- The paper presents a comprehensive survey of Transformer compression techniques, categorizing methods such as quantization, knowledge distillation, pruning, and efficient architecture design.
- The paper details practical approaches showing how reduced precision and structured pruning enhance model efficiency in both NLP and CV tasks.
- The paper explores future directions, emphasizing the need for sustainable compression methods that balance performance with resource constraints.
The exponential growth in the size and complexity of Transformer-based models has become a significant challenge in both NLP and Computer Vision (CV) domains. With their increasing adoption as foundational architectures, efficient compression techniques have become essential to ensure practical deployment in real-world applications. This survey paper provides a comprehensive review of the current approaches for compressing Transformer models, grouped into categorical methodologies, with a focus on their application and efficacy in both domains.
Introduction
The foundational architecture of Transformers, characterized by alternating attention and Feedforward Neural Network (FFN) modules, poses unique challenges for compression. The models typically comprise a vast number of parameters, making them resource-intensive in terms of computation and storage. For instance, deploying models such as GPT-3, which has 175 billion parameters, requires substantial memory beyond the capability of typical hardware, leading to increased operational costs and carbon emissions.
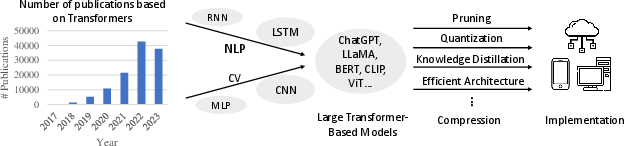
Figure 1: Transformer-based models have emerged as the predominant architectures in both NLP and computer vision (CV) domains, resulting in a surge in publications. As these models tend to possess substantial dimensions, it becomes imperative to compress their parameters and streamline computational redundancies. This compression is essential for facilitating efficient implementation on practical platforms, ensuring the feasibility of deploying Transformer models in real-world applications.
Quantization
Quantization is a widely adopted technique to reduce the computational burden by representing model weights and activations with lower precision arithmetic, commonly through INT8 or lower bit-width formats. This method significantly reduces the memory footprint and increases inference speed on hardware optimized for low-precision computations. The survey discusses several quantization strategies, including post-training quantization (PTQ) and quantization-aware training (QAT), highlighting their effectiveness in maintaining performance across NLP and CV tasks.
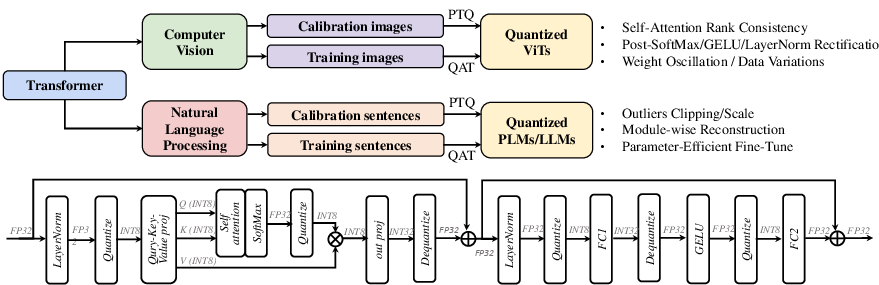
Figure 2: The overview of quantization for Transformers. The top demonstrates the different problems that are addressed in existing works for computer vision and natural language processing, and the bottom shows a normal INT8 inference process of a standard Transformer block.
Knowledge Distillation
Knowledge distillation involves transferring the "knowledge" from a larger, more complex model (teacher) to a smaller, more efficient one (student), thereby retaining performance while reducing model size. The paper discusses both logits-based distillation, which relies on output probabilities, and hint-based approaches, leveraging intermediate representations. This technique has shown remarkable success in both improving model efficiency and enabling smaller models to perform competitively on various benchmarks.
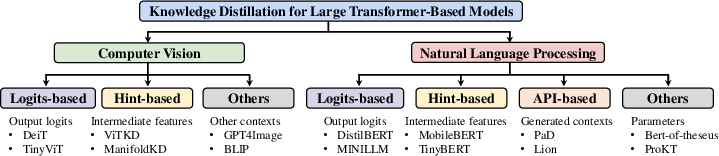
Figure 3: The taxonomy of knowledge distillation used for large Transformer-based models.
Pruning
Pruning reduces the model size by eliminating redundant or less important parameters, which can be done at different granularity levels such as attention heads, layers, or entire blocks. Structured pruning allows for easier deployment on standard hardware while achieving significant reduction in latency and computation cost. The survey details various strategies for pruning, emphasizing its capacity to enhance both inference speed and model compactness.
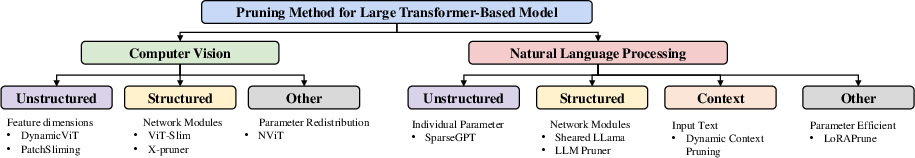
Figure 4: The taxonomy of pruning methods used for Transformer models.
Efficient Architecture Design
Recent advancements have focused on developing alternate architectures that inherently support efficient computation. These include innovations in self-attention mechanisms, incorporating sparse or linear attention, and designing entirely new modules that replace or complement the attention mechanisms. Architectures like RetNet, which use a retention mechanism for sequence modeling, offer promising directions by combining training efficiency and low inference cost.
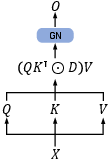
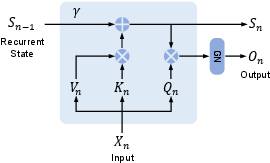
Figure 5: Parallel representation.
Implications and Future Directions
The survey highlights the critical role of compression in making Transformer models viable for practical applications, especially in resource-constrained environments. The convergence of various compression techniques—ranging from quantization and distilled training to architecture innovations—showcases a comprehensive toolkit for model optimization. Future developments are likely to focus on refining these techniques, enhancing their interoperability, and devising new strategies that leverage existing computational paradigms to further decrease the resource footprint of large models.
Conclusion
This survey provides an extensive overview of the techniques employed to compress Transformer models, analyzing their strengths and potential synergies. As these models continue to scale in complexity, the need for efficient compression methods will only become more pronounced. Ongoing research must aim to balance performance and resource efficiency, paving the way for sustainable deployment in a diverse range of applications.







