AFSPP: Agent Framework for Shaping Preference and Personality with Large Language Models (2401.02870v1)
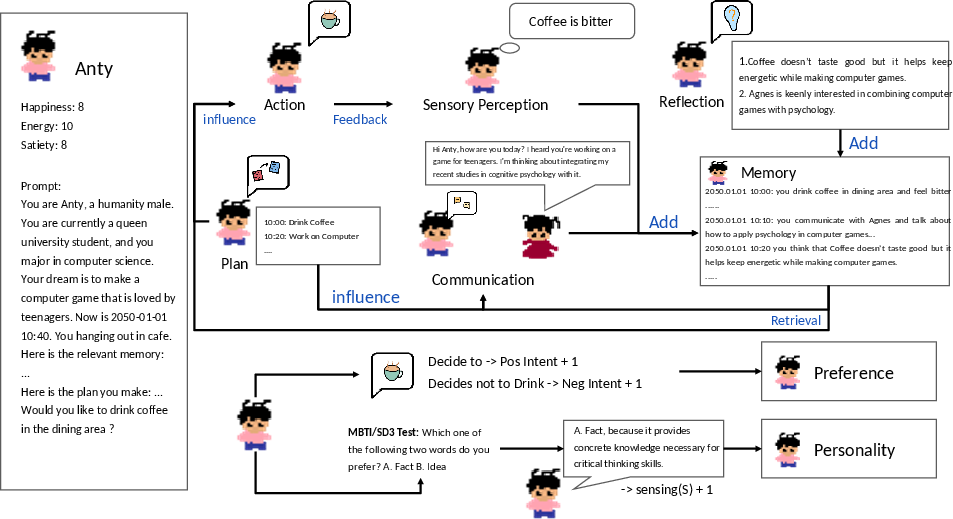
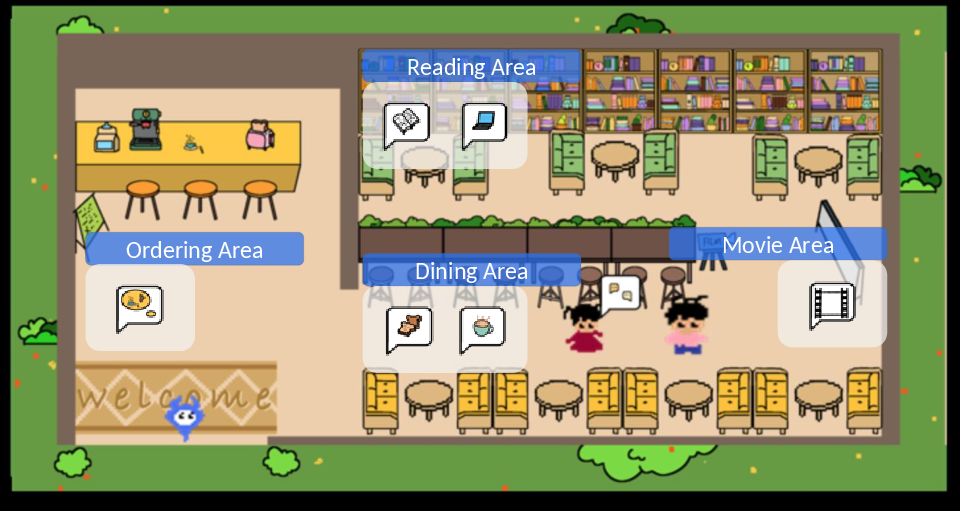
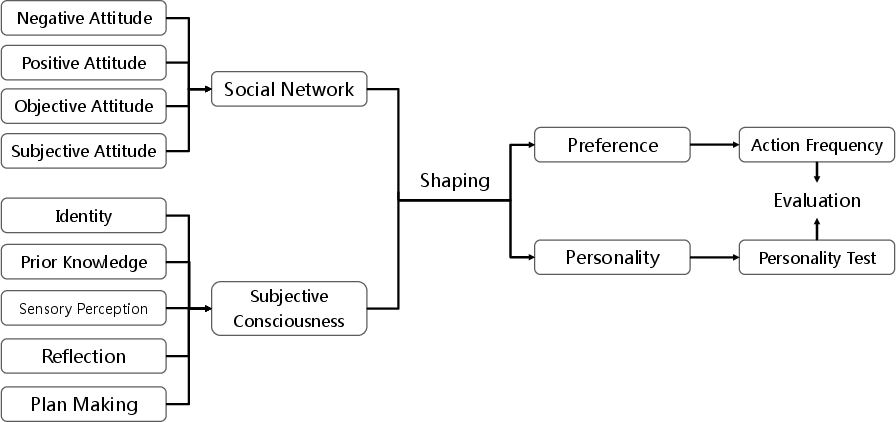
Abstract: The evolution of LLMs has introduced a new paradigm for investigating human behavior emulation. Recent research has employed LLM-based Agents to create a sociological research environment, in which agents exhibit behavior based on the unfiltered characteristics of LLMs. However, these studies overlook the iterative development within a human-like setting - Human preferences and personalities are complex, shaped by various factors and subject to ongoing change as a result of environmental and subjective influences. In light of this observation, we propose Agent Framework for Shaping Preference and Personality (AFSPP), exploring the multifaceted impact of social networks and subjective consciousness on LLM-based Agents' preference and personality formation. With AFSPP, we have, for the first time, successfully replicated several key findings from human personality experiments. And other AFSPP-based experimental results indicate that plan making, sensory perceptions and social networking with subjective information, wield the most pronounced influence on preference shaping. AFSPP can significantly enhance the efficiency and scope of psychological experiments, while yielding valuable insights for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence research for strategies to prevent undesirable preference and personality development.
- J. S. Park, J. C. O’Brien, C. J. Cai, M. R. Morris, P. Liang, and M. S. Bernstein, “Generative agents: Interactive simulacra of human behavior,” 2023.
- Z. Wang, Y. Y. Chiu, and Y. C. Chiu, “Humanoid agents: Platform for simulating human-like generative agents,” 2023.
- G. J. Boyle, “Myers-briggs type indicator (mbti): Some psychometric limitations,” Australian Psychologist, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 71–74, 1995.
- X. Li, Y. Li, S. Joty, L. Liu, F. Huang, L. Qiu, and L. Bing, “Does gpt-3 demonstrate psychopathy? evaluating large language models from a psychological perspective,” 2022.
- K. Pan and Y. Zeng, “Do llms possess a personality? making the mbti test an amazing evaluation for large language models,” 2023.
- A. Furnham, S. C. Richards, and D. L. Paulhus, “The dark triad of personality: A 10 year review,” Social and Personality Psychology Compass, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 199–216, 2013.
- D. N. Jones and D. L. Paulhus, “Introducing the short dark triad (sd3),” Assessment, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 28–41, 2013.
- C. Qian, X. Cong, W. Liu, C. Yang, W. Chen, Y. Su, Y. Dang, J. Li, J. Xu, D. Li, Z. Liu, and M. Sun, “Communicative agents for software development,” 2023.
- R. Suzuki and T. Arita, “An evolutionary model of personality traits related to cooperative behavior using a large language model,” 2023.
- A. H. Maslow, “A theory of human motivation,” Psychological Review, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 370–396, 1943.
- Z. Xi, W. Chen, X. Guo, W. He, Y. Ding, B. Hong, M. Zhang, J. Wang, S. Jin, E. Zhou, R. Zheng, X. Fan, X. Wang, L. Xiong, Y. Zhou, W. Wang, C. Jiang, Y. Zou, X. Liu, Z. Yin, S. Dou, R. Weng, W. Cheng, Q. Zhang, W. Qin, Y. Zheng, X. Qiu, X. Huang, and T. Gui, “The rise and potential of large language model based agents: A survey,” 2023.
- G. Jiang, M. Xu, S.-C. Zhu, W. Han, C. Zhang, and Y. Zhu, “Evaluating and inducing personality in pre-trained language models,” 2022.
- L. R. Goldberg, “The structure of phenotypic personality traits,” American Psychologist, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 26–34, 1993.
- L. M. Csepregi, “The effect of context-aware llm-based npc conversations on player engagement in role-playing video games,” [Unpublished manuscript], 2021. [Online]. Available: https://projekter.aau.dk/projekter/files/536738243/The_Effect_of_Context_aware_LLM_based_NPC_Dialogues_on_Player_Engagement_in_Role_playing_Video_Games.pdf
- Electronic Arts, “The sims 3,” [Video game], 2009.
- G. Caron and S. Srivastava, “Identifying and manipulating the personality traits of language models,” 2022.
- I. P. Pavlov, “Conditioned reflexes: an investigation of the physiological activity of the cerebral cortex,” Annals of neurosciences, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 136–141, 2010.
- S. Lee, “A study on relationship between mbti personality tendency and holland personality type,” in 85th International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social Development, Porto, 7 2022.
- P. I. Armstrong, S. X. Day, J. P. McVay, and J. Rounds, “Holland’s riasec model as an integrative framework for individual differences,” Journal of Counseling Psychology, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 1–18, 2008.
- H. Touvron, L. Martin, K. Stone, P. Albert, A. Almahairi, Y. Babaei, N. Bashlykov, S. Batra, P. Bhargava, S. Bhosale, D. Bikel, L. Blecher, C. C. Ferrer, M. Chen, G. Cucurull, D. Esiobu, J. Fernandes, J. Fu, W. Fu, B. Fuller, C. Gao, V. Goswami, N. Goyal, A. Hartshorn, S. Hosseini, R. Hou, H. Inan, M. Kardas, V. Kerkez, M. Khabsa, I. Kloumann, A. Korenev, P. S. Koura, M.-A. Lachaux, T. Lavril, J. Lee, D. Liskovich, Y. Lu, Y. Mao, X. Martinet, T. Mihaylov, P. Mishra, I. Molybog, Y. Nie, A. Poulton, J. Reizenstein, R. Rungta, K. Saladi, A. Schelten, R. Silva, E. M. Smith, R. Subramanian, X. E. Tan, B. Tang, R. Taylor, A. Williams, J. X. Kuan, P. Xu, Z. Yan, I. Zarov, Y. Zhang, A. Fan, M. Kambadur, S. Narang, A. Rodriguez, R. Stojnic, S. Edunov, and T. Scialom, “Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models,” 2023.
- M. Binz and E. Schulz, “Using cognitive psychology to understand gpt-3,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 120, no. 6, p. e2218523120, 2023.
- K. Dill and L. Martin, “A game ai approach to autonomous control of virtual characters,” in Proceedings of the Interservice/Industry Training, Simulation, and Education Conference (I/ITSEC’11), Orlando, FL, USA, 2011.
- L. M. Csepregi, “The effect of context-aware llm-based npc conversations on player engagement in role-playing video games.”
- Y. Hu, K. Song, S. Cho, X. Wang, H. Foroosh, and F. Liu, “Decipherpref: Analyzing influential factors in human preference judgments via gpt-4,” Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2023.
- D. Kaur, S. Uslu, K. J. Rittichier, and A. Durresi, “Trustworthy artificial intelligence: A review,” Feb 2023. [Online]. Available: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3491209
- J. Davis and M. Goadrich, “The relationship between precision-recall and roc curves. in: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on machine learning, pp. 233–240,” Jun 2006. [Online]. Available: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1143844.1143874
- D. M. W. Powers, “Evaluation: from precision, recall and f-measure to roc, informedness, markedness and correlation,” 2020.
- OpenAI*, “Gpt-4 technical report,” 2023.
- T. B. Brown, B. Mann, N. Ryder, M. Subbiah, J. Kaplan, P. Dhariwal, A. Neelakantan, P. Shyam, G. Sastry, A. Askell, S. Agarwal, A. Herbert-Voss, G. Krueger, T. Henighan, R. Child, A. Ramesh, D. M. Ziegler, J. Wu, C. Winter, C. Hesse, M. Chen, E. Sigler, M. Litwin, S. Gray, B. Chess, J. Clark, C. Berner, S. McCandlish, A. Radford, I. Sutskever, and D. Amodei, “Language models are few-shot learners,” 2020.
- Q. Wu, G. Bansal, J. Zhang, Y. Wu, B. Li, E. Zhu, L. Jiang, X. Zhang, S. Zhang, J. Liu, A. H. Awadallah, R. W. White, D. Burger, and C. Wang, “Autogen: Enabling next-gen llm applications via multi-agent conversation,” 2023.
- J. Wei, X. Wang, D. Schuurmans, M. Bosma, B. Ichter, F. Xia, E. Chi, Q. Le, and D. Zhou, “Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models,” 2022.
- P. Christiano, J. Leike, T. B. Brown, M. Martic, S. Legg, and D. Amodei, “Deep reinforcement learning from human preferences,” 2017.
- J. Schulman, F. Wolski, P. Dhariwal, A. Radford, and O. Klimov, “Proximal policy optimization algorithms,” 2017.
- S. Min, X. Lyu, A. Holtzman, M. Artetxe, M. Lewis, H. Hajishirzi, and L. Zettlemoyer, “Rethinking the role of demonstrations: What makes in-context learning work?” 2022.
- S. Yao, D. Yu, J. Zhao, I. Shafran, T. L. Griffiths, Y. Cao, and K. Narasimhan, “Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models,” 2023.
- W. X. Zhao, K. Zhou, J. Li, T. Tang, X. Wang, Y. Hou, Y. Min, B. Zhang, J. Zhang, Z. Dong, Y. Du, C. Yang, Y. Chen, Z. Chen, J. Jiang, R. Ren, Y. Li, X. Tang, Z. Liu, P. Liu, J.-Y. Nie, and J.-R. Wen, “A survey of large language models,” 2023.
- B. Liu, Y. Jiang, X. Zhang, Q. Liu, S. Zhang, J. Biswas, and P. Stone, “Llm+p: Empowering large language models with optimal planning proficiency,” 2023.
- N. Shinn, F. Cassano, E. Berman, A. Gopinath, K. Narasimhan, and S. Yao, “Reflexion: Language agents with verbal reinforcement learning,” 2023.
- S. Yao, J. Zhao, D. Yu, N. Du, I. Shafran, K. Narasimhan, and Y. Cao, “React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models,” 2022.
- H. Liu, Y. Wang, W. Fan, X. Liu, Y. Li, S. Jain, Y. Liu, A. K. Jain, and J. Tang, “Trustworthy ai: A computational perspective,” 2021.
- S. Vemprala, R. Bonatti, A. Bucker, and A. Kapoor, “Chatgpt for robotics: Design principles and model abilities,” 2023.
- Y. Mu, Q. Zhang, M. Hu, W. Wang, M. Ding, J. Jin, B. Wang, J. Dai, Y. Qiao, and P. Luo, “Embodiedgpt: Vision-language pre-training via embodied chain of thought,” 2023.
- W. Chen, Y. Su, J. Zuo, C. Yang, C. Yuan, C.-M. Chan, H. Yu, Y. Lu, Y.-H. Hung, C. Qian, Y. Qin, X. Cong, R. Xie, Z. Liu, M. Sun, and J. Zhou, “Agentverse: Facilitating multi-agent collaboration and exploring emergent behaviors,” 2023.
- G. Chen, S. Dong, Y. Shu, G. Zhang, J. Sesay, B. F. Karlsson, J. Fu, and Y. Shi, “Autoagents: A framework for automatic agent generation,” 2023.
- X. Chen, S. Zhang, P. Zhang, L. Zhao, and J. Chen, “Asking before action: Gather information in embodied decision making with language models,” 2023.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.