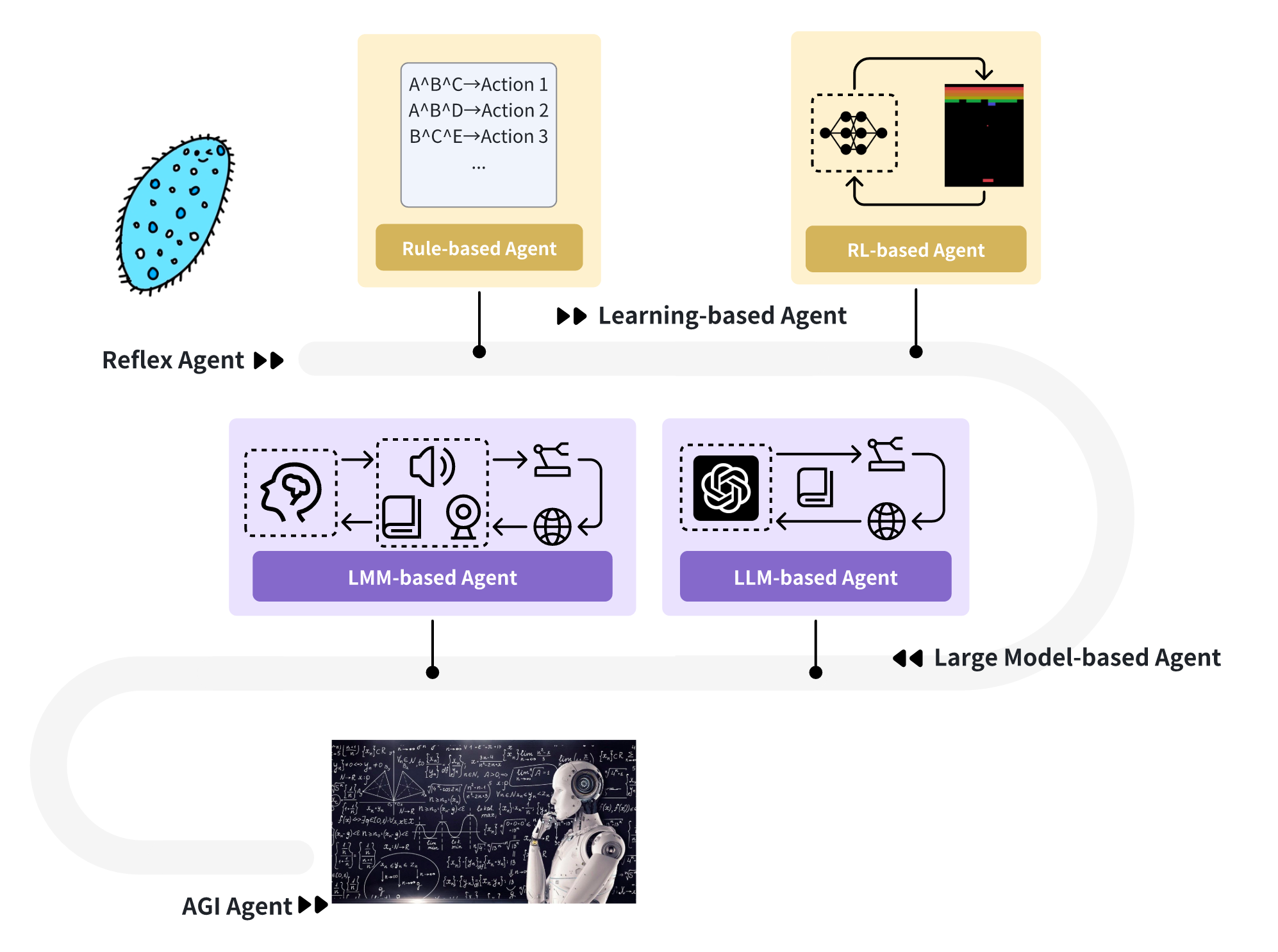
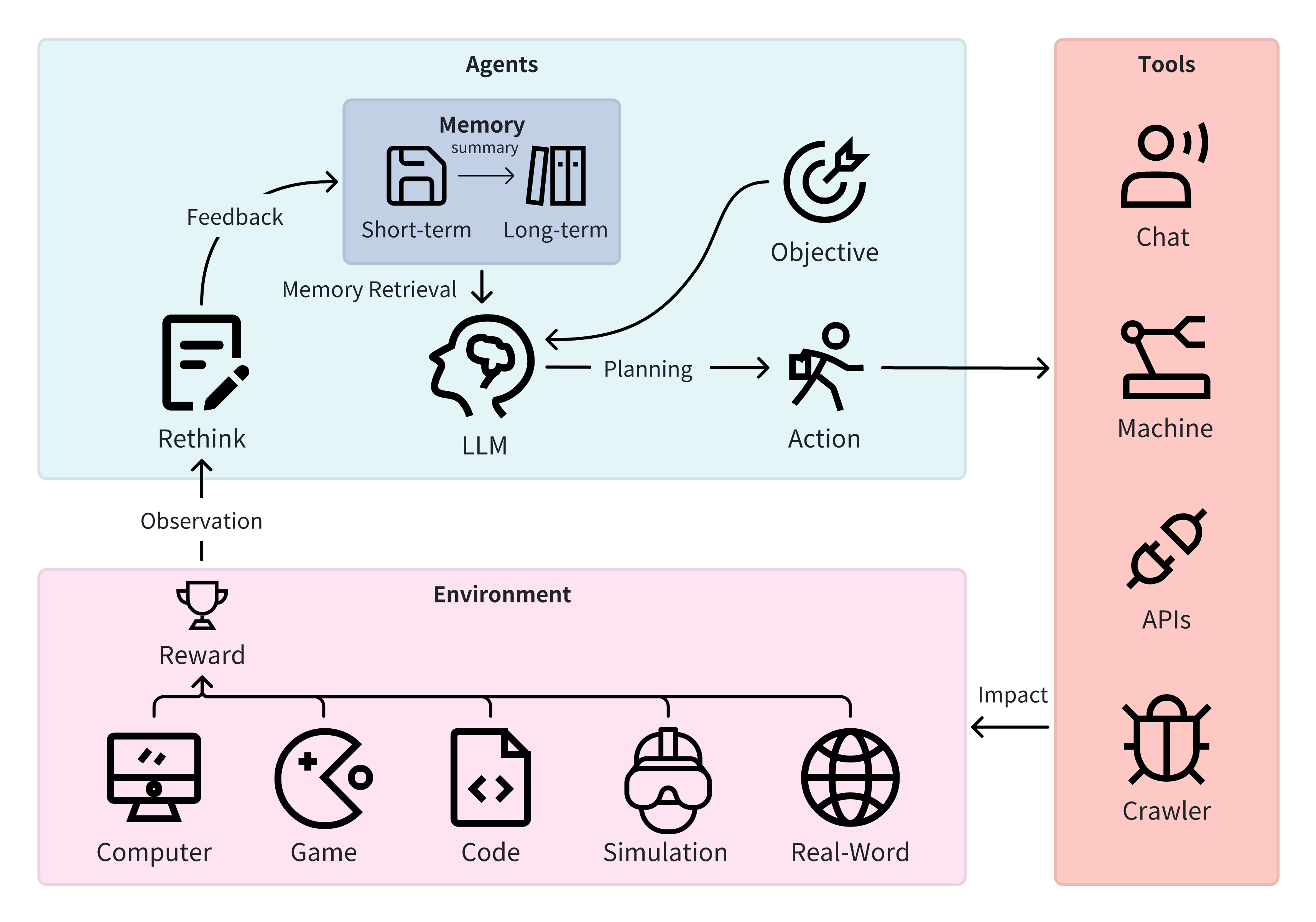
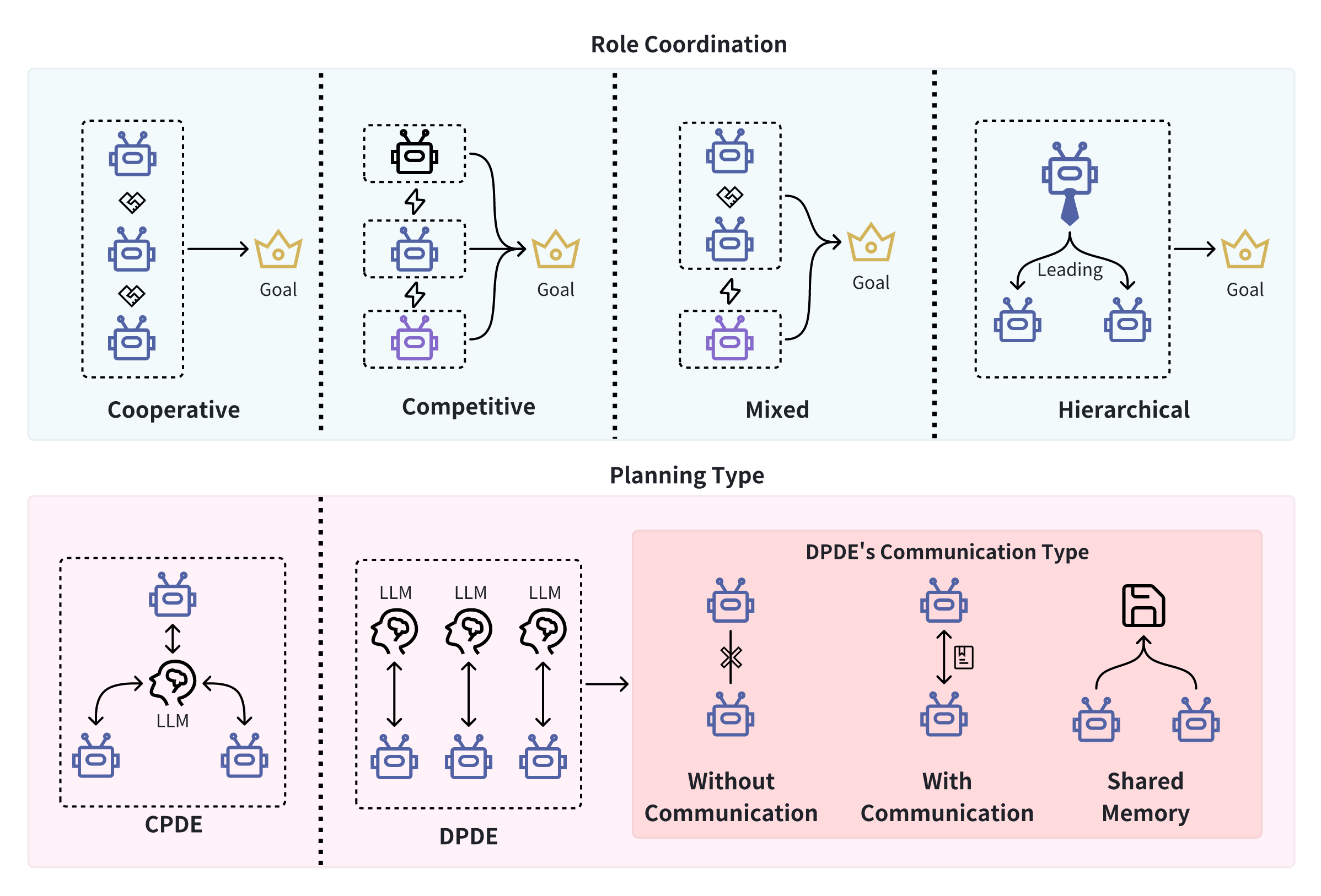
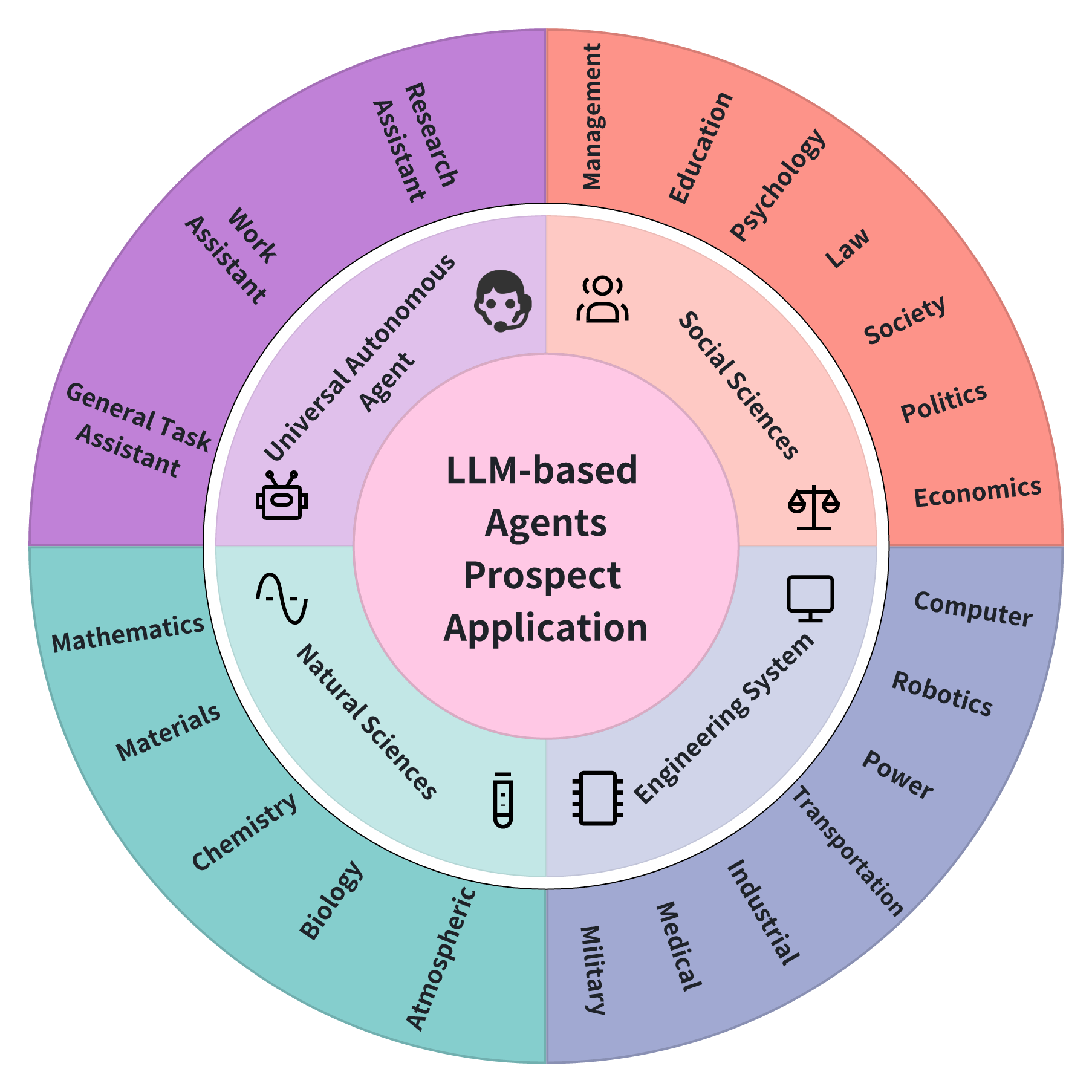
Exploring Large Language Model based Intelligent Agents: Definitions, Methods, and Prospects
Abstract: Intelligent agents stand out as a potential path toward artificial general intelligence (AGI). Thus, researchers have dedicated significant effort to diverse implementations for them. Benefiting from recent progress in LLMs, LLM-based agents that use universal natural language as an interface exhibit robust generalization capabilities across various applications -- from serving as autonomous general-purpose task assistants to applications in coding, social, and economic domains, LLM-based agents offer extensive exploration opportunities. This paper surveys current research to provide an in-depth overview of LLM-based intelligent agents within single-agent and multi-agent systems. It covers their definitions, research frameworks, and foundational components such as their composition, cognitive and planning methods, tool utilization, and responses to environmental feedback. We also delve into the mechanisms of deploying LLM-based agents in multi-agent systems, including multi-role collaboration, message passing, and strategies to alleviate communication issues between agents. The discussions also shed light on popular datasets and application scenarios. We conclude by envisioning prospects for LLM-based agents, considering the evolving landscape of AI and natural language processing.
- Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (4th Edition). Pearson Education, Inc., 2010.
- Multiagent systems: A survey from a machine learning perspective. Autonomous Robots, 8:345–383, 2000.
- Michael Wooldridge. An introduction to multiagent systems. John wiley & sons, 2009.
- Is it an agent, or just a program?: A taxonomy for autonomous agents. In International workshop on agent theories, architectures, and languages, pages 21–35. Springer, 1996.
- Reinforcement learning: A survey. Journal of artificial intelligence research, 4:237–285, 1996.
- Categorizing approaches combining rule-based and case-based reasoning. Expert Systems, 24(2):97–122, 2007.
- Reinforcement learning: An introduction. MIT press, 2018.
- Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. nature, 518(7540):529–533, 2015.
- Where does alphago go: From church-turing thesis to alphago thesis and beyond. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 3(2):113–120, 2016.
- Reinforcement learning in robotics: A survey. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 32(11):1238–1274, 2013.
- Deep reinforcement learning for autonomous driving: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 23(6):4909–4926, 2021.
- Deep reinforcement learning for multiagent systems: A review of challenges, solutions, and applications. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 50(9):3826–3839, 2020.
- R Andrew McCallum. Hidden state and reinforcement learning with instance-based state identification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 26(3):464–473, 1996.
- A survey of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.18223, 2023a.
- Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.12712, 2023.
- Chateval: Towards better llm-based evaluators through multi-agent debate. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07201, 2023.
- BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In NAACL-HLT (1), 2019.
- A generalist agent. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.06175, 2022.
- OpenAI. Gpt-4 technical report. ArXiv, abs/2303.08774, 2023.
- Cognitive architectures for language agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.02427, 2023.
- Lilian Weng. Llm-powered autonomous agents. lilianweng.github.io, Jun 2023. URL https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/.
- A decentralized cluster formation containment framework for multirobot systems. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 37(6):1936–1955, 2021.
- Marvin Minsky. Society of mind. Simon and Schuster, 1988.
- Mindstorms in natural language-based societies of mind. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17066, 2023.
- Keith S Decker. Distributed problem-solving techniques: A survey. IEEE transactions on systems, man, and cybernetics, 17(5):729–740, 1987.
- H Van Dyke Parunak. Applications of distributed artificial intelligence in industry. Foundations of distributed artificial intelligence, 2(1):18, 1996.
- Yaodong Yang. Many-agent reinforcement learning. PhD thesis, UCL (University College London), 2021.
- Marllib: Extending rllib for multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.13708, 2022.
- Out of one, many: Using language models to simulate human samples. Political Analysis, 31(3):337–351, 2023.
- John J Horton. Large language models as simulated economic agents: What can we learn from homo silicus? Technical report, National Bureau of Economic Research, 2023.
- Social simulacra: Creating populated prototypes for social computing systems. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, pages 1–18, 2022.
- The socialai school: Insights from developmental psychology towards artificial socio-cultural agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.07871, 2023.
- S3: Social-network simulation system with large language model-empowered agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14984, 2023.
- Are you in a masquerade? exploring the behavior and impact of large language model driven social bots in online social networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.10337, 2023a.
- Quantifying the impact of large language models on collective opinion dynamics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03313, 2023b.
- Chatlaw: Open-source legal large language model with integrated external knowledge bases. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.16092, 2023.
- Sil Hamilton. Blind judgement: Agent-based supreme court modelling with gpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.05327, 2023.
- Chemcrow: Augmenting large-language models with chemistry tools. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.05376, 2023.
- Chatmof: An autonomous ai system for predicting and generating metal-organic frameworks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.01423, 2023.
- Math agents: Computational infrastructure, mathematical embedding, and genomics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02502, 2023.
- A neural network solves, explains, and generates university math problems by program synthesis and few-shot learning at human level. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 119(32):e2123433119, 2022.
- Improving grounded language understanding in a collaborative environment by interacting with agents through help feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.10750, 2023.
- AntonOsika. GitHub - AntonOsika/gpt-engineer: Specify what you want it to build, the AI asks for clarification, and then builds it. — github.com. https://github.com/AntonOsika/gpt-engineer. [Accessed 12-09-2023].
- smol ai. GitHub - smol-ai/developer: the first library to let you embed a developer agent in your own app! — github.com. https://github.com/smol-ai/developer. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- melih unsal. GitHub - melih-unsal/DemoGPT: Create LangChain apps by just using prompts. https://github.com/melih-unsal/DemoGPT. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- Industrial engineering with large language models: A case study of chatgpt’s performance on oil & gas problems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14354, 2023.
- Dialogue shaping: Empowering agents through npc interaction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15833, 2023a.
- Do embodied agents dream of pixelated sheep?: Embodied decision making using language guided world modelling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.12050, 2023.
- Llm-planner: Few-shot grounded planning for embodied agents with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.04088, 2022.
- Voyager: An open-ended embodied agent with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16291, 2023a.
- Ghost in the minecraft: Generally capable agents for open-world enviroments via large language models with text-based knowledge and memory. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17144, 2023a.
- Enabling intelligent interactions between an agent and an llm: A reinforcement learning approach.
- Plan, eliminate, and track–language models are good teachers for embodied agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.02412, 2023a.
- Large language model is semi-parametric reinforcement learning agent. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.07929, 2023a.
- Towards a unified agent with foundation models. In Workshop on Reincarnating Reinforcement Learning at ICLR 2023, 2023.
- Do as i can and not as i say: Grounding language in robotic affordances. In arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.01691, 2022.
- eumemic. GitHub - eumemic/ai-legion: An LLM-powered autonomous agent platform — github.com. https://github.com/eumemic/ai-legion. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- Josh-XT. GitHub - Josh-XT/AGiXT: AGiXT is a dynamic AI Automation Platform that seamlessly orchestrates instruction management and complex task execution across diverse AI providers. Combining adaptive memory, smart features, and a versatile plugin system, AGiXT delivers efficient and comprehensive AI solutions. — github.com. https://github.com/Josh-XT/AGiXT. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- yoheinakajima. GitHub - yoheinakajima/babyagi — github.com. https://github.com/yoheinakajima/babyagi. [Accessed 11-09-2023].
- farizrahman4u. GitHub - farizrahman4u/loopgpt: Modular Auto-GPT Framework — github.com. https://github.com/farizrahman4u/loopgpt. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- assafelovic. GitHub - assafelovic/gpt-researcher: GPT based autonomous agent that does online comprehensive research on any given topic — github.com. https://github.com/assafelovic/gpt-researcher. [Accessed 11-09-2023].
- TransformerOptimus. GitHub - TransformerOptimus/SuperAGI: SuperAGI - A dev-first open source autonomous AI agent framework. Enabling developers to build, manage and run useful autonomous agents quickly and reliably. — github.com. https://github.com/TransformerOptimus/SuperAGI. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- Generative agents: Interactive simulacra of human behavior. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03442, 2023.
- Epidemic modeling with generative agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04986, 2023.
- Emergent autonomous scientific research capabilities of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.05332, 2023a.
- Communicative agents for software development. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.07924, 2023.
- Metagpt: Meta programming for multi-agent collaborative framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00352, 2023a.
- Self-collaboration code generation via chatgpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.07590, 2023a.
- Towards autonomous system: flexible modular production system enhanced with large language model agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14721, 2023.
- Collaborating with language models for embodied reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.00763, 2023.
- Proagent: Building proactive cooperative ai with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11339, 2023b.
- Semantically aligned task decomposition in multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10865, 2023c.
- Building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02485, 2023c.
- Toolllm: Facilitating large language models to master 16000+ real-world apis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.16789, 2023a.
- Significant-Gravitas. GitHub - Significant-Gravitas/Auto-GPT: An experimental open-source attempt to make GPT-4 fully autonomous. — github.com. https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/Auto-GPT. [Accessed 10-09-2023].
- xlang ai. GitHub - xlang-ai/xlang: An open-source framework for building and evaluating language model agents via executable language grounding — github.com. https://github.com/xlang-ai/xlang. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- langchain ai. GitHub - langchain-ai/langchain: ⚡ Building applications with LLMs through composability ⚡ — github.com. https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain. [Accessed 17-09-2023].
- XAgent Team. Xagent: An autonomous agent for complex task solving, 2023.
- Openagents: An open platform for language agents in the wild, 2023.
- team openpm. GitHub - team-openpm/workgpt: A GPT agent framework for invoking APIs — github.com. https://github.com/team-openpm/workgpt. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- reworkd. GitHub - reworkd/AgentGPT: Assemble, configure, and deploy autonomous AI Agents in your browser. — github.com. https://github.com/reworkd/AgentGPT. [Accessed 14-09-2023].
- Formally specifying the high-level behavior of llm-based agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.08535, 2023.
- Autogen: Enabling next-gen llm applications via multi-agent conversation framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.08155, 2023b.
- Agentverse: Facilitating multi-agent collaboration and exploring emergent behaviors in agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10848, 2023a.
- Autoagents: The automatic agents generation framework. arXiv preprint, 2023b.
- Agents: An open-source framework for autonomous language agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07870, 2023b.
- A method for the shortest path search by extended dijkstra algorithm. In Smc 2000 conference proceedings. 2000 ieee international conference on systems, man and cybernetics.’cybernetics evolving to systems, humans, organizations, and their complex interactions’(cat. no. 0, volume 3, pages 2316–2320. IEEE, 2000.
- Anthony R Cassandra. A survey of pomdp applications. In Working notes of AAAI 1998 fall symposium on planning with partially observable Markov decision processes, volume 1724, 1998.
- Chain of thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.11903, 2022.
- Complexity-based prompting for multi-step reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.00720, 2022.
- Automatic chain of thought prompting in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03493, 2022.
- Large language models are zero-shot reasoners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:22199–22213, 2022.
- Self-consistency improves chain of thought reasoning in language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.11171, 2022.
- Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10601, 2023a.
- Least-to-most prompting enables complex reasoning in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.10625, 2022.
- Skeleton-of-thought: Large language models can do parallel decoding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15337, 2023.
- Graph of thoughts: Solving elaborate problems with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09687, 2023.
- Progressive-hint prompting improves reasoning in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09797, 2023a.
- Self-refine: Iterative refinement with self-feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17651, 2023a.
- Llm+ p: Empowering large language models with optimal planning proficiency. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.11477, 2023a.
- Dynamic planning with a llm. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.06391, 2023.
- Reasoning with language model is planning with world model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14992, 2023.
- Synergistic integration of large language models and cognitive architectures for robust ai: An exploratory analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09830, 2023.
- Context-aware composition of agent policies by markov decision process entity embeddings and agent ensembles. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.14521, 2023.
- Swiftsage: A generative agent with fast and slow thinking for complex interactive tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17390, 2023a.
- A survey for in-context learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.00234, 2022.
- Self-refine: Iterative refinement with self-feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17651, 2023b.
- Pddl| the planning domain definition language. Technical Report, Tech. Rep., 1998.
- Leveraging pre-trained large language models to construct and utilize world models for model-based task planning, 2023.
- Large language models as commonsense knowledge for large-scale task planning, 2023b.
- How far are large language models from agents with theory-of-mind?, 2023c.
- Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind? Behavioral and brain sciences, 1(4):515–526, 1978.
- Language agent tree search unifies reasoning acting and planning in language models, 2023d.
- Think-on-graph: Deep and responsible reasoning of large language model on knowledge graph, 2023a.
- Knowledge graph embedding: A survey of approaches and applications. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 29(12):2724–2743, 2017.
- Experimental study of big raster and vector database systems. In 2021 IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pages 2243–2248. IEEE, 2021.
- Expel: Llm agents are experiential learners. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10144, 2023c.
- Reflexion: Language agents with verbal reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.11366, 2023.
- Memgpt: Towards llms as operating systems, 2023.
- Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive NLP tasks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33:9459–9474, 2020.
- Lagr-seq: Language-guided reinforcement learning with sample-efficient querying. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.13542, 2023.
- Synapse: Trajectory-as-exemplar prompting with memory for computer control, 2023b.
- Think before you act: Decision transformers with internal working memory, 2023.
- Jarvis-1: Open-world multi-task agents with memory-augmented multimodal language models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2311.05997, 2023b.
- React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03629, 2022a.
- Chain of hindsight aligns language models with feedback, 2023b.
- Let’s verify step by step. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.20050, 2023.
- Introspective tips: Large language model for in-context decision making. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11598, 2023c.
- Solving challenging math word problems using gpt-4 code interpreter with code-based self-verification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07921, 2023e.
- Retroformer: Retrospective large language agents with policy gradient optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.02151, 2023b.
- Rex: Rapid exploration and exploitation for ai agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.08962, 2023.
- Large language models can implement policy iteration, 2023.
- On the advance of making language models better reasoners. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.02336, 2022.
- Describe, explain, plan and select: Interactive planning with large language models enables open-world multi-task agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.01560, 2023c.
- Reason for future, act for now: A principled framework for autonomous llm agents with provable sample efficiency, 2023c.
- Adapting llm agents through communication, 2023d.
- Proximal policy optimization algorithms, 2017.
- Language models can solve computer tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17491, 2023.
- WebArena: A Realistic Web Environment for Building Autonomous Agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.13854, 2023f.
- WebGPT: Browser-Assisted Question-Answering with Human Feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.09332, 2021.
- Mobile-env: An evaluation platform and benchmark for interactive agents in llm era, 2023d.
- Sheetcopilot: Bringing software productivity to the next level through large language models, 2023d.
- Agentsims: An open-source sandbox for large language model evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.04026, 2023b.
- Llm-deliberation: Evaluating llms with interactive multi-agent negotiation games, 2023.
- The hitchhiker’s guide to program analysis: A journey with large language models, 2023e.
- Embodied task planning with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.01848, 2023c.
- Alexa, play with robot: Introducing the first alexa prize simbot challenge on embodied ai. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05221, 2023.
- Synergizing human-ai agency: A guide of 23 heuristics for service co-creation with llm-based agents, 2023c.
- Trafficgpt: Viewing, processing and interacting with traffic foundation models, 2023e.
- Microscopic traffic simulation using sumo. In 2018 21st international conference on intelligent transportation systems (ITSC), pages 2575–2582. IEEE, 2018.
- Put your money where your mouth is: Evaluating strategic planning and execution of llm agents in an auction arena, 2023d.
- Mrkl systems: A modular, neuro-symbolic architecture that combines large language models, external knowledge sources and discrete reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.00445, 2022.
- Talm: Tool augmented language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.12255, 2022.
- Toolformer: Language models can teach themselves to use tools. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04761, 2023.
- Hugginggpt: Solving ai tasks with chatgpt and its friends in huggingface. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17580, 2023.
- Chameleon: Plug-and-play compositional reasoning with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09842, 2023.
- Gorilla: Large language model connected with massive apis, 2023.
- Restgpt: Connecting large language models with real-world applications via restful apis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06624, 2023.
- Llm as dba. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05481, 2023g.
- Avis: Autonomous visual information seeking with large language model agent, 2023.
- Chatcot: Tool-augmented chain-of-thought reasoning on chat-based large language models, 2023e.
- Tptu: Task planning and tool usage of large language model-based ai agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03427, 2023a.
- Gentopia: A collaborative platform for tool-augmented llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.04030, 2023a.
- Large language models as tool makers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17126, 2023.
- Craft: Customizing llms by creating and retrieving from specialized toolsets, 2023.
- Taskmatrix.ai: Completing tasks by connecting foundation models with millions of apis, 2023a.
- Bolaa: Benchmarking and orchestrating llm-augmented autonomous agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05960, 2023d.
- Cgmi: Configurable general multi-agent interaction framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12503, 2023.
- Encouraging divergent thinking in large language models through multi-agent debate. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.19118, 2023b.
- Exploring large language models for communication games: An empirical study on werewolf. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.04658, 2023b.
- From text to tactic: Evaluating llms playing the game of avalon, 2023.
- Unleashing cognitive synergy in large language models: A task-solving agent through multi-persona self-collaboration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.05300, 2023e.
- Camel: Communicative agents for" mind" exploration of large scale language model society. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17760, 2023f.
- Wireless multi-agent generative ai: From connected intelligence to collective intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02757, 2023.
- Roco: Dialectic multi-robot collaboration with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04738, 2023.
- Interact: Exploring the potentials of chatgpt as a cooperative agent, 2023.
- Alfworld: Aligning text and embodied environments for interactive learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.03768, 2020.
- Dynamic llm-agent network: An llm-agent collaboration framework with agent team optimization, 2023e.
- Corex: Pushing the boundaries of complex reasoning through multi-model collaboration, 2023b.
- Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30, 2017.
- Mindagent: Emergent gaming interaction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.09971, 2023.
- On the utility of learning about humans for human-ai coordination. Advances in neural information processing systems, 32, 2019.
- Hierarchical decision making by generating and following natural language instructions. Advances in neural information processing systems, 32, 2019.
- John R Searle. Speech acts: An essay in the philosophy of language, volume 626. Cambridge university press, 1969.
- Kqml as an agent communication language. In Proceedings of the third international conference on Information and knowledge management, pages 456–463, 1994.
- Let models speak ciphers: Multiagent debate through embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06272, 2023.
- Simple synthetic data reduces sycophancy in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03958, 2023a.
- A survey of hallucination in large foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.05922, 2023.
- Chain-of-verification reduces hallucination in large language models, 2023.
- Hotpotqa: A dataset for diverse, explainable multi-hop question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.09600, 2018.
- Measuring coding challenge competence with apps. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.09938, 2021.
- Program synthesis with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07732, 2021.
- Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03374, 2021.
- Webshop: Towards scalable real-world web interaction with grounded language agents. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:20744–20757, 2022b.
- Fever: a large-scale dataset for fact extraction and verification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.05355, 2018.
- Tool learning with foundation models, 2023b.
- Robonet: Large-scale multi-robot learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.11215, 2019.
- Bridgedata v2: A dataset for robot learning at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12952, 2023.
- Using large language models to simulate multiple humans and replicate human subject studies. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 337–371. PMLR, 2023.
- Playing repeated games with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16867, 2023.
- Can large language models transform computational social science? arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.03514, 2023.
- Smartplay : A benchmark for llms as intelligent agents, 2023d.
- Benchmarking large language models as ai research agents, 2023a.
- Metatool benchmark for large language models: Deciding whether to use tools and which to use, 2023b.
- Evaluating multi-agent coordination abilities in large language models, 2023.
- Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN’95-international conference on neural networks, volume 4, pages 1942–1948. IEEE, 1995.
- Tutorial on agent-based modeling and simulation. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference, 2005., pages 14–pp. IEEE, 2005.
- Multicommodity, multimode freight transportation: A general modeling and algorithmic framework for the service network design problem. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 20(3):225–242, 1986.
- Leandojo: Theorem proving with retrieval-augmented language models, 2023a.
- Large language model for science: A study on p vs. np, 2023b.
- Large language models for automated open-domain scientific hypotheses discovery. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.02726, 2023b.
- Tora: A tool-integrated reasoning agent for mathematical problem solving, 2023.
- A language-agent approach to formal theorem-proving, 9 2023.
- Design of efficient molecular organic light-emitting diodes by a high-throughput virtual screening and experimental approach. Nature materials, 15(10):1120–1127, 2016.
- Optimization of molecules via deep reinforcement learning. Scientific reports, 9(1):10752, 2019.
- Graph convolutional policy network for goal-directed molecular graph generation. Advances in neural information processing systems, 31, 2018.
- Towards foundational models for molecular learning on large-scale multi-task datasets, 2023.
- Autonomous chemical research with large language models. Nature, 624(7992):570–578, 2023b.
- Swarm intelligence: from natural to artificial systems. Number 1. Oxford university press, 1999.
- Individual-based modeling of ecological and evolutionary processes. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst., 36:147–168, 2005.
- An introduction to agent-based modeling: modeling natural, social, and engineered complex systems with NetLogo. Mit Press, 2015.
- Biological sequence design with gflownets. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 9786–9801. PMLR, 2022.
- Bioplanner: Automatic evaluation of llms on protocol planning in biology, 2023.
- Oceangpt: A large language model for ocean science tasks, 2023.
- Wander Jager. Using agent-based modelling to explore behavioural dynamics affecting our climate. Current opinion in psychology, 42:133–139, 2021.
- A review of agent-based modeling of climate-energy policy. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 11(4):e647, 2020.
- Enhancing large language models with climate resources, 2023.
- Modelscope-agent: Building your customizable agent system with open-source large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.00986, 2023g.
- Augmenting autotelic agents with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.12487, 2023.
- Kani: A lightweight and highly hackable framework for building language model applications, 2023b.
- Towards an on-device agent for text rewriting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11807, 2023c.
- To infinity and beyond: Show-1 and showrunner agents in multi-agent simulations. arXiv preprint, 2023.
- Layoutgpt: Compositional visual planning and generation with large language models, 2023a.
- Musicagent: An ai agent for music understanding and generation with large language models, 2023.
- Walking down the memory maze: Beyond context limit through interactive reading, 2023f.
- Asset pricing under endogenous expectations in an artificial stock market. In The economy as an evolving complex system II, pages 15–44. CRC Press, 2018.
- Handbook of computational economics: agent-based computational economics. Elsevier, 2006.
- Emergent bartering behaviour in multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.06760, 2022.
- The ai economist: Improving equality and productivity with ai-driven tax policies. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.13332, 2020.
- Callum Tilbury. Reinforcement learning in macroeconomic policy design: A new frontier? arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.08781, 2022.
- Of models and tin men–a behavioural economics study of principal-agent problems in ai alignment using large-language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.11137, 2023.
- Suspicion-agent: Playing imperfect information games with theory of mind aware gpt4, 2023.
- Alpha-gpt: Human-ai interactive alpha mining for quantitative investment, 2023f.
- Tradinggpt: Multi-agent system with layered memory and distinct characters for enhanced financial trading performance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.03736, 2023h.
- Growing artificial societies: social science from the bottom up. Brookings Institution Press, 1996.
- Abstractions, ensembles, and virtualizations: simplicity and complexity in agent-based modeling. Comparative Politics, 41(2):223–244, 2009.
- Modeling complex socio-technical systems using multi-agent simulation methods. KI, 18(2):23–28, 2004.
- Building a foundation for data-driven, interpretable, and robust policy design using the ai economist. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.02904, 2021.
- Christopher A Bail. Can generative ai improve social science?
- Welfare diplomacy: Benchmarking language model cooperation, 2023.
- From factors to actors: Computational sociology and agent-based modeling. Annual review of sociology, 28(1):143–166, 2002.
- Simulation for the social scientist. McGraw-Hill Education (UK), 2005.
- An artificial intelligence-based framework to achieve the sustainable development goals in the context of bangladesh. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.11703, 2023a.
- Training socially aligned language models in simulated human society. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16960, 2023f.
- The role of summarization in generative agents: A preliminary perspective. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.01253, 2023b.
- Multi-party chat: Conversational agents in group settings with humans and models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.13835, 2023b.
- Where would i go next? large language models as human mobility predictors. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.15197, 2023g.
- Using large language model annotations for valid downstream statistical inference in social science: Design-based semi-supervised learning, 2023.
- Generative agent-based modeling: Unveiling social system dynamics through coupling mechanistic models with generative artificial intelligence, 2023.
- Lyfe agents: Generative agents for low-cost real-time social interactions, 2023.
- A model of legal reasoning with cases incorporating theories and values. Artificial Intelligence, 150(1-2):97–143, 2003.
- L Karl Branting. Reasoning with rules and precedents: a computational model of legal analysis. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013.
- A comprehensive evaluation of large language models on legal judgment prediction, 2023.
- Ron Sun. Cognition and multi-agent interaction: From cognitive modeling to social simulation. Cambridge University Press, 2006.
- Ema: A process model of appraisal dynamics. Cognitive Systems Research, 10(1):70–90, 2009.
- Understanding the benefits and challenges of using large language model-based conversational agents for mental well-being support. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15810, 2023.
- Humanoid agents: Platform for simulating human-like generative agents, 2023h.
- Exploring collaboration mechanisms for llm agents: A social psychology view, 2023f.
- Beverly Park Woolf. Building intelligent interactive tutors: Student-centered strategies for revolutionizing e-learning. Morgan Kaufmann, 2010.
- A computational approach to analyzing online knowledge sharing interaction. In Proceedings of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 2003.
- Managing business complexity: discovering strategic solutions with agent-based modeling and simulation. Oxford University Press, 2007.
- Eric Bonabeau. Agent-based modeling: Methods and techniques for simulating human systems. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 99(suppl_3):7280–7287, 2002.
- Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for multi-echelon inventory management. Available at SSRN, 2022.
- Metaagents: Simulating interactions of human behaviors for llm-based task-oriented coordination via collaborative generative agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06500, 2023i.
- Decision-oriented dialogue for human-ai collaboration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.20076, 2023c.
- Sapien: Affective virtual agents powered by large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03022, 2023b.
- A real-world webagent with planning, long context understanding, and program synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12856, 2023.
- Out of the cage: How stochastic parrots win in cyber security environments. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12086, 2023.
- Llms for semi-automated data science: Introducing caafe for context-aware automated feature engineering, 2023.
- Towards autonomous testing agents via conversational large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05152, 2023.
- Rcagent: Cloud root cause analysis by autonomous agents with tool-augmented large language models, 2023i.
- Recagent: A novel simulation paradigm for recommender systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.02552, 2023j.
- On generative agents in recommendation, 2023g.
- Edward Junprung. Exploring the intersection of large language models and agent-based modeling via prompt engineering. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07411, 2023.
- clembench: Using game play to evaluate chat-optimized language models as conversational agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.13455, 2023.
- Tachikuma: Understading complex interactions with multi-character and novel objects by large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12573, 2023c.
- Ambient adventures: Teaching chatgpt on developing complex stories. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.01734, 2023g.
- Gamegpt: Multi-agent collaborative framework for game development, 2023h.
- Multiple mobile robot systems. Springer handbook of robotics, pages 1335–1384, 2016.
- A comprehensive survey of multiagent reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 38(2):156–172, 2008.
- Progprompt: Generating situated robot task plans using large language models, 2022.
- Inner monologue: Embodied reasoning through planning with language models, 2022.
- Language models meet world models: Embodied experiences enhance language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10626, 2023.
- 3d-llm: Injecting the 3d world into large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12981, 2023b.
- Agent-based modeling and simulation of a smart grid: A case study of communication effects on frequency control. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 33:91–98, 2014.
- Applications of multi-agent systems in smart grids: A survey. In 2014 International conference on multimedia computing and systems (ICMCS), pages 1088–1094. IEEE, 2014.
- Fixed-time distributed voltage and reactive power compensation of islanded microgrids using sliding-mode and multi-agent consensus design. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 10(1):232–240, 2020.
- Agent-based models in electricity markets: A literature review. 2019 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT Asia), pages 3026–3031, 2019.
- A multi-agent reinforcement learning approach for investigating and optimising peer-to-peer prosumer energy markets. Applied Energy, 334:120705, 2023.
- Adaptive traffic signal control with deep recurrent q-learning. In 2018 IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium (IV), pages 1215–1220. IEEE, 2018.
- Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for large-scale traffic signal control. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 21(3):1086–1095, 2019.
- Llm powered sim-to-real transfer for traffic signal control. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.14284, 2023.
- Dilu: A knowledge-driven approach to autonomous driving with large language models, 2023.
- Agent-based systems for intelligent manufacturing: a state-of-the-art survey. Knowledge and information systems, 1:129–156, 1999.
- Applications of agent-based systems in intelligent manufacturing: An updated review. Advanced engineering INFORMATICS, 20(4):415–431, 2006.
- Gpt-in-the-loop: Adaptive decision-making for multiagent systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10435, 2023.
- From English to PCSEL: LLM helps design and optimize photonic crystal surface emitting lasers. 14 pages, 9 graphics, August 2023j. URL https://hal.science/hal-04175312.
- Gary An. Agent-based computer simulation and sirs: building a bridge between basic science and clinical trials. Shock, 16(4):266–273, 2001.
- Pathway mapping tools for analysis of high content data. High content screening: A powerful approach to systems cell biology and drug discovery, pages 319–350, 2006.
- The epitheliome: agent-based modelling of the social behaviour of cells. Biosystems, 76(1-3):89–100, 2004.
- Large language models encode clinical knowledge. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.13138, 2022.
- Deep learning enables rapid identification of potent ddr1 kinase inhibitors. Nature biotechnology, 37(9):1038–1040, 2019.
- A platform for the biomedical application of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06488, 2023.
- Large language models as agents in the clinic. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.10895, 2023.
- Andrew Ilachinski. Artificial war: Multiagent-based simulation of combat. World Scientific, 2004.
- A multi-agent architecture for modelling and simulation of small military unit combat in asymmetric warfare. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(2):1331–1343, 2010.
- Literature review of teamwork models. Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, 31(31):1–31, 2006.
- Agentbench: Evaluating llms as agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03688, 2023g.
- Memorybank: Enhancing large language models with long-term memory, 2023.
- Emotionally numb or empathetic? evaluating how llms feel using emotionbench, 2023.
- Mm-react: Prompting chatgpt for multimodal reasoning and action, 2023c.
- Idealgpt: Iteratively decomposing vision and language reasoning via large language models, 2023.
- Vipergpt: Visual inference via python execution for reasoning, 2023.
- The dawn of lmms: Preliminary explorations with gpt-4v(ision), 2023d.
- Minigpt-v2: large language model as a unified interface for vision-language multi-task learning, 2023i.
- Visual instruction tuning, 2023h.
- Palm-e: An embodied multimodal language model, 2023.
- Lost in the middle: How language models use long contexts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.03172, 2023i.
- Siren’s song in the ai ocean: A survey on hallucination in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.01219, 2023h.
- Large language model cascades with mixture of thoughts representations for cost-efficient reasoning, 2023.
- Enhancing trust in llm-based ai automation agents: New considerations and future challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05391, 2023.
- Identifying the risks of lm agents with an lm-emulated sandbox, 2023b.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.