- The paper introduces video diffusion models, detailing innovations for generating coherent video content from multimodal inputs.
- It examines key architectural adaptations such as UNet variants and cascaded models to efficiently handle spatial and temporal challenges.
- The study outlines challenges like temporal consistency and data limitations while proposing future directions for model advancements.
Video Diffusion Models: A Survey
Introduction
The paper "Video Diffusion Models: A Survey" (2405.03150) provides a comprehensive overview of video diffusion models, exploring key aspects such as applications, architectures, and temporal dynamics modeling. The survey elucidates various advancements in diffusion models applied to video generation, highlighting their potential advantages, challenges, and future directions.
Diffusion Models and Their Significance
Diffusion generative models have showcased remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality visual outputs, initially being prominent in image generation tasks. The extension of these models to video generation opens up pathways to creating coherent, realistic video content from diverse input modalities such as text, images, and audio. Adapting diffusion models for video involves addressing unique challenges such as ensuring temporal consistency across frames, managing lengthy video generation, and optimizing computational costs.
Applications of Video Diffusion Models
Video diffusion models cater to an array of applications. Notably, these models are instrumental in:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Producing video segments directly from textual descriptions, which necessitates intricate modeling to achieve both spatial and temporal coherence.
- Image-to-Video Generation: Animating static images by providing additional contextual information to guide the temporal evolution of imagery.
- Video Editing and Completion: Leveraging diffusion models for sophisticated video editing tasks like inpainting, style adjustment, and augmentation.
- Audio-Conditioned Video Synthesis: Integrating auditory signals to generate or modify videos, enhancing multimodal experiences and synchronization.
Architectural Considerations
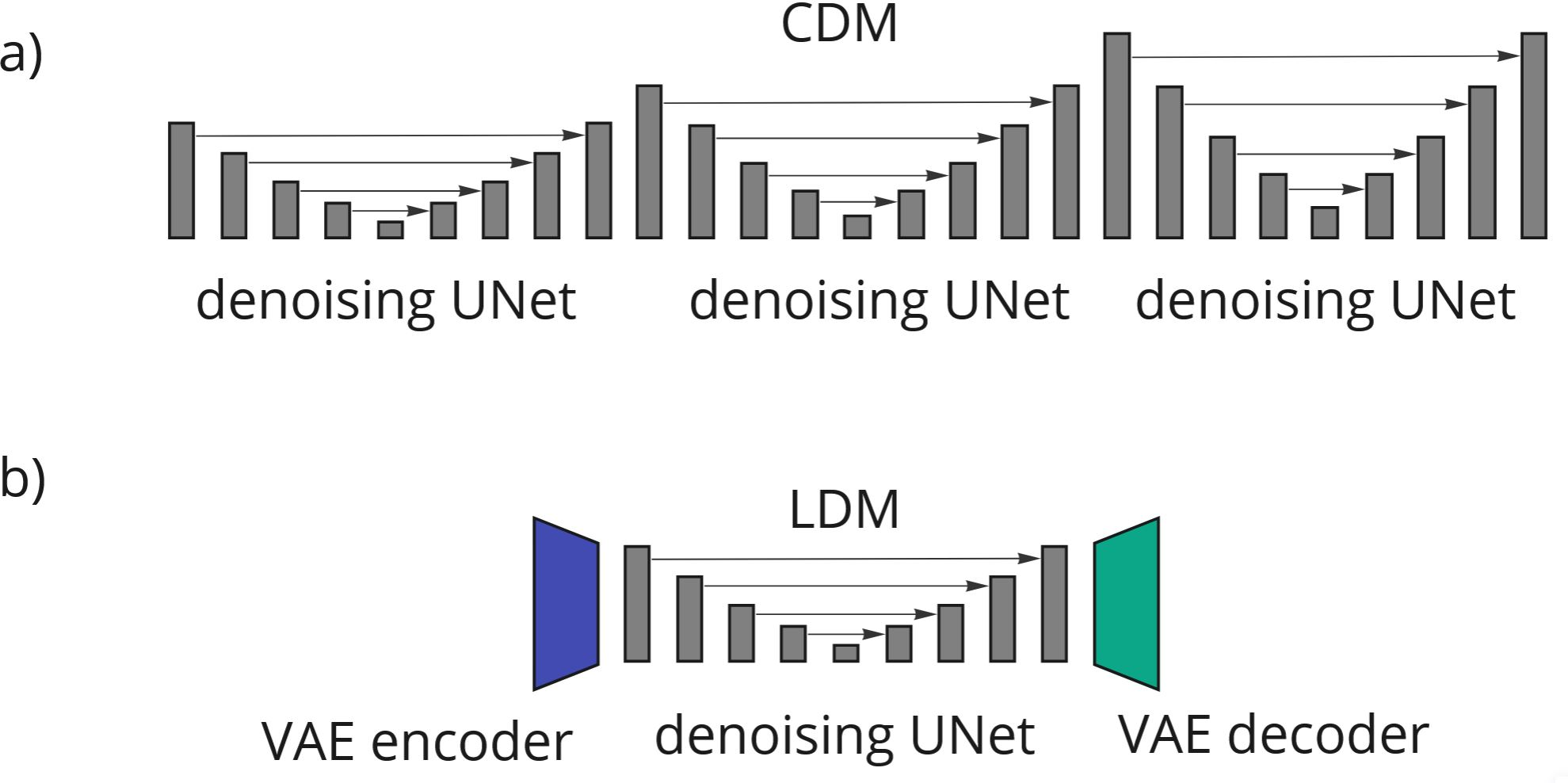
The predominant choice for architecture in video diffusion applications is the UNet, which has been effectively adapted from its success in image-based tasks. Variations such as 3D UNets, which incorporate spatial and temporal convolutions, have been employed to better manage the dynamic nature of video data (Figure 1). The survey also discusses latent and cascaded diffusion models that enhance the resolution and efficiency of video generation:
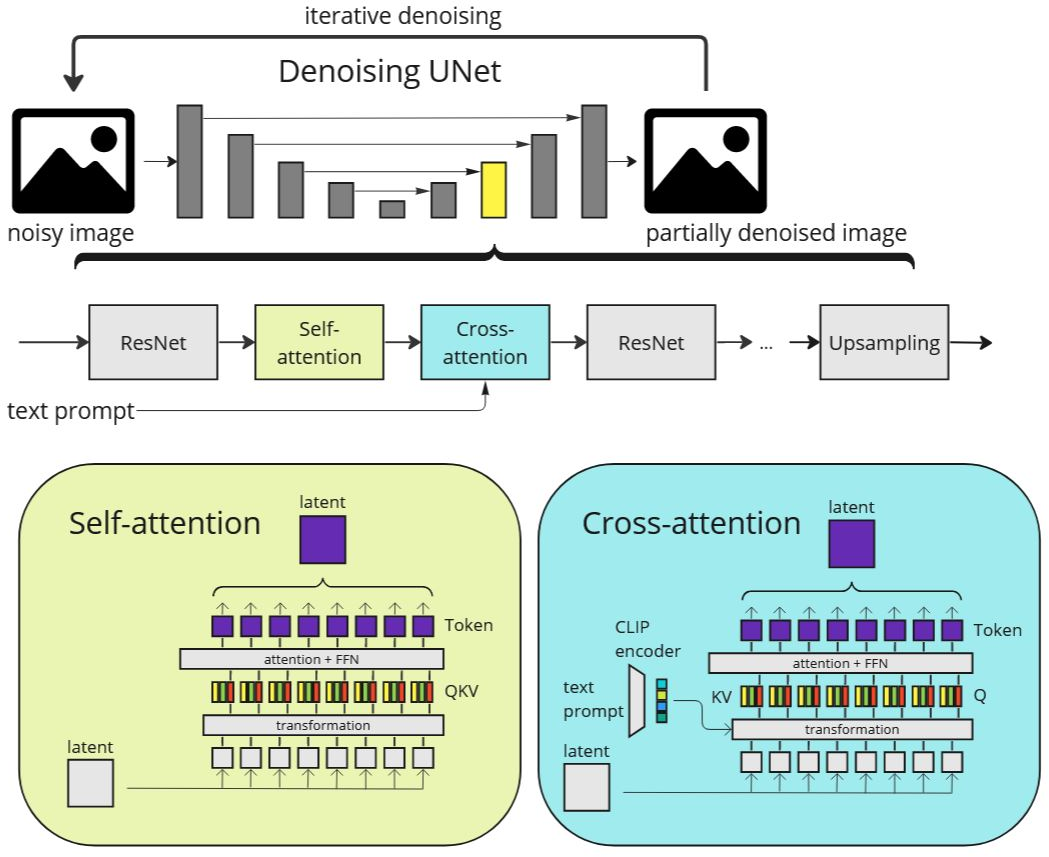
Figure 1: The denoising UNet architecture typically used in text-to-image diffusion models.
Modeling Temporal Dynamics
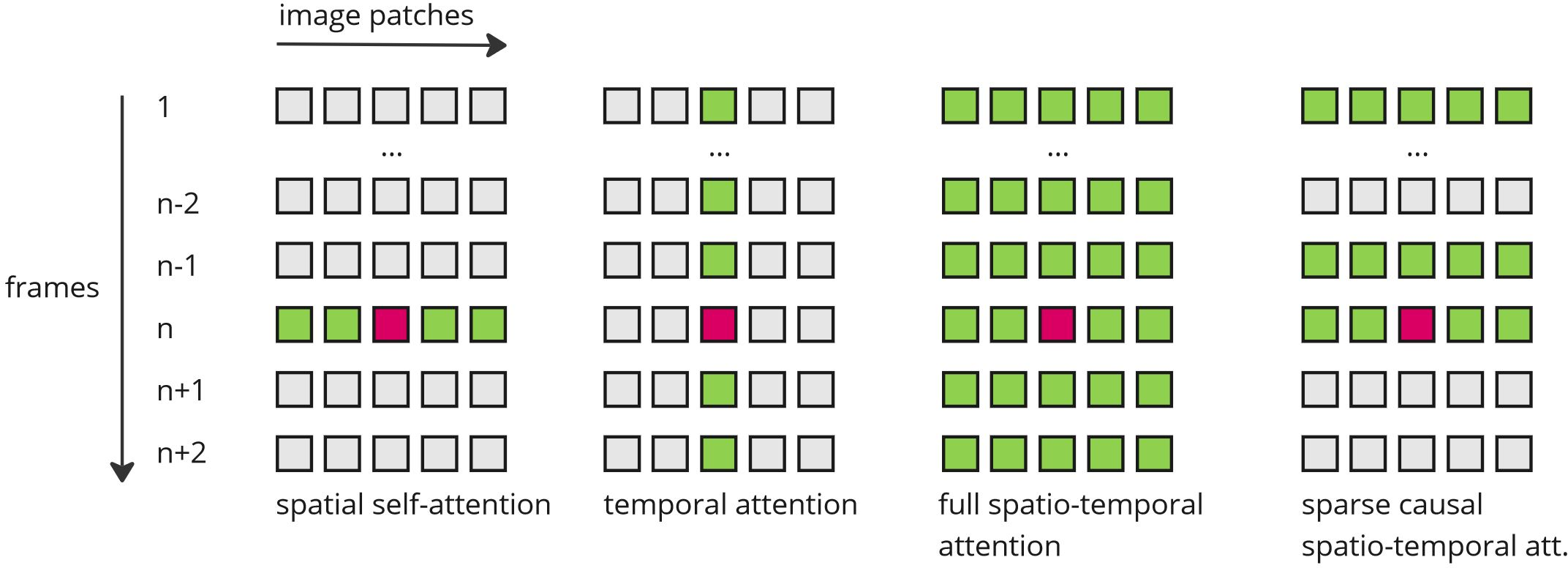
Temporal consistency is crucial for video generation, necessitating architectural innovations to address frame-to-frame coherence problems (Figure 3). The paper analyzes different strategies, such as:

Figure 3: Limitations of text-to-video diffusion models for generating consistent videos.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite advancements, several challenges persist, such as the need for larger, well-annotated video datasets for training, and mitigating the computational demands of video models. The pursuit of more efficient architectures and improved training techniques is ongoing. The survey suggests possible advancements, including better data curation strategies and optimization of model architectures to exploit hardware capabilities better.
Conclusion
The survey underscores the transformative potential of diffusion models in video generation, emphasizing their flexibility and utility across multiple domains. It articulates the current state of research, outlines ongoing challenges, and projects future pathways for enhancing video diffusion methodologies.