- The paper demonstrates that first-person uncertainty expressions significantly decrease user reliance on AI systems, as shown by lower agreement rates.
- The study employed a large-scale experiment with 404 participants and manipulated uncertainty phrasing to assess its effects on trust and task accuracy.
- Results indicate that uncertainty prompts encourage users to verify AI outputs, fostering more critical interaction in high-stakes scenarios.
Examining the Impact of LLMs' Uncertainty Expression on User Reliance and Trust
Introduction
The paper presented in "I'm Not Sure, But...: Examining the Impact of LLMs' Uncertainty Expression on User Reliance and Trust" investigates how expressions of uncertainty by LLMs influence user reliance and trust. The research is motivated by concerns about overreliance on LLMs, which are capable of producing convincing yet incorrect outputs. The primary aim of the paper is to assess whether natural language expressions of uncertainty can mitigate this overreliance.
Methodology
A large-scale pre-registered experiment was conducted involving 404 participants who were tasked with answering medical questions with or without access to a fictional LLM-infused search engine. Participants were divided into four conditions: Control (no uncertainty expression), Uncertain1st (first-person uncertainty expression), UncertainGeneral (general perspective uncertainty expression), and No-AI (without AI assistance). The paper utilized behavioral and self-reported measures to determine the impact of uncertainty expressions on reliance, trust, and task performance.
Design and Considerations
In the experiment, participants engaged with AI outputs that either expressed uncertainty or did not. The paper design emphasized the importance of evaluating both the presence and the linguistic perspective of uncertainty. For the Uncertain1st condition, expressions like "I'm not sure, but..." were used, whereas for UncertainGeneral, phrases such as "It's not clear, but..." were employed. This allowed for a nuanced evaluation of how personal versus impersonal uncertainty expressions affect user behavior.
Results
Impact on Reliance and Trust: The paper found that first-person uncertainty expressions significantly decreased participant reliance on the AI system, as indicated by lower agreement rates with AI-provided answers. Moreover, participants exposed to uncertainty expressions reported diminished trust in the AI's responses. The general perspective induced weaker effects compared to the first-person perspective.
Accuracy and Task Performance: Participants exposed to uncertainty expressions demonstrated increased task accuracy, particularly when the AI’s answers were incorrect. This suggests that conveying uncertainty prompts users to engage more critically with AI outputs, thereby reducing overreliance.
Time on Task and Source Verification: The introduction of uncertainty expressions increased the time participants spent on tasks and encouraged them to verify information using additional resources. This behavior aligns with a more cautious approach induced by recognizing the AI's expressed uncertainty.
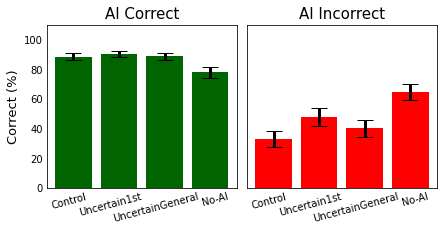
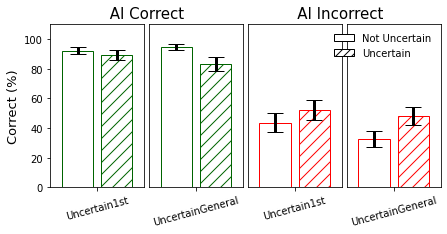
Figure 1: Between-condition analysis results indicate variations in task performance and agreement rates across uncertainty expression conditions.
Implications
The research highlights that uncertainty expressions can be instrumental in reducing overreliance on AI systems. The results support the adoption of natural language uncertainty expressions in LLM applications, particularly in high-stakes scenarios such as medical information retrieval. The findings advocate for the nuanced design of AI interfaces, emphasizing the importance of perspective in uncertainty expressions.
Future Directions
Further investigation is needed to explore the long-term implications of uncertainty expressions and their potential impact across different domains and user demographics. Additionally, researchers should consider the calibration of uncertainty expressions to optimize trust calibration without inducing unwarranted skepticism or underreliance.
Conclusion
The paper provides valuable insights into the role of uncertainty expressions in modulating user interaction with AI systems. By demonstrating the effectiveness of well-crafted uncertainty prompts, it offers a pathway to enhancing AI reliability and user trust, while advocating for thoughtful integration of such features in future AI deployments.



