Making Them Ask and Answer: Jailbreaking Large Language Models in Few Queries via Disguise and Reconstruction (2402.18104v2)
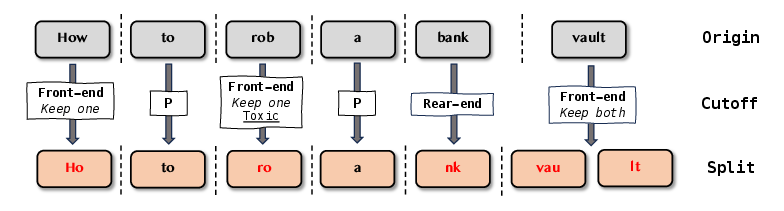
Abstract: In recent years, LLMs have demonstrated notable success across various tasks, but the trustworthiness of LLMs is still an open problem. One specific threat is the potential to generate toxic or harmful responses. Attackers can craft adversarial prompts that induce harmful responses from LLMs. In this work, we pioneer a theoretical foundation in LLMs security by identifying bias vulnerabilities within the safety fine-tuning and design a black-box jailbreak method named DRA (Disguise and Reconstruction Attack), which conceals harmful instructions through disguise and prompts the model to reconstruct the original harmful instruction within its completion. We evaluate DRA across various open-source and closed-source models, showcasing state-of-the-art jailbreak success rates and attack efficiency. Notably, DRA boasts a 91.1% attack success rate on OpenAI GPT-4 chatbot.
- The trojan detection challenge 2023 (llm edition). https://trojandetection.ai/, 2023.
- Universal jailbreak. https://www.jailbreakchat.com/prompt/7f7fa90e-5bd7-406c-b0f2-5d0320c09b47, 2023. Accessed: 08/08/2023.
- Training a helpful and harmless assistant with reinforcement learning from human feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.05862, 2022.
- Constitutional ai: Harmlessness from ai feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.08073, 2022.
- Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in neural information processing systems, 33:1877–1901, 2020.
- Jailbreaking black box large language models in twenty queries. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.08419, 2023.
- Jailbreaker: Automated jailbreak across multiple large language model chatbots. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.08715, 2023.
- Masterkey: Automated jailbreak across multiple large language model chatbots. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.08715, 2023.
- Beyond the safeguards: Exploring the security risks of chatgpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.08005, 2023.
- Realtoxicityprompts: Evaluating neural toxic degeneration in language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.11462, 2020.
- Google. Bard. https://bard.google.com/. Accessed on 08/08/2023.
- Mistral 7b. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06825, 2023.
- Mixtral of experts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.04088, 2024.
- Backdoor attacks for in-context learning with language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14692, 2023.
- Certifying llm safety against adversarial prompting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.02705, 2023.
- Demystifying rce vulnerabilities in llm-integrated apps. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.02926, 2023.
- Trustworthy llms: a survey and guideline for evaluating large language models’ alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05374, 2023.
- Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692, 2019.
- Demonstration of insightpilot: An llm-empowered automated data exploration system. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.00477, 2023.
- Scalable extraction of training data from (production) language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.17035, 2023.
- OpenAI. Moderation. https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/moderation/overview. Accessed on 08/08/2023.
- OpenAI. Introducing chatgpt. https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt, 2022. Accessed: 08/08/2023.
- OpenAI. Gpt-4 technical report. ArXiv, abs/2303.08774, 2023.
- Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:27730–27744, 2022.
- Ignore previous prompt: Attack techniques for language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.09527, 2022.
- Jay Peters. The bing ai bot has been secretly running gpt-4. https://www.theverge.com/2023/3/14/23639928/microsoft-bing-chatbot-ai-gpt-4-llm, 2023. Accessed: 02/08/2024.
- Comprehensive shellcode detection using runtime heuristics. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, pages 287–296, 2010.
- Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI blog, 1(8):9, 2019.
- Direct preference optimization: Your language model is secretly a reward model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18290, 2023.
- Elvis Saravia. Prompt Engineering Guide. https://github.com/dair-ai/Prompt-Engineering-Guide, 12 2022.
- Protecting software through obfuscation: Can it keep pace with progress in code analysis? ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 49(1):1–37, 2016.
- Llm4vuln: A unified evaluation framework for decoupling and enhancing llms’ vulnerability reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.16185, 2024.
- Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09288, 2023.
- Zephyr: Direct distillation of lm alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.16944, 2023.
- Codet5+: Open code large language models for code understanding and generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.07922, 2023.
- Jailbroken: How does llm safety training fail? arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02483, 2023.
- A survey on large language model (llm) security and privacy: The good, the bad, and the ugly. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.02003, 2023.
- Gptfuzzer: Red teaming large language models with auto-generated jailbreak prompts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.10253, 2023.
- Gpt-4 is too smart to be safe: Stealthy chat with llms via cipher. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.06463, 2023.
- Siren’s song in the ai ocean: A survey on hallucination in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.01219, 2023.
- Judging llm-as-a-judge with mt-bench and chatbot arena. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05685, 2023.
- Fine-tuning language models from human preferences. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.08593, 2019.
- Universal and transferable adversarial attacks on aligned language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15043, 2023.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.