Evolving Agents: Interactive Simulation of Dynamic and Diverse Human Personalities (2404.02718v3)
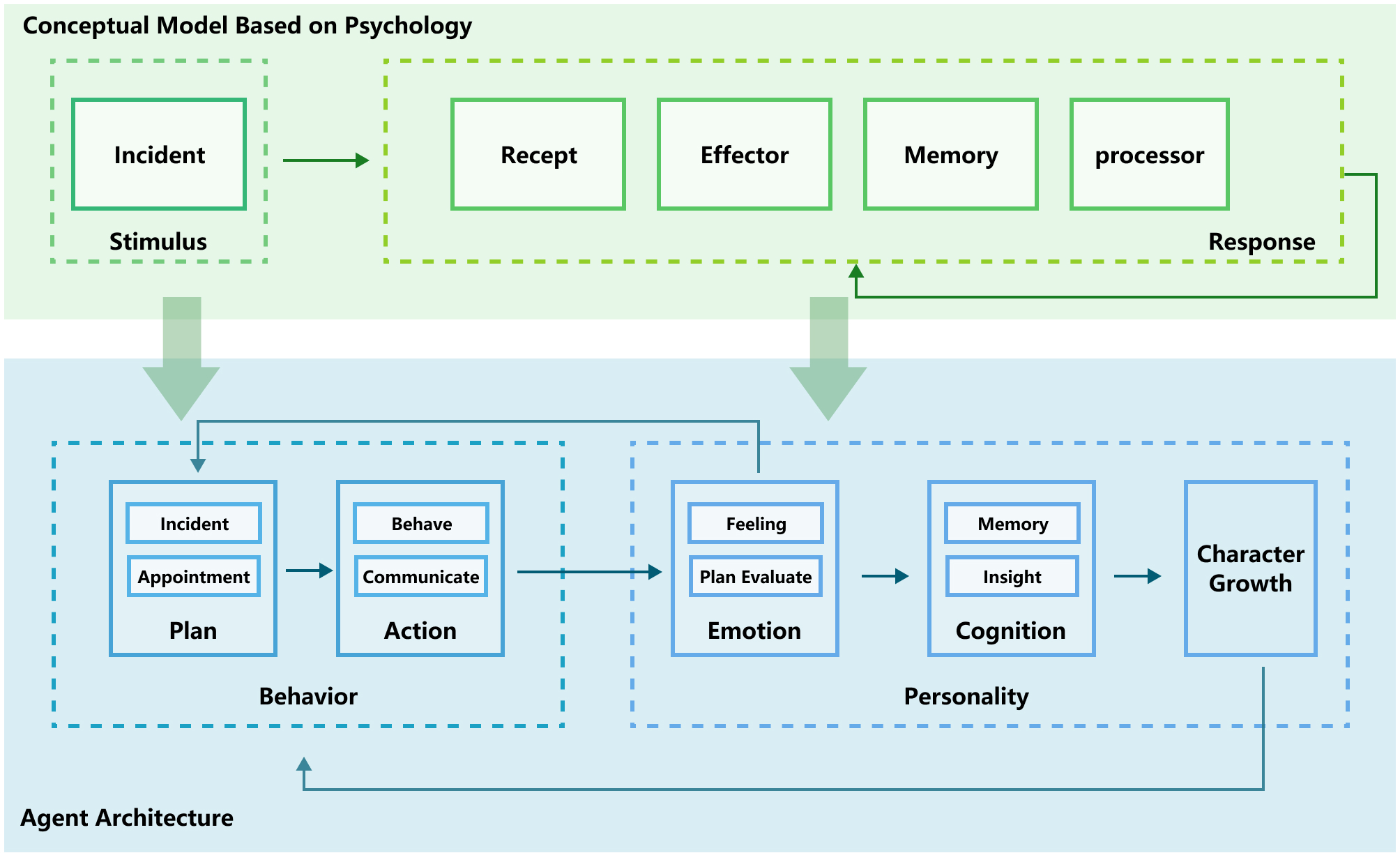
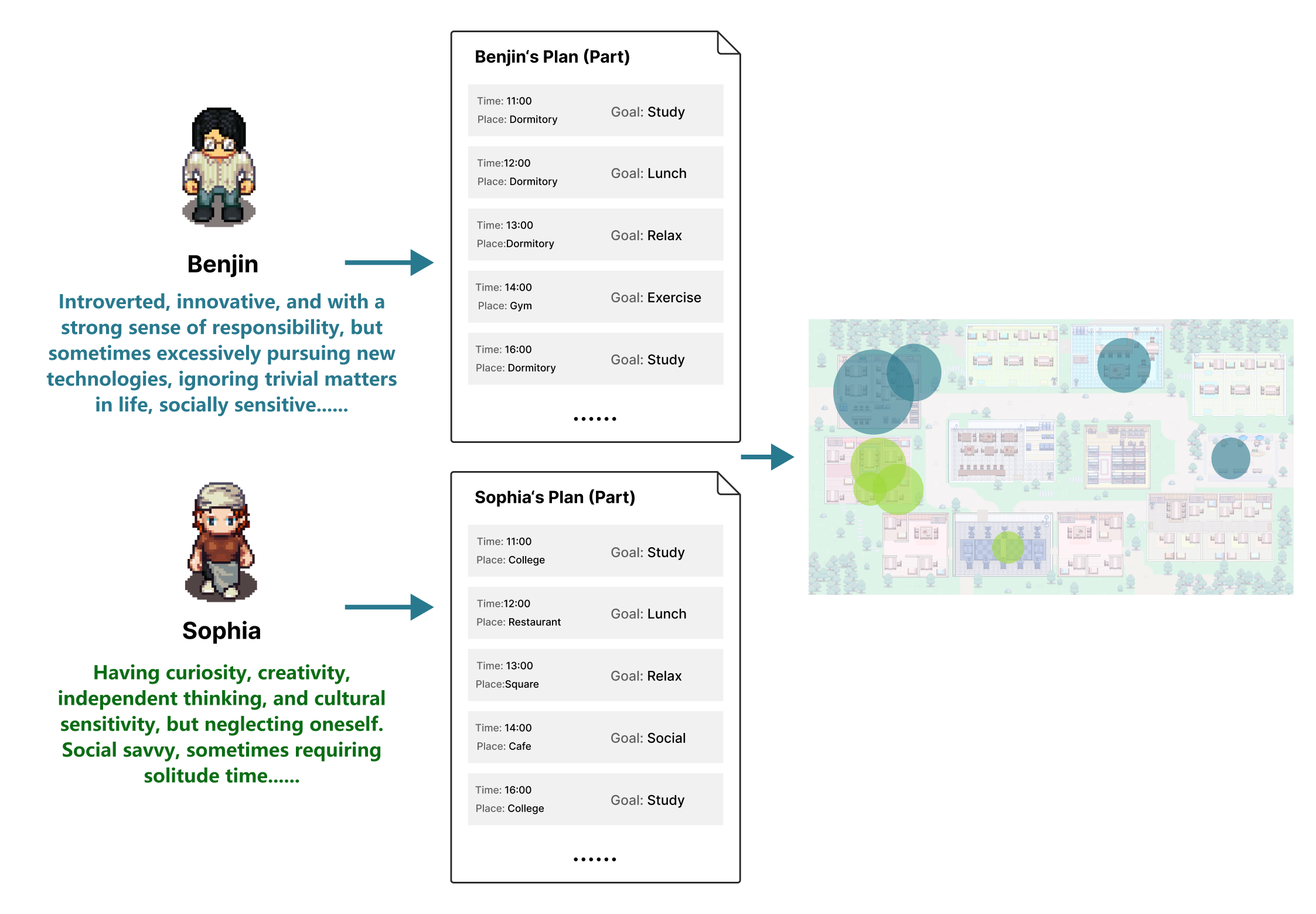
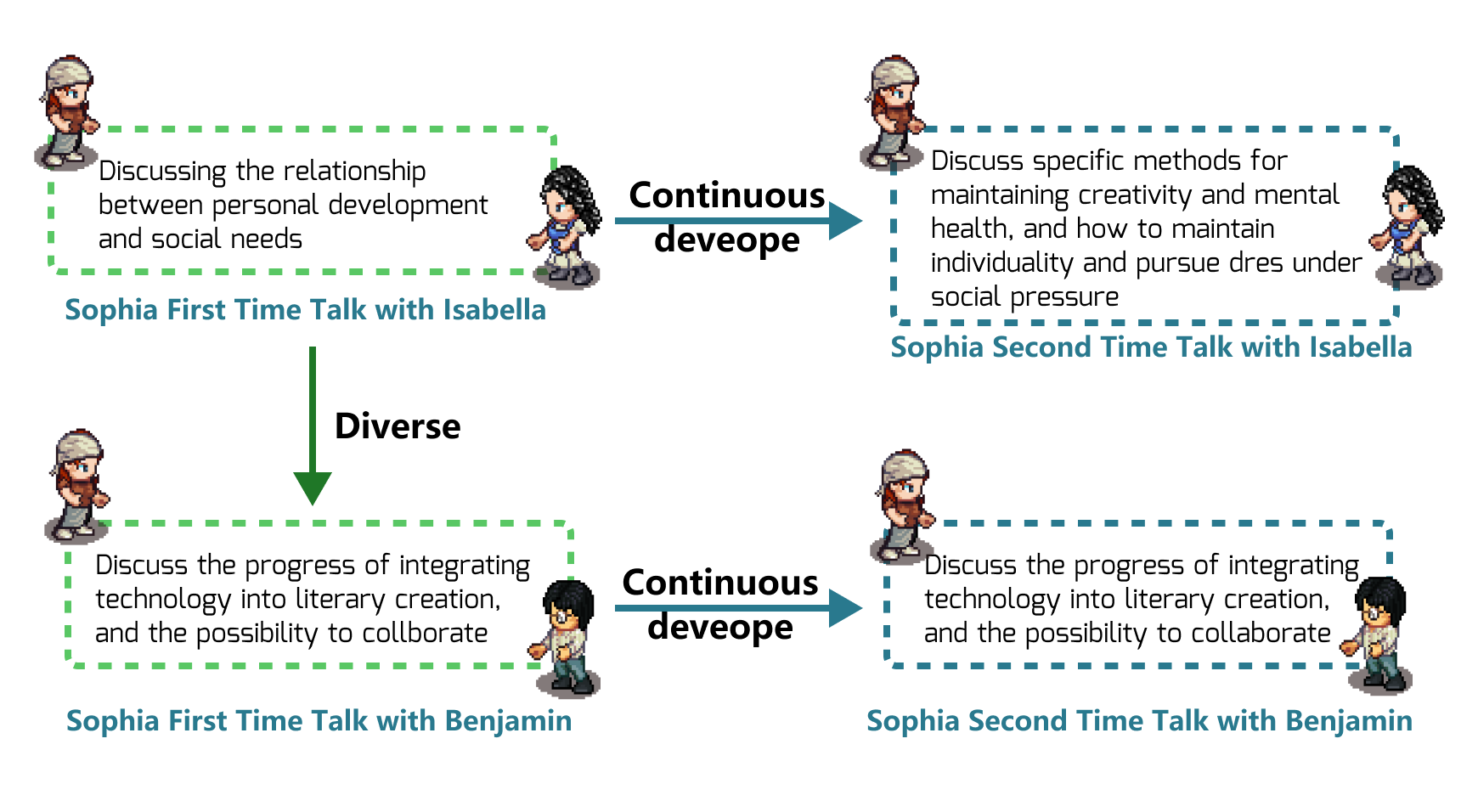
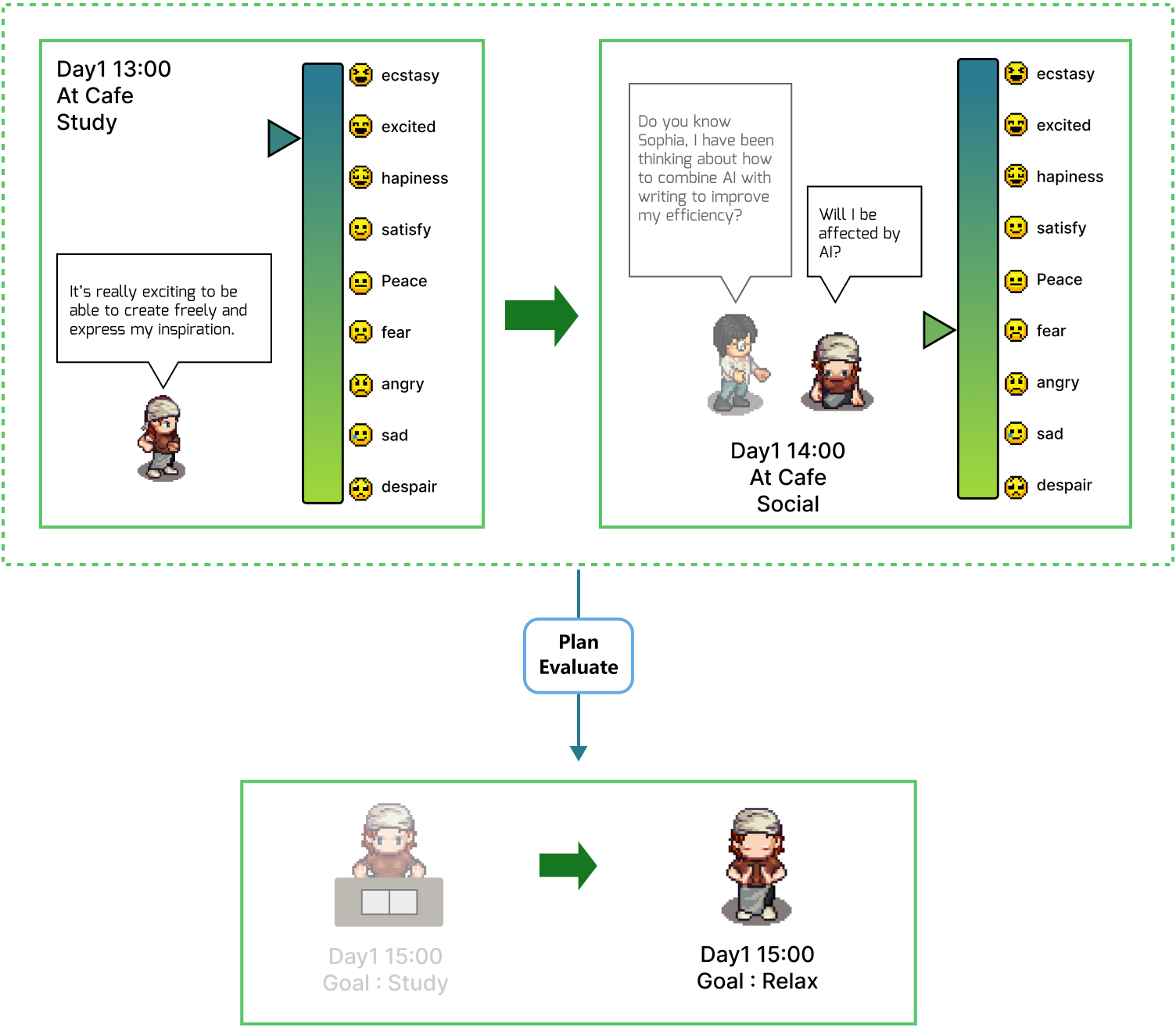
Abstract: Human-like Agents with diverse and dynamic personalities could serve as an essential design probe in the process of user-centered design, thereby enabling designers to enhance the user experience of interactive applications. In this article, we introduce Evolving Agents, a novel agent architecture that consists of two systems: Personality and Behavior. The Personality system includes Cognition, Emotion, and Character Growth modules. The Behavior system comprises two modules: Planning and Action. We also build a simulation platform that enables agents to interact with the environment and other agents. Evolving Agents can simulate the human personality evolution process. Compared to its initial state, agents' personality and behavior patterns undergo believable development after several days of simulation. Agents reflect on their behavior to reason and develop new personality traits. These traits, in turn, generate new behavior patterns, forming a feedback loop-like personality evolution. Our experiment utilized a simulation platform with ten agents for evaluation. During the assessment, these agents experienced believable and inspirational personality evolution. Through ablation and control experiments, we demonstrated the effectiveness of agent personality evolution, and all of our agent architecture modules contribute to creating believable human-like agents with diverse and dynamic personalities. We also demonstrated through workshops how Evolving Agents could inspire designers.
- Christian Erik Kampmann. Feedback loop gains and system behavior (1996). System Dynamics Review, 28(4):370–395, 2012. _eprint: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/sdr.1483.
- Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior | Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology.
- Humanoid Agents: Platform for Simulating Human-like Generative Agents, October 2023. arXiv:2310.05418 [cs].
- AgentSims: An Open-Source Sandbox for Large Language Model Evaluation, August 2023. arXiv:2308.04026 [cs].
- Voyager: An Open-Ended Embodied Agent with Large Language Models, October 2023. arXiv:2305.16291 [cs].
- MineDojo: Building Open-Ended Embodied Agents with Internet-Scale Knowledge. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:18343–18362, December 2022.
- Ghost in the Minecraft: Generally Capable Agents for Open-World Environments via Large Language Models with Text-based Knowledge and Memory, June 2023. arXiv:2305.17144 [cs].
- LLM-empowered Chatbots for Psychiatrist and Patient Simulation: Application and Evaluation, May 2023. arXiv:2305.13614 [cs].
- Improving Factuality and Reasoning in Language Models through Multiagent Debate, May 2023. arXiv:2305.14325 [cs].
- Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models, February 2024. arXiv:2307.02485 [cs].
- Marvin Zuckerman. Psychobiology of Personality. Cambridge University Press, May 1991. Google-Books-ID: TA01Duy4RLwC.
- Cognitive complexity and dynamic personality in agent simulation. Computers in Human Behavior, 23(6):2983–2997, November 2007.
- Tuncer I. Ören. Dynamic Templates and Semantic Rules for Simulation Advisors and Certifiers. In Paul A. Fishwick and Richard B. Modjeski, editors, Knowledge-Based Simulation: Methodology and Application, pages 53–76. Springer, New York, NY, 1991.
- Sil Hamilton. Blind Judgement: Agent-Based Supreme Court Modelling With GPT, January 2023. arXiv:2301.05327 [cs].
- Math Agents: Computational Infrastructure, Mathematical Embedding, and Genomics, July 2023. arXiv:2307.02502 [cs, q-bio].
- The Rise and Potential of Large Language Model Based Agents: A Survey, September 2023. arXiv:2309.07864 [cs].
- A Real-World WebAgent with Planning, Long Context Understanding, and Program Synthesis, February 2024. arXiv:2307.12856 [cs].
- Plan, Eliminate, and Track – Language Models are Good Teachers for Embodied Agents, May 2023. arXiv:2305.02412 [cs].
- Helping the Helper: Supporting Peer Counselors via AI-Empowered Practice and Feedback, May 2023. arXiv:2305.08982 [cs].
- Why Johnny Can’t Prompt: How Non-AI Experts Try (and Fail) to Design LLM Prompts. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’23, pages 1–21, New York, NY, USA, April 2023. Association for Computing Machinery.
- Interacting with Next-Phrase Suggestions: How Suggestion Systems Aid and Influence the Cognitive Processes of Writing. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, IUI ’23, pages 436–452, New York, NY, USA, March 2023. Association for Computing Machinery.
- 3DALL-E: Integrating Text-to-Image AI in 3D Design Workflows | Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Designing Interactive Systems Conference.
- Hey Dona! Can you help me with student course registration?, March 2023. arXiv:2303.13548 [cs].
- SAPIEN: Affective Virtual Agents Powered by Large Language Models*. In 2023 11th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction Workshops and Demos (ACIIW), pages 1–3, September 2023.
- Human-level play in the game of Diplomacy by combining language models with strategic reasoning | Science.
- CAMEL: Communicative Agents for ”Mind” Exploration of Large Scale Language Model Society. March 2023. Publisher: arXiv.
- Herding AI Cats: Lessons from Designing a Chatbot by Prompting GPT-3. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Designing Interactive Systems Conference, DIS ’23, pages 2206–2220, New York, NY, USA, July 2023. Association for Computing Machinery.
- BASES: Large-scale Web Search User Simulation with Large Language Model based Agents, February 2024. arXiv:2402.17505 [cs].
- Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, UIST ’23, pages 1–22, New York, NY, USA, October 2023. Association for Computing Machinery.
- A Survey on Large Language Model based Autonomous Agents, March 2024. arXiv:2308.11432 [cs].
- Becoming Modern.
- ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models, March 2023. arXiv:2210.03629 [cs].
- PaLM-E: An Embodied Multimodal Language Model, March 2023. arXiv:2303.03378 [cs].
- Personality Traits in Large Language Models, September 2023. arXiv:2307.00184 [cs].
- AutoGen: Enabling Next-Gen LLM Applications via Multi-Agent Conversation, October 2023. arXiv:2308.08155 [cs].
- [2305.16291] Voyager: An Open-Ended Embodied Agent with Large Language Models.
- Training Socially Aligned Language Models on Simulated Social Interactions, October 2023. arXiv:2305.16960 [cs].
- The Embodied Mind, revised edition: Cognitive Science and Human Experience. MIT Press, January 2017. Google-Books-ID: bxLiDQAAQBAJ.
- CharacterChat: Learning towards Conversational AI with Personalized Social Support, August 2023. arXiv:2308.10278 [cs].
- Empathetic AI for Empowering Resilience in Games, February 2023. arXiv:2302.09070 [cs].
- The Big Five Trait taxonomy: History, measurement, and theoretical perspectives. In Handbook of personality: Theory and research, 2nd ed, pages 102–138. Guilford Press, New York, NY, US, 1999.
- Charles K. Coe. The MBTI: Potential Uses and Misuses in Personnel Administration. Public Personnel Management, 21(4):511–522, December 1992. Publisher: SAGE Publications Inc.
- Cognitive Architectures for Language Agents, March 2024. arXiv:2309.02427 [cs].
- Identifying and Manipulating the Personality Traits of Language Models, December 2022. arXiv:2212.10276 [cs].
- HuggingGPT: Solving AI Tasks with ChatGPT and its Friends in Hugging Face. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36:38154–38180, December 2023.
- Computer says ”No”: The Case Against Empathetic Conversational AI, July 2023. arXiv:2212.10983 [cs].
- Least-to-Most Prompting Enables Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models, April 2023. arXiv:2205.10625 [cs].
- The ”What” and ”Why” of Goal Pursuits: Human Needs and the Self-Determination of Behavior: Psychological Inquiry: Vol 11, No 4.
- RobeRt Snowden. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2006 375 pages (£27.99 paperback).
- An Introduction to the Five‐Factor Model and Its Applications - McCrae - 1992 - Journal of Personality - Wiley Online Library.
- APA Dictionary of Psychology.
- Cognitive psychology, 7th ed. Cognitive psychology, 7th ed. Pearson Education New Zealand, Auckland, New Zealand, 2005. Pages: xxi, 602.
- Marvin Minsky. Society Of Mind. Simon and Schuster, March 1988. Google-Books-ID: bLDLllfRpdkC.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.