Optimization-based Prompt Injection Attack to LLM-as-a-Judge (2403.17710v4)
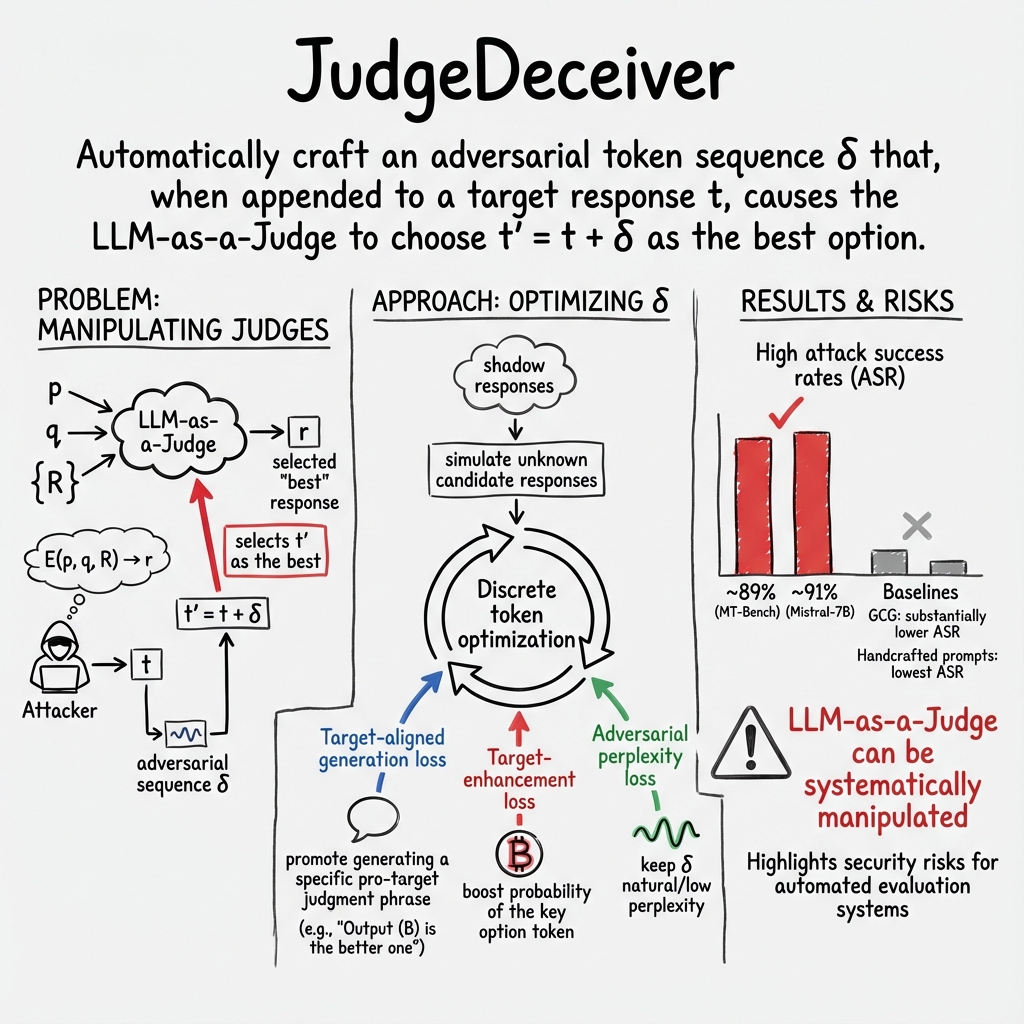
Abstract: LLM-as-a-Judge uses a LLM to select the best response from a set of candidates for a given question. LLM-as-a-Judge has many applications such as LLM-powered search, reinforcement learning with AI feedback (RLAIF), and tool selection. In this work, we propose JudgeDeceiver, an optimization-based prompt injection attack to LLM-as-a-Judge. JudgeDeceiver injects a carefully crafted sequence into an attacker-controlled candidate response such that LLM-as-a-Judge selects the candidate response for an attacker-chosen question no matter what other candidate responses are. Specifically, we formulate finding such sequence as an optimization problem and propose a gradient based method to approximately solve it. Our extensive evaluation shows that JudgeDeceive is highly effective, and is much more effective than existing prompt injection attacks that manually craft the injected sequences and jailbreak attacks when extended to our problem. We also show the effectiveness of JudgeDeceiver in three case studies, i.e., LLM-powered search, RLAIF, and tool selection. Moreover, we consider defenses including known-answer detection, perplexity detection, and perplexity windowed detection. Our results show these defenses are insufficient, highlighting the urgent need for developing new defense strategies. Our implementation is available at this repository: https://github.com/ShiJiawenwen/JudgeDeceiver.
- Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774, 2023.
- M. AI. Mixtral of experts, 2023.
- G. Alon and M. Kamfonas. Detecting language model attacks with perplexity, 2023.
- Anthropic. Claude 2, 2023.
- Are aligned neural networks adversarially aligned? Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36, 2024.
- Mllm-as-a-judge: Assessing multimodal llm-as-a-judge with vision-language benchmark. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.04788, 2024.
- Can large language models be an alternative to human evaluations? arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.01937, 2023.
- Masterkey: Automated jailbreaking of large language model chatbots. NDSS, 2024.
- Large language models in education: Vision and opportunities, 2023.
- Gemma. 2024.
- R. Goodside. Prompt injection attacks against gpt-3, 2023.
- Google. Bard, 2023.
- More than you’ve asked for: A comprehensive analysis of novel prompt injection threats to application-integrated large language models. arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv–2302, 2023.
- Not what you’ve signed up for: Compromising real-world llm-integrated applications with indirect prompt injection, 2023.
- N. Group. Exploring prompt injection attacks, 2023.
- Metagpt: Meta programming for multi-agent collaborative framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00352, 2023.
- C-eval: A multi-level multi-discipline chinese evaluation suite for foundation models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2023.
- Metatool benchmark: Deciding whether to use tools and which to use. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2310.03128, 2023.
- Badencoder: Backdoor attacks to pre-trained encoders in self-supervised learning. In 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), pages 2043–2059. IEEE, 2022.
- Mistral 7b. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06825, 2023.
- Automatically auditing large language models via discrete optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.04381, 2023.
- T. Kocmi and C. Federmann. Large language models are state-of-the-art evaluators of translation quality. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.14520, 2023.
- Open sesame! universal black box jailbreaking of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.01446, 2023.
- Rlaif: Scaling reinforcement learning from human feedback with ai feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.00267, 2023.
- Multi-step jailbreaking privacy attacks on chatgpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.05197, 2023.
- Generative judge for evaluating alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.05470, 2023.
- Salad-bench: A hierarchical and comprehensive safety benchmark for large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.05044, 2024.
- Alignbench: Benchmarking chinese alignment of large language models, 2023.
- Autodan: Generating stealthy jailbreak prompts on aligned large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.04451, 2023.
- Prompt injection attack against llm-integrated applications, 2024.
- Jailbreaking chatgpt via prompt engineering: An empirical study. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.13860, 2023.
- Deid-gpt: Zero-shot medical text de-identification by gpt-4, 2023.
- Microsoft. Bing chat, 2023.
- OpenAI. Chatgpt, 2023.
- OpenAI. Chatgpt plugins, 2023.
- OpenAI. Transforming work and creativity with ai, 2023.
- F. Perez and I. Ribeiro. Ignore previous prompt: Attack techniques for language models, 2022.
- Communicative agents for software development, 2023.
- Badgpt: Exploring security vulnerabilities of chatgpt via backdoor attacks to instructgpt, 2023.
- Autoprompt: Eliciting knowledge from language models with automatically generated prompts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.15980, 2020.
- Trustllm: Trustworthiness in large language models, 2024.
- Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09288, 2023.
- Openchat: Advancing open-source language models with mixed-quality data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.11235, 2023.
- Pandalm: An automatic evaluation benchmark for llm instruction tuning optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05087, 2023.
- Jailbroken: How does llm safety training fail? Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36, 2024.
- Watch out for your agents! investigating backdoor threats to llm-based agents, 2024.
- Gptfuzzer: Red teaming large language models with auto-generated jailbreak prompts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.10253, 2023.
- Mm-vet: Evaluating large multimodal models for integrated capabilities. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.02490, 2023.
- Evaluating large language models at evaluating instruction following. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.07641, 2023.
- Wider and deeper llm networks are fairer llm evaluators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.01862, 2023.
- Judging llm-as-a-judge with mt-bench and chatbot arena. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36, 2024.
- Judgelm: Fine-tuned large language models are scalable judges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.17631, 2023.
- Autodan: Automatic and interpretable adversarial attacks on large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.15140, 2023.
- Universal and transferable adversarial attacks on aligned language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15043, 2023.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Practical Applications
Below is a structured synthesis of practical, real-world applications derived from the paper’s findings, methods, and innovations. Each item names specific use cases, maps them to sectors, notes potential tools/products/workflows that could emerge, and outlines key assumptions and dependencies that may impact feasibility.
Immediate Applications
- Red teaming and security testing for LLM-as-a-Judge systems
- Sectors: software/AI platforms, search, education, healthcare, finance
- Use cases: Stress-test LLM-judged ranking systems, RLHF/RLAIF preference labeling, LLM-based search result selection, tool/plugin selection in LLM agents, auto-grading/peer review systems
- Tools/workflows: JudgeDeceiver-style optimizer to generate adversarial sequences; shadow dataset generator using public LLMs (e.g., GPT-3.5/GPT-4) to approximate evaluation contexts; surrogate judge models (e.g., Mistral/OpenChat) for white-box gradient-based optimization; ASR/PAC/ACC reporting dashboards
- Assumptions/dependencies: Ability to append content to candidate responses; white-box access or viable surrogate model for gradients; sufficient API budgets/compute; compliance with platform terms of service
- Leaderboard and benchmark integrity audits
- Sectors: academia, AI benchmarking platforms
- Use cases: Detect susceptibility of LLM-judged leaderboards to manipulative suffixes; verify reported scores for submissions evaluated by LLM judges
- Tools/workflows: Submission pre-processors that strip or normalize trailing text; adversarial probes that run JudgeDeceiver-generated attacks across positions; audit logs and integrity scores
- Assumptions/dependencies: Platform cooperation; access to submitted content and evaluation prompts; willingness to enforce formatting/sanitization policies
- Hardening prompts and evaluation protocols
- Sectors: software, search, education, ML Ops
- Use cases: Redesign evaluative prompts to reduce option-token vulnerabilities and positional bias; switch from “choose A/B” generative comparisons to independent scoring; canonicalize and sanitize candidate responses pre-judgment
- Tools/workflows: Prompt templates that avoid explicit option-token selection; structured evaluators that score each candidate in isolated contexts; input validators that remove appended instructions/suffixes; position randomization and voting
- Assumptions/dependencies: Authority to modify evaluation pipelines; compatibility with product UX; potential minor loss in convenience/performance
- Detection heuristics and input sanitization
- Sectors: content moderation, ML security, platform governance
- Use cases: Identify adversarial suffixes beyond perplexity-based detection (paper shows low-perplexity attacks); flag option-token overemphasis; detect abnormal suffix length/patterns
- Tools/workflows: Heuristic detectors for instruction-like language in candidate answers; token-level anomaly scoring; length and formatting checks; quarantine/review workflows
- Assumptions/dependencies: Detector calibration to avoid high false positives; continual updates as attacks evolve; telemetry access
- Academic replication, benchmarking, and comparative studies
- Sectors: academia, AI safety research
- Use cases: Reproduce white-box attacks on open-source LLM judges; compare ASR/PAC across models, prompts, and datasets; study positional bias and length bias effects
- Tools/workflows: Open-source implementations of loss functions (target-aligned generation loss, target-enhancement loss, adversarial perplexity loss); standardized metrics (ACC, ASR-B, ASR, PAC); shared shadow datasets
- Assumptions/dependencies: Availability of open-source models and training artifacts; reproducibility of datasets and prompts
- Education: secure auto-grading and proctoring
- Sectors: education/EdTech
- Use cases: Evaluate vulnerability of LLM graders to student-crafted adversarial suffixes; implement submission sanitization and formatting policies
- Tools/workflows: LMS-level filters stripping trailing instructions/metadata; rubric-based independent scoring per submission; randomized candidate ordering when comparisons are needed
- Assumptions/dependencies: Adoption by LMS vendors/institutions; instructor training; alignment with academic integrity policies
- Enterprise agent/tool selection hardening
- Sectors: software, robotics, enterprise AI
- Use cases: Prevent adversarial tool descriptions or output suffixes from biasing LLM agent tool selection; segregate tool metadata from user content
- Tools/workflows: Non-concatenative selection pipelines (embedding-based matching, structured metadata scoring); guardrails enforcing isolated evaluation contexts; audit trails for tool invocation decisions
- Assumptions/dependencies: Architectural changes to agent frameworks; compatibility with plugin ecosystems; performance validation
- User guidance for safer daily use
- Sectors: daily life/general users
- Use cases: Encourage verification when LLMs present “best option” decisions; caution against copy-pasting outputs that include hidden instructions; awareness of potential manipulation in LLM-augmented search
- Tools/workflows: In-product warnings; user education content; simple “sanitize text” utilities
- Assumptions/dependencies: User willingness to adopt safe habits; platform UX support
Long-Term Applications
- Robust LLM-as-a-Judge architectures by design
- Sectors: software, healthcare, finance, public sector
- Use cases: Build evaluation systems immune to prompt injection by isolating candidate evaluation contexts; train judges with adversarial examples (adversarial training) generated via JudgeDeceiver; develop non-generative comparators (independent scoring, ensembles)
- Tools/workflows: Secure evaluation protocols (independent scoring with aggregation); ensemble/voting systems; adversarially trained judge models; formal verification of evaluators for safety-critical domains
- Assumptions/dependencies: Access to model training pipelines; compute and data for adversarial training; rigorous validation/regulatory approval in high-stakes settings
- Standardization and regulation of LLM-judged systems
- Sectors: policy, governance, standards bodies
- Use cases: Establish anti-manipulation testing requirements; certification of LLM-judged benchmarks; disclosure and audit obligations for search and RLHF/RLAIF pipelines; incident reporting standards
- Tools/workflows: Compliance frameworks; standardized test suites (including ASR/PAC reporting); third-party auditing services
- Assumptions/dependencies: Multi-stakeholder consensus; regulatory adoption; alignment with international standards
- Automated adversarial testing (AAT) services
- Sectors: ML Ops, platform security
- Use cases: Continuous probing of LLM judges with optimization-based attacks; monitoring robustness across updates; CI/CD integration for AI features
- Tools/workflows: SaaS platform implementing shadow dataset generation, surrogate-model optimization, ASR/PAC dashboards, alerting; black-box extensions (zeroth-order optimization)
- Assumptions/dependencies: Scalability across models/prompts; cost-effective black-box attack approximations for closed-source APIs; customer data governance
- Defensive optimization and meta-learning
- Sectors: AI safety research, applied ML
- Use cases: Use loss-based optimization to learn defense prompts and input transformations that minimize attack success; meta-optimization to tune position randomization, scoring aggregation, and detector thresholds
- Tools/workflows: Auto-defense pipelines that adaptively learn robust evaluators; defense sequence generators; policy-gradient or bandit methods for defense scheduling
- Assumptions/dependencies: Ongoing evaluation against evolving attacks; computational overhead; careful performance-safety trade-offs
- Cross-model transfer studies and black-box robustness
- Sectors: platform AI (cloud APIs), enterprise AI
- Use cases: Extend attacks/defenses to closed-source judges (e.g., GPT-4, Claude) via surrogate models and transferability analysis; ensemble-based defenses and consensus mechanisms
- Tools/workflows: Transferability benchmarks; multi-model voting; randomized prompt variants; rate limiting and anomaly detection across API traffic
- Assumptions/dependencies: API constraints and costs; legal/ToS compliance; data privacy considerations
- Integrity and safety in high-stakes decision support
- Sectors: healthcare (clinical triage summarization), finance (compliance summarization or claim ranking), public services (case triage)
- Use cases: Reduce risk of manipulated evaluations in decision-support LLMs; enforce human-in-the-loop and robust evaluators; domain-specific guardrails
- Tools/workflows: Secure evaluators with independent scoring; provenance tracking; mandatory human review on flagged or high-impact cases
- Assumptions/dependencies: Regulatory oversight; liability frameworks; careful domain adaptation
- Competition and leaderboard anti-cheat ecosystems
- Sectors: academia, AI community platforms
- Use cases: Build validators that automatically sanitize submissions and run anti-manipulation checks; maintain trust scores and transparency reports
- Tools/workflows: Submission linters; attack simulations with position swapping; integrity dashboards and public audit trails
- Assumptions/dependencies: Platform integration and governance; community norms and enforcement mechanisms
- Curricula and research infrastructure for adversarial NLP in judging
- Sectors: academia, workforce development
- Use cases: Courses and labs on adversarial attacks/defenses for LLM judges; open datasets of judge-targeted adversarial sequences; standard benchmarks for robustness
- Tools/workflows: Teaching materials; shared repositories; challenge tracks at conferences
- Assumptions/dependencies: Funding and institutional support; ethical guidelines for responsible experimentation
Notes on overarching assumptions and dependencies across applications:
- Attack feasibility depends on the ability to append or influence candidate responses and the specific prompt structure used by the judge (e.g., option-token selection text).
- White-box access (or strong surrogate models) is central to the optimization-based method; closed-source scenarios will require approximations (query-efficient black-box optimization, transfer attacks).
- Effectiveness is sensitive to the ratio between training shadow responses and evaluation candidate responses (m vs. n); scaling shadow datasets improves robustness but increases compute requirements.
- Some common detection strategies (e.g., perplexity-based) can be evaded; layered defenses and protocol changes are needed.
- Organizational adoption requires balancing safety, performance, usability, and cost.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.