The Butterfly Effect of Altering Prompts: How Small Changes and Jailbreaks Affect Large Language Model Performance
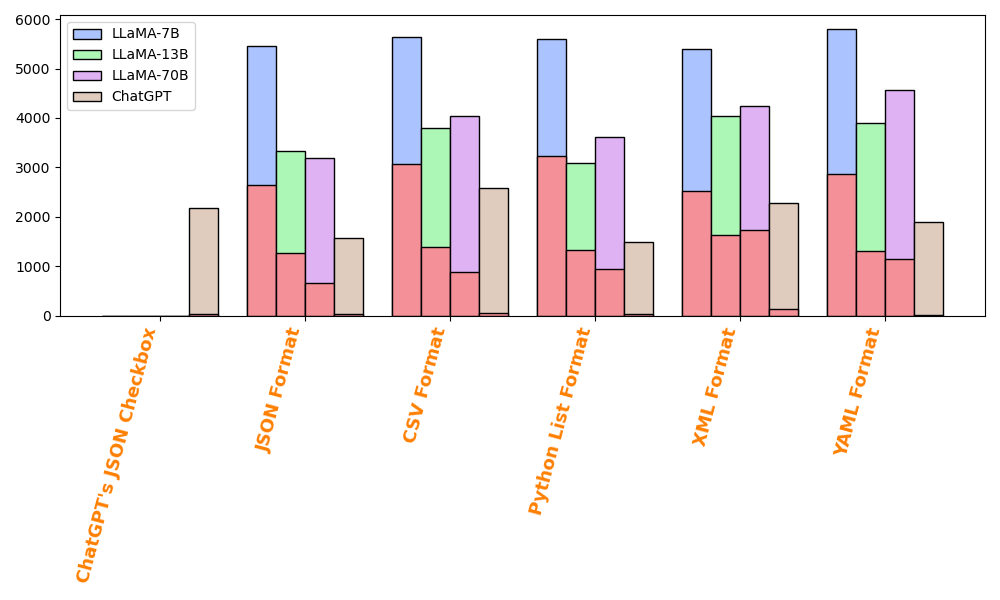
Abstract: LLMs are regularly being used to label data across many domains and for myriad tasks. By simply asking the LLM for an answer, or ``prompting,'' practitioners are able to use LLMs to quickly get a response for an arbitrary task. This prompting is done through a series of decisions by the practitioner, from simple wording of the prompt, to requesting the output in a certain data format, to jailbreaking in the case of prompts that address more sensitive topics. In this work, we ask: do variations in the way a prompt is constructed change the ultimate decision of the LLM? We answer this using a series of prompt variations across a variety of text classification tasks. We find that even the smallest of perturbations, such as adding a space at the end of a prompt, can cause the LLM to change its answer. Further, we find that requesting responses in XML and commonly used jailbreaks can have cataclysmic effects on the data labeled by LLMs.
- Mathqa: Towards interpretable math word problem solving with operation-based formalisms.
- Issa Annamoradnejad and Gohar Zoghi. 2022. Colbert: Using bert sentence embedding in parallel neural networks for computational humor.
- Jigsaw unintended bias in toxicity classification.
- Boolq: Exploring the surprising difficulty of natural yes/no questions. In NAACL.
- Are large language model-based evaluators the solution to scaling up multilingual evaluation? arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07462.
- Warp: Word-level adversarial reprogramming. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 4921–4933.
- How can we know what language models know? Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 8:423–438.
- Chatgpt: Jack of all trades, master of none. Information Fusion, 99:101861.
- Race: Large-scale reading comprehension dataset from examinations.
- Making large language models better data creators. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 15349–15360.
- The hitchhiker’s guide to program analysis: A journey with large language models. arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv–2308.
- Pre-train, prompt, and predict: A systematic survey of prompting methods in natural language processing. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(9):1–35.
- Learning word vectors for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 142–150, Portland, Oregon, USA. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- SemEval-2016 task 6: Detecting stance in tweets. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2016), pages 31–41, San Diego, California. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Silviu Oprea and Walid Magdy. 2020. iSarcasm: A dataset of intended sarcasm. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 1279–1289, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Guanghui Qin and Jason Eisner. 2021. Learning how to ask: Querying lms with mixtures of soft prompts. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT).
- Choice of plausible alternatives: An evaluation of commonsense causal reasoning. In 2011 AAAI Spring Symposium Series.
- Timo Schick and Hinrich Schütze. 2020. Few-shot text generation with pattern-exploiting training. arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv–2012.
- Quantifying social biases using templates is unreliable. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.04337.
- Superglue: A stickier benchmark for general-purpose language understanding systems.
- Neural Network Acceptability Judgments. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 7:625–641.
- Can chatgpt reproduce human-generated labels? a study of social computing tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.10145.
- Guido Zuccon and Bevan Koopman. 2023. Dr chatgpt, tell me what i want to hear: How prompt knowledge impacts health answer correctness. arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv–2302.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.