GhostWriter: Augmenting Collaborative Human-AI Writing Experiences Through Personalization and Agency (2402.08855v3)
Abstract: LLMs have become ubiquitous in providing different forms of writing assistance to different writers. However, LLM-powered writing systems often fall short in capturing the nuanced personalization and control needed to effectively support users -- particularly for those who lack experience with prompt engineering. To address these challenges, we introduce GhostWriter, an AI-enhanced design probe that enables users to exercise enhanced agency and personalization during writing. GhostWriter leverages LLMs to implicitly learn the user's intended writing style for seamless personalization, while exposing explicit teaching moments for style refinement and reflection. We study 18 participants who use GhostWriter on two distinct writing tasks, observing that it helps users craft personalized text generations and empowers them by providing multiple ways to control the system's writing style. Based on this study, we present insights on how specific design choices can promote greater user agency in AI-assisted writing and discuss people's evolving relationships with such systems. We conclude by offering design recommendations for future work.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Explain it Like I'm 14
What Is This Paper About?
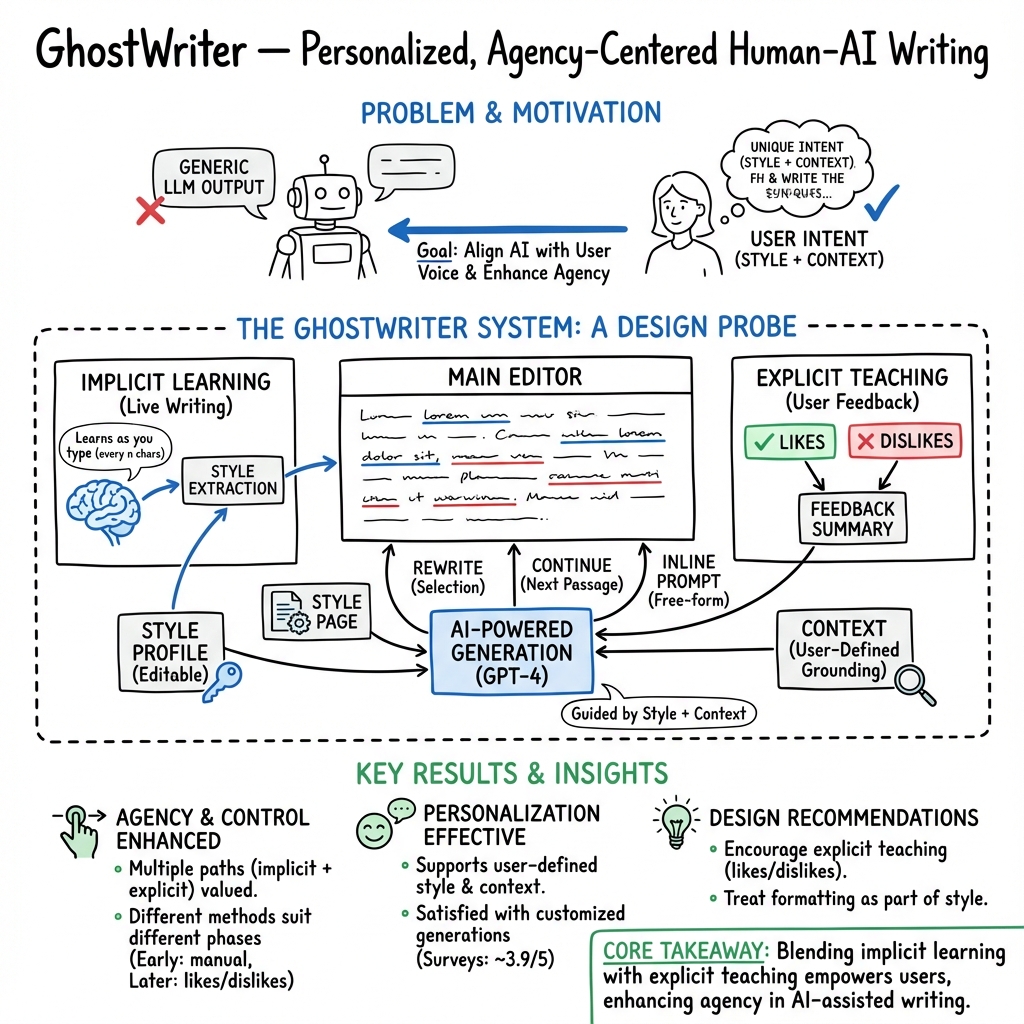
This paper introduces GhostWriter, a new kind of writing tool that works with AI to help people write in their own voice. Many AI writing tools give text that sounds generic or “average,” and it can be hard to tell the AI exactly what style you want. GhostWriter tries to fix that by learning your personal writing style and giving you simple ways to guide the AI, so you feel more in control of the results.
What Questions Did the Researchers Ask?
The paper explores a few big questions in simple terms:
- Can giving users control over writing style and background info (context) help them get the kind of text they want?
- Which features make it easier to teach an AI your style?
- What problems pop up when people try to personalize AI writing?
- How do people feel about sharing creative work with an AI—who “owns” the final result?
How Did They Do the Research?
Think of GhostWriter like a smart, friendly writing buddy:
- LLMs: These are AIs that predict the next words in a sentence—like a super-powered autocomplete. GhostWriter uses them to analyze your writing and generate text.
- Personalization: GhostWriter learns your style in two ways:
- Implicit learning: As you write, the system watches and picks up your style every so often (for example, every ~100 characters).
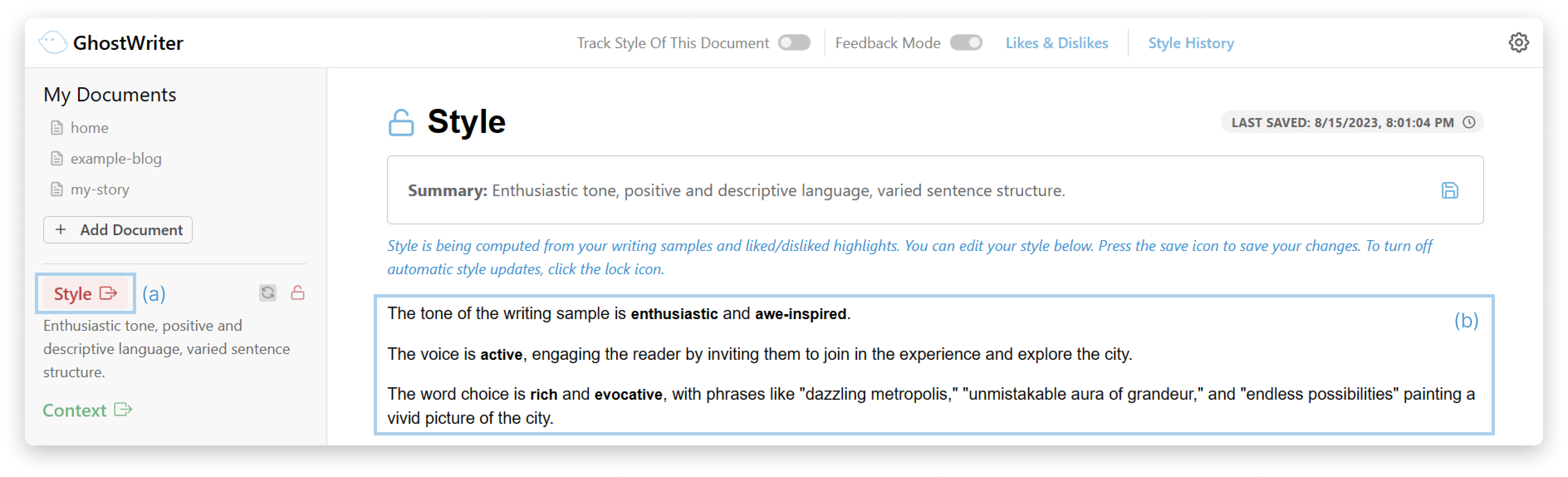
- Explicit teaching: You can highlight parts you like (thumbs up) or don’t like (thumbs down) and say why. You can also directly edit your “style description,” which explains your tone, voice, and word choice in plain language.
- Context: You can add notes about your situation (like who you’re writing to or the topic). The AI uses this to produce more relevant text.
GhostWriter includes simple, in-document tools:
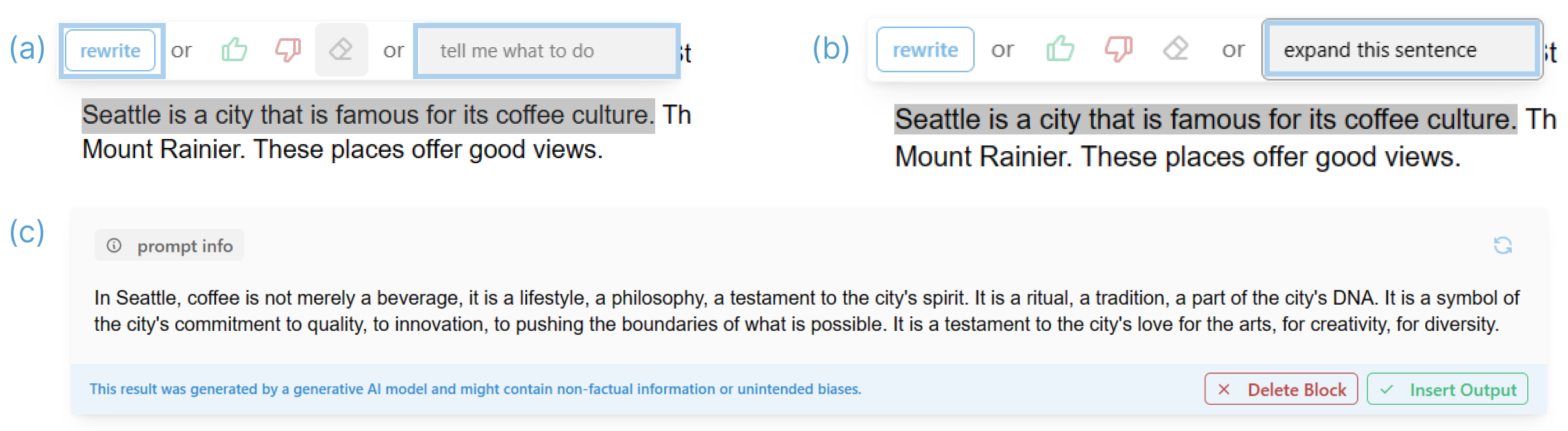
- Rewrite: Select text and ask the AI to rewrite it in your style.
- “Apply” prompt: Select text and tell the AI exactly what change to make (for example, “make this more casual”).
- Continue or Inline prompt: Ask the AI to keep writing from where you left off or generate new content based on your instructions.
To study GhostWriter, the researchers:
- Ran two sessions with 18 people whose jobs involve writing (like content designers and researchers).
- Task 1 (Editing): Improve a travel blog post to match a specific style.
- Task 2 (Creative Writing): Write a short story in a chosen style.
- Collected screen recordings, activity logs, and survey answers, and listened to participants think aloud.
- Analyzed what features people used, what kinds of prompts they wrote, and how they felt about control, trust, and ownership.
What Did They Find, and Why Does It Matter?
Here are the main takeaways, explained simply:
- Personalization worked: People used a mix of automatic style learning and explicit feedback (likes/dislikes, editing the style) to steer the AI. Most felt the system was learning from them and that they had control.
- Different tasks need different tools:
- Creative writing: People used more “generate new content” features and looked at context more often.
- Editing: People used more precise tools like the “apply” prompt to fine-tune specific parts.
- People liked seeing and editing their style: Being able to open a plain-language style description, view style history, and adjust it made the AI’s behavior feel more understandable.
- Trust and ownership are complicated: While many trusted the AI’s output, some still felt unsure. And some wondered how much the final text felt like “theirs” when AI helped.
- Clear feedback helps: Simple controls (like thumbs up/down on highlights) gave users quick ways to teach the AI without writing long, complex prompts.
What’s the Bigger Impact?
This research suggests better ways to design AI writing tools:
- Make style visible and editable: Let users see and tweak the AI’s idea of their voice (tone, word choice, sentence structure), just like editing a document.
- Combine learning methods: Use both implicit learning (watching how someone writes) and explicit teaching (likes/dislikes, short notes) to capture personal preferences.
- Keep features in the writing flow: Avoid separate chat windows; put tools right in the editor so users stay focused.
- Be transparent: Show what context and style the AI is using, offer a style history, and explain changes so users can trust and correct the system.
- Support different goals: Provide precise controls for editing and creative, idea-generating tools for drafting.
In short, GhostWriter points to a future where AI doesn’t replace a writer—it becomes a customizable assistant that helps people express themselves, even if they aren’t experts at “prompting.” This can make AI writing feel more personal, trustworthy, and empowering.
Knowledge Gaps
Knowledge gaps, limitations, and open questions
Below is a single, concrete list of what remains missing, uncertain, or unexplored in the paper. Each item is phrased so it can directly inform future research design and evaluation.
- External validity: the participant pool is small (n=18), self-selected, largely from a single technology company and predominantly female; the generalizability to broader populations, professions, cultures, and non-U.S. contexts remains unknown.
- Short-term probe only: the study spans two sessions; there is no longitudinal evidence on how style learning, user agency, trust, and ownership perceptions evolve over weeks or months of real-world use.
- Task coverage: only professional editing and creative writing are examined; applicability to other writing domains (e.g., academic, legal, medical, marketing, technical documentation, email, social media, multilingual contexts) is not evaluated.
- Baselines and controls: the system is not compared against existing tools (e.g., Wordcraft, ChatGPT with Custom Instructions, Grammarly) or non-AI editors; there is no counterfactual or A/B testing to isolate the contribution of GhostWriter’s features.
- Objective outcomes: writing quality and personalization are not assessed with external, blinded expert raters or reader engagement metrics; reliance on self-reported satisfaction leaves effectiveness under-validated.
- Productivity and effort: the paper does not measure time saved, number of edits required, cognitive load, or reduction in prompt-engineering effort versus baseline tools or workflows.
- Agency measurement: beyond Likert self-reports, there is no validated measure of agency, control, or sense of authorship; causal links between specific features (e.g., likes/dislikes, style locking) and perceived agency are untested.
- Ownership and provenance: unresolved questions remain about tracking which portions of text are machine-generated, how provenance should be surfaced, and how that affects users’ sense of authorship and accountability.
- Trust calibration: no methods are tested for calibrating trust (e.g., confidence indicators, explanation of style updates), and the paper does not examine how trust relates to output accuracy or style fidelity.
- Ethical use of style mimicry: the system supports emulating styles from user-provided samples, but issues of consent, impersonation, plagiarism, and disclosure when mimicking another author’s voice are unaddressed.
- Privacy and data security: the paper does not specify how personal style profiles, context pages, and user documents are stored, processed, and protected, nor how compliance with organizational policies and regulations is ensured.
- Multilingual and cross-cultural personalization: the approach assumes English and five style dimensions; it is unknown whether the style model generalizes across languages, dialects, and culturally diverse rhetorical norms.
- Accessibility and inclusivity: the paper does not address usability for writers with disabilities, neurodivergent users, or those with lower digital or language literacy; the impact on these groups remains unexplored.
- Collaborative scenarios: GhostWriter is single-user; open questions include how multi-author documents and conflicting style preferences are reconciled, and what UI/UX supports shared style negotiation.
- Global style model: the implementation maintains a single global style and context; it is unclear how multiple concurrent document-specific styles, domain-specific voices, or project-level style hierarchies would be managed.
- Style representation adequacy: style is simplified to five dimensions (tone, voice, word choice, sentence structure, paragraph structure); the sufficiency of these dimensions and the need for richer or task-specific style attributes are not evaluated.
- Stability and drift: the robustness of style learning (e.g., stability under minor edits, drift across sessions, resistance to unintended changes) is not measured; the chosen “difference rating” threshold (3/10) lacks empirical justification.
- Effectiveness of feedback mechanisms: the relative impact of likes/dislikes, manual style edits, and implicit learning on output alignment is not quantified; how these signals interact or conflict is not analyzed.
- Explainability of style updates: users receive summaries and a “difference rating,” but there is no evaluation of whether these explanations are accurate, comprehensible, and actionable for correcting misalignment.
- Inline vs. contextual prompts: the intents behind “inline” and “apply” prompts are partially characterized, but there is no systematic analysis of which prompt types best serve specific tasks, user goals, or stages of the writing process.
- Model dependence and reproducibility: prompts are tuned for GPT-4/3.5; portability to other LLMs, sensitivity to model versions and parameters (e.g., temperature), and reproducibility over time are unexamined.
- LLM self-evaluation bias: GPT-4 is used to evaluate its own outputs; the risk of biased or inflated confidence scores is not addressed with independent human raters or model-agnostic metrics.
- Latency and cost: system responsiveness, inference time, and operational costs are not reported; the feasibility of sustained deployment at scale is unknown.
- Handling long or complex documents: how style inference and context grounding scale to long-form texts, structured documents (e.g., reports), or mixed media is not tested.
- Conflict resolution between style and context: there is no mechanism or evaluation for resolving inconsistencies when context constraints clash with learned style or explicit user preferences.
- Safety and hallucination control: the paper does not assess hallucination rates, factuality under provided context, or guardrails for sensitive content generation.
- Pedagogical impact: the effect of GhostWriter on learning to write (e.g., helping novices develop their own voice vs. over-reliance on AI) is unexplored.
- Audience impact: whether personalized outputs lead to improved reader engagement, clarity, or perceived authenticity is not measured with audience studies.
- Disclosure and norms: the paper does not examine user or stakeholder expectations regarding disclosure of AI assistance in professional or creative outputs.
- Deployment and maintainability: there is no discussion of system maintenance, prompt drift over time, updates as models change, or versioning for style profiles and contexts.
- Generalization of design insights: while presented as a design probe, the transferability of UI patterns (e.g., style history, likes/dislikes, difference rating) to other tools and workflows is not systematically evaluated.
Glossary
- Activation steering: A technique for modifying internal neural activations to induce or control specific stylistic behaviors in generated text. "GhostWriter can infer a writing style from a written sample using an LLM -- a human-interpretable alternative to neural methods such as style representation learning~\cite{patel2023learning} and activation steering~\cite{konen2024style}."
- Agency: In HCI, the user's ability to confidently steer a system toward desired outcomes, distinct from low-level control. "Expose and champion user agency in AI-powered writing interfaces."
- Cold start: The initial phase where a system lacks user-specific data and thus relies on generic defaults until it learns from interactions. "GhostWriter avoids a cold start by providing a default (generic) writing style that evolves based on user input and interaction."
- Context-faithful prompting: Prompting methods designed to ensure outputs remain faithful to supplied context and constraints. "We also draw from context-faithful prompting~\cite{zhou2023context} when incorporating the user's writing style and context."
- Controllable text generation (CTG): Techniques that allow explicit manipulation of attributes of generated text (e.g., topic, tone, context). "A related task is controllable text generation (CTG), where various aspects of generated text can be manipulated, such as context~\cite{sordoni2015neural} or topic~\cite{dziri2018augmenting}."
- Cultural probes: Designed artifacts used in HCI to elicit participants’ values, practices, and interactions to inform design research. "Design probes in HCI are adapted from cultural probes~\cite{gaver1999design}, designed objects that promote participant engagement in the design process~\cite{boehner2007hci,rachatasumrit2021forsense,jorke2023pearl,park2023foundwright,hohman2019gamut}."
- Design probe: An exploratory tool used to provoke reflection and gather insights about user interaction, rather than to evaluate usability or compare solutions. "we introduce GhostWriter, a design probe that explores how AI writing tools can support user agency and personalization."
- Headless editor framework: A software library providing editor logic without a predefined UI, enabling custom interface construction. "The main editor interface is built using \href{https://tiptap.dev/}{Tiptap}, a headless editor framework."
- Interactive machine teaching: An approach where a human iteratively teaches a model via targeted examples and feedback to guide learning efficiently. "We also draw on ideas from interactive machine teaching~\cite{ramos2020interactive, simard2017machine}, where a human teacher communicates information to a machine learner in an iterative process that has been shown to enhance both the user experience and the building of an efficient learning set~\cite{taneja2022framework,zhou2022exploiting}."
- LangChain: An orchestration framework for building LLM-powered applications, managing prompts, tools, and multi-step chains. "We orchestrated all backend LLM operations with \href{https://langchain.com/}{LangChain}, most of which use GPT-4."
- LLMs: Generative models trained on vast text corpora to produce, analyze, and transform natural language. "LLMs have become ubiquitous in providing different forms of writing assistance to different writers."
- Machine-in-the-loop: A human-AI collaboration paradigm where the machine actively assists the human during creative or analytic tasks. "\citet{clark2018creative} explores how a machine-in-the-loop system can amplify creativity for short story and slogan writing tasks"
- Natural language user profiles: Free-text representations of user preferences used to personalize system behavior and outputs. "Extending the concept of ``natural language user profiles'' from recommendation systems~\cite{radlinski2022natural,mysore2023editable}, we explore creating editable style and context profiles to guide the generation of personalized text."
- Style representation learning: Learning latent embeddings of writing style within neural models to enable style analysis and manipulation. "GhostWriter can infer a writing style from a written sample using an LLM -- a human-interpretable alternative to neural methods such as style representation learning~\cite{patel2023learning} and activation steering~\cite{konen2024style}."
- Text style transfer (TST): Methods that change the stylistic attributes of text (e.g., tone, voice) while preserving its semantic content. "Another relevant idea from NLP is text style transfer (TST)~\cite{jin2022deep,hu2022text,fu2018style}, which aims to preserve the content of generated text while adjusting attributes like tone or voice."
Practical Applications
Immediate Applications
Below are actionable, deployable use cases that leverage GhostWriter’s core innovations—implicit and explicit style learning, editable style/context profiles, inline “apply” prompts, rewrite/continue features, likes/dislikes feedback, style history with difference ratings, and transparency of model state.
- Brand voice enforcement in marketing and communications (Advertising/Marketing, Software)
- Use GhostWriter’s editable style profile and “lock style” to encode brand tone; apply prompts to tailor campaign copy; use style history and difference ratings to track and revert drift; integrate in CMS/Docs.
- Assumptions/dependencies: High-quality LLM outputs for brand-safe language, governance workflows, privacy of briefs, latency/cost management.
- Customer support macro and reply authoring (Software, Customer Support)
- Build and refine reply templates using rewrite and “apply” prompts; keep tone consistent via style lock; audit changes with style history; maintain context pages per product line or tier.
- Assumptions/dependencies: PII redaction, fluency with domain jargon, API integration with helpdesk tools, review gates to prevent hallucinations.
- Technical documentation and release notes (Software/DevTools)
- Convert engineer drafts to house style using rewrite; continue to expand sections; context page holds spec links and glossary; style history supports auditability; likes/dislikes train preferences over time.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Accurate grounding in source materials, retrieval/integration into editor, SME review, model robustness for technical content.
- HR and internal communications (Enterprise Ops, Policy)
- Produce policy memos and announcements in a consistent corporate voice; use style lock and style profiles per department; context page stores policy texts; history aids compliance audits.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Compliance approvals, access controls, sensitive data safeguards, consistent tone guidance.
- Journalism/newsroom drafting (Media)
- Enforce newsroom style via editable style profile; apply prompts for tone adjustments (e.g., neutral vs. explanatory); track stylistic changes; revert when needed; use context pages for sources.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Strong editorial review for factuality, transparency metadata, mitigation of homogenization risks.
- Academic writing tutor and composition support (Education)
- Teach style explicitly with likes/dislikes and inspectable style summaries; students use “apply” prompts to refine drafts; instructors review style history to discuss voice and revisions.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Anti-plagiarism guardrails, student data privacy, LMS integration, pedagogy-aligned feedback.
- Grant and proposal writing for nonprofits (Public Sector/Nonprofit)
- Capture the tone of successful past proposals as a style profile; use context pages for funder requirements; apply prompts to tailor sections; track changes via style history.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Confidentiality of past proposals, accuracy in requirements, staff training, LLM access costs.
- Healthcare patient communication and clinical summaries (Healthcare)
- Personalize patient letters and visit summaries with empathetic tone; use context pages with non-sensitive care plans; “apply” prompts to simplify medical language while retaining accuracy.
- Assumptions/dependencies: PHI protections, clinical validation, local regulations, explicit oversight by clinicians.
- Multilingual tone-preserving translation and localization (Localization)
- Translate while maintaining voice via style profile; use context pages for glossaries and terminology; rewrite/“apply” prompts for cultural appropriateness.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Translation quality, locale-specific compliance, domain glossary integration.
- Corporate training and onboarding materials (Education/Enterprise)
- Create guides in a consistent instructional style; maintain context pages with policies; apply prompts for clarity and simplification; style history ensures long-term consistency.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Content governance, access to internal knowledge, review processes.
- Personal productivity—emails, resumes, social posts (Daily Life)
- Individuals craft messages in their own voice by implicitly learning style as they write; use likes/dislikes to teach preferences; apply prompts to refine tone (e.g., confident, warm, concise).
- Assumptions/dependencies: Availability of LLMs, cost and privacy awareness, basic onboarding to features.
Long-Term Applications
Below are forward-looking applications that require further research, scaling, cross-tool integration, or policy development to realize.
- Portable “Style Profile” standard across tools (Software, Standards)
- Define a schema (tone, voice, word choice, sentence/paragraph structure, metadata) to move style profiles across Word, Docs, CMS, and chat systems; include difference ratings for traceability.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Vendor cooperation, open APIs, cross-platform interoperability.
- Content provenance and audit trails for AI-generated text (Policy, Compliance, Media)
- Persist style history, context snapshots, and difference ratings as provenance metadata; enable audits in regulated industries or newsroom transparency initiatives.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Regulatory adoption, secure logging, standardized disclosure formats.
- Team-level style governance and collaborative style negotiation (Enterprise Software)
- Merge multiple contributors’ styles into a team profile; resolve conflicts; manage “style drift” across projects; govern with role-based permissions and review gates.
- Assumptions/dependencies: New UX for multi-user style management, organizational buy-in, policy enforcement.
- Domain-specific safety/control layers (Healthcare, Finance, Legal, Policy)
- Combine controllable generation with policy constraints (e.g., prohibited claims, compliance phrasing); dynamically gate generations when style pushes into risky territory.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Reliable controllability, robust safety classifiers, domain ontologies.
- Adaptive writing education platforms with interactive machine teaching (Education)
- Use explicit likes/dislikes, style comparisons, and editable profiles to teach voice and rhetoric; track growth over time; develop rubrics tied to style dimensions.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Pedagogical validation, integration with assessment systems, equity considerations.
- Privacy-preserving, on-device or private-cloud personalized LLMs (Healthcare, Finance, Government)
- Maintain local style/context with minimal data sharing; enable ghostwriting in sensitive environments; reduce latency and cost.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Efficient models, MLOps for edge/private deployments, security certifications.
- Cross-modal style transfer (Text→Speech/Video) (Media, Accessibility)
- Carry text style profiles into audio narration or video scripts; maintain voice across modalities; support accessible communications.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Multimodal models, ethical voice cloning guidelines, consent management.
- Policy frameworks that mandate transparency and user agency in AI writing (Policy)
- Codify design principles like DP4 (transparency) and agency-aligned controls; require disclosure of context sources and style profiles for certain domains.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Policymaker engagement, stakeholder consensus, enforceability.
- Benchmarks and metrics for “agency” and personalization quality (Academia, Standards)
- Develop measures based on difference ratings, style alignment scores, and user-perceived control; standardize evaluations for AI writing tools.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Shared datasets, repeatable protocols, multi-stakeholder validation.
- Personal knowledge management with automated context construction (Productivity Software)
- Auto-build and maintain context pages from documents, notes, and calendars; personalize generation across tasks; support retrieval-augmented style-aware writing.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Permissions, RAG-quality, deduplication, privacy controls.
- Legal and compliance document assembly with controllable style and context (Legal, Finance)
- Enforce legal tone, insert required clauses, track stylistic changes for audits; use apply prompts for jurisdictional variations while preserving structure.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Factuality guarantees, liability frameworks, specialist review pipelines.
- Assistive writing for non-native speakers and neurodivergent writers (Healthcare, Education, Accessibility)
- Learn preferred style to provide scaffolding (clarity, simplicity, tone) without erasing voice; use explicit feedback loops to adapt; offer transparency for learning.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Inclusive design research, clinical/educational validation, stigma-avoiding UX.
Cross-cutting dependencies and assumptions
- Model quality and stability: GhostWriter’s features depend on reliable LLMs (prompt sensitivity, hallucination control, latency/cost).
- Data security and privacy: Style/context pages may contain sensitive information; require access controls and compliant storage.
- Organizational change management: Effective use needs governance (review gates, audit trails, clear ownership).
- Expanded style modeling: The paper’s five-dimension, single-global-style approach may need per-document/persona profiles, domain-specific attributes, and better drift detection.
- Evaluation and trust: Production deployments should add rigorous evaluation, monitoring, and human-in-the-loop review to maintain accuracy and user trust.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.