language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.05997 (2023).
- Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (2022), 24824–24837.
- Judith Wewerka and Manfred Reichert. 2020. Robotic Process Automation–A Systematic Literature Review and Assessment Framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.11951 (2020).
- WebUI: A Dataset for Enhancing Visual UI Understanding with Web Semantics. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 1–14.
- Autogen: Enabling next-gen llm applications via multi-agent conversation framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.08155 (2023).
- OS-Copilot: Towards Generalist Computer Agents with Self-Improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.07456 (2024).
- Gpt-4v in wonderland: Large multimodal models for zero-shot smartphone gui navigation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.07562 (2023).
- Set-of-mark prompting unleashes extraordinary visual grounding in gpt-4v. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.11441 (2023).
- AppAgent: Multimodal Agents as Smartphone Users. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.13771 (2023).
- React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03629 (2022).
- ProAgent: From Robotic Process Automation to Agentic Process Automation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.10751 (2023).
- Agflow: Agent-based cross-enterprise workflow management system. In VLDB. 697–698.
- UFO: A UI-Focused Agent for Windows OS Interaction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.07939 (2024).
- Vision-Language Models for Vision Tasks: A Survey. arXiv:2304.00685 [cs.CV]
- GPT-4V(ision) is a Generalist Web Agent, if Grounded. arXiv:2401.01614 [cs.IR]
- Webarena: A realistic web environment for building autonomous agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.13854 (2023).
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.