Enhancing Open-Domain Task-Solving Capability of LLMs via Autonomous Tool Integration from GitHub
Abstract: LLMs excel in traditional natural language processing tasks but struggle with problems that require complex domain-specific calculations or simulations. While equipping LLMs with external tools to build LLM-based agents can enhance their capabilities, existing approaches lack the flexibility to address diverse and ever-evolving user queries in open domains. Currently, there is also no existing dataset that evaluates LLMs on open-domain knowledge that requires tools to solve. To this end, we introduce OpenAct benchmark to evaluate the open-domain task-solving capability, which is built on human expert consultation and repositories in GitHub. It comprises 339 questions spanning 7 diverse domains that need to be solved with domain-specific methods. In our experiments, even state-of-the-art LLMs and LLM-based agents demonstrate unsatisfactory success rates, underscoring the need for a novel approach. Furthermore, we present OpenAgent, a novel LLM-based agent system that can tackle evolving queries in open domains through autonomously integrating specialized tools from GitHub. OpenAgent employs 1) a hierarchical framework where specialized agents handle specific tasks and can assign tasks to inferior agents, 2) a bi-level experience learning mechanism to learn from both humans' and its own experiences to tackle tool flaws. Experiments demonstrate its superior effectiveness and efficiency, which significantly outperforms baselines. Our data and code are open-source at https://github.com/OpenBMB/OpenAct.
- Do as i can, not as i say: Grounding language in robotic affordances. ArXiv preprint, abs/2204.01691, 2022.
- AutoGPT. Autogpt. URL https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT.
- Graph of thoughts: Solving elaborate problems with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09687, 2023.
- Large language models as tool makers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17126, 2023.
- Chateval: Towards better llm-based evaluators through multi-agent debate. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07201, 2023.
- Agentverse: Facilitating multi-agent collaboration and exploring emergent behaviors in agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10848, 2023.
- Visual programming: Compositional visual reasoning without training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14953–14962, 2023.
- Reasoning with language model is planning with world model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14992, 2023a.
- Toolkengpt: Augmenting frozen language models with massive tools via tool embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11554, 2023b.
- Language models as zero-shot planners: Extracting actionable knowledge for embodied agents. In Kamalika Chaudhuri, Stefanie Jegelka, Le Song, Csaba Szepesvári, Gang Niu, and Sivan Sabato (eds.), International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2022, 17-23 July 2022, Baltimore, Maryland, USA, volume 162 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 9118–9147. PMLR, 2022.
- Genegpt: Augmenting large language models with domain tools for improved access to biomedical information. ArXiv, 2023.
- Camel: Communicative agents for ”mind” exploration of large scale language model society, 2023.
- Webgpt: Browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. ArXiv preprint, abs/2112.09332, 2021.
- OpenAI. Chatgpt plugins. URL https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt-plugins.
- OpenAI. OpenAI: Introducing ChatGPT, 2022. URL https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt.
- OpenAI. Gpt-4 technical report, 2023.
- Talm: Tool augmented language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.12255, 2022.
- Generative agents: Interactive simulacra of human behavior. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03442, 2023.
- Gorilla: Large language model connected with massive apis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15334, 2023.
- Communicative agents for software development. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.07924, 2023a.
- Creator: Disentangling abstract and concrete reasonings of large language models through tool creation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14318, 2023b.
- Webcpm: Interactive web search for chinese long-form question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06849, 2023a.
- Tool learning with foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08354, 2023b.
- Toolllm: Facilitating large language models to master 16000+ real-world apis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.16789, 2023c.
- Toolformer: Language models can teach themselves to use tools. ArXiv preprint, abs/2302.04761, 2023.
- Algorithm of thoughts: Enhancing exploration of ideas in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10379, 2023.
- Hugginggpt: Solving ai tasks with chatgpt and its friends in huggingface, 2023.
- Reflexion: Language agents with verbal reinforcement learning, 2023.
- Restgpt: Connecting large language models with real-world applications via restful apis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06624, 2023.
- Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971, 2023a.
- Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09288, 2023b.
- Chatgpt for robotics: Design principles and model abilities. Technical Report MSR-TR-2023-8, Microsoft, February 2023.
- Voyager: An open-ended embodied agent with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16291, 2023a.
- Recagent: A novel simulation paradigm for recommender systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.02552, 2023b.
- Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models, 2023.
- Visual chatgpt: Talking, drawing and editing with visual foundation models. ArXiv preprint, abs/2303.04671, 2023a.
- Autogen: Enabling next-gen llm applications via multi-agent conversation framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.08155, 2023b.
- XAgent. Xagent: An autonomous agent for complex task solving, 2023.
- Chatgpt is not enough: Enhancing large language models with knowledge graphs for fact-aware language modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.11489, 2023.
- React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. ArXiv preprint, abs/2210.03629, 2022.
- Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10601, 2023.
- Large language model as autonomous decision maker. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12519, 2023.
- Wider and deeper llm networks are fairer llm evaluators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.01862, 2023.
- D-bot: Database diagnosis system using large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.01454, 2023.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Explain it Like I'm 14
What is this paper about?
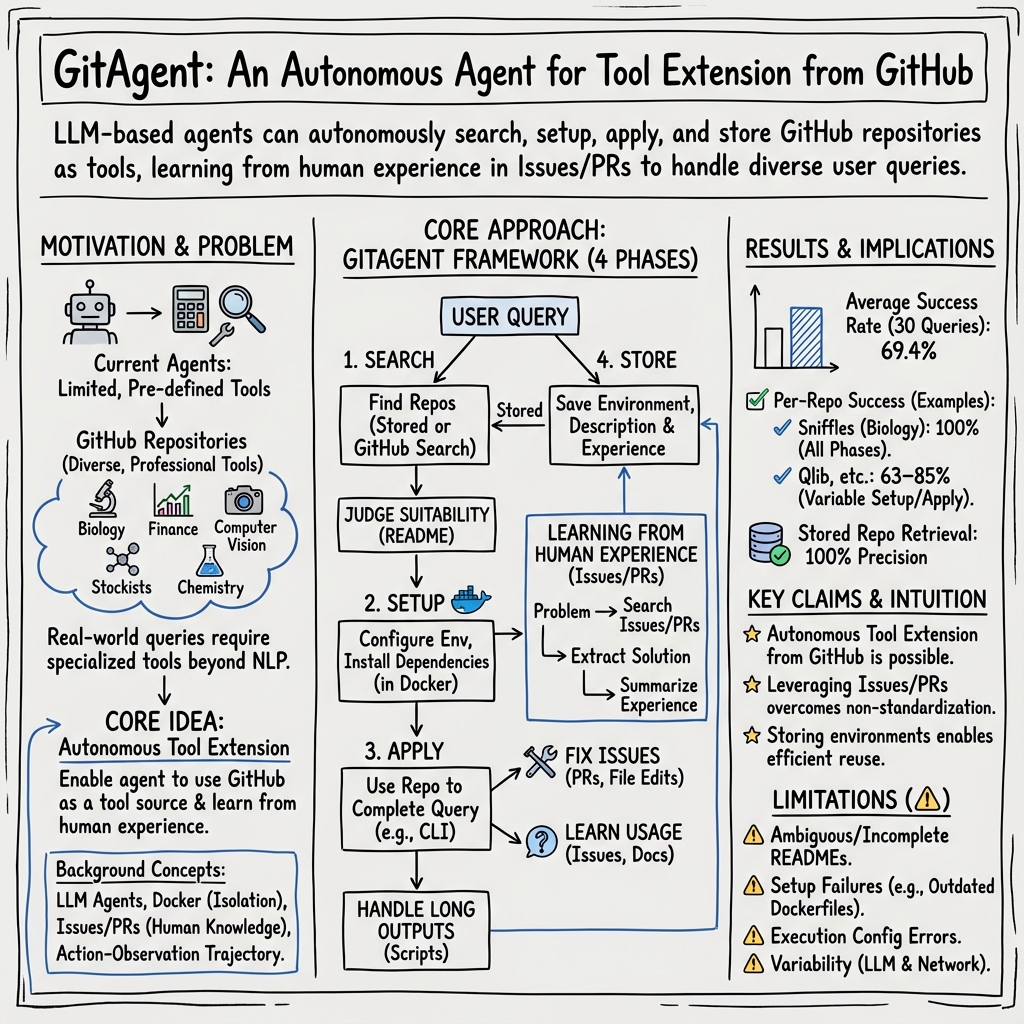
This paper introduces GitAgent, a smart AI helper that can find, set up, and use tools from GitHub (a huge website where people share code) all by itself. The goal is to help the AI solve real-world tasks that need special tools—for example, fixing old photos, doing finance experiments, analyzing DNA data, or planning chemical reactions—without a human having to install or configure anything manually.
What questions is the paper trying to answer?
The paper focuses on three simple questions:
- How can an AI automatically find the right tool from the thousands of projects on GitHub?
- How can it set up that tool safely and correctly, even if the instructions are unclear or the code has bugs?
- How can it use the tool to solve the user’s problem and remember what it learned for next time?
How does GitAgent work?
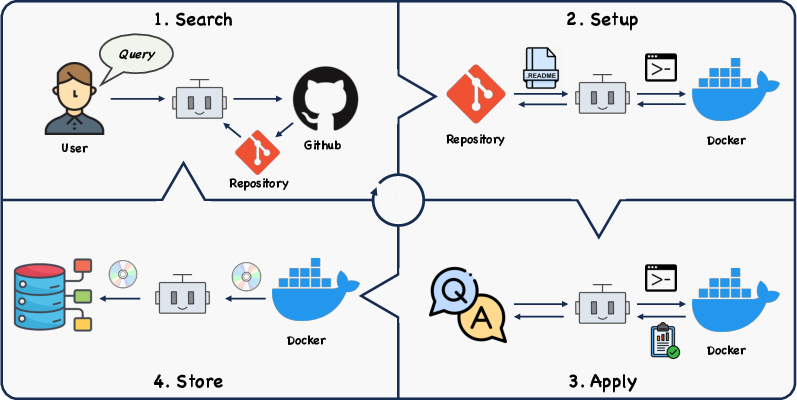
Think of GitAgent like a student solving a project using online resources. It follows a four-step plan:
- Search: It looks for the best GitHub repository (project) that matches the user’s request. If it already has a suitable tool saved from before, it reuses that to save time.
- Setup: It downloads the repository and prepares the environment (like installing software and files). It runs everything inside a safe “sandbox” called a Docker container, so it doesn’t harm the computer.
- Apply: It uses the tool to actually solve the task (like restoring a photo or running a finance model).
- Store: If the tool works, it saves the tool and its setup for future tasks, along with notes on how to use it.
A key idea in this paper is “learning from human experience.” When GitAgent runs into problems—like broken instructions or code bugs—it searches GitHub Issues and Pull Requests (these are like discussion threads and fixes posted by developers) to see how people solved similar problems. It then applies those solutions, such as changing code files or updating settings.
Under the hood, GitAgent uses GPT-4 (a very capable LLM) to plan actions like “search GitHub,” “run commands,” or “edit files,” and to summarize what it learns. You can think of GPT-4 as the “brain” that decides what to do next.
What did the experiments show?
The team tested GitAgent with 30 different tasks across four specialized areas:
- Finance (Qlib): running quantitative investment experiments
- Computer vision (Bringing Old Photos Back to Life): restoring old or damaged photos
- Biology (Sniffles): analyzing genetic structural variants
- Chemistry (AiZynthFinder): planning how to make molecules
Here are the key results:
- Overall success: GitAgent solved about 69% of tasks on average—roughly 7 out of 10.
- Searching and applying the tools were the hardest parts: Finding the right repository and using it correctly can be tricky because GitHub projects vary a lot in quality and documentation.
- Storing and reusing tools works well: When GitAgent saved tools and tried similar tasks later, it always picked the right saved tool (100% Precision@1), making future tasks faster and easier.
- Costs: Using tools with complex setup or lots of file edits required more “thinking” time and actions, which means more API calls and tokens (the way GPT-4 measures work). Simpler tools needed fewer resources.
They also analyzed common failures:
- Picking the wrong repository: Sometimes the README didn’t clearly explain what a project could do, so GitAgent chose a tool that didn’t actually fit the task.
- Setup problems: Some tools had outdated instructions or broken setup files, and the best fixes were hidden inside pull requests that the agent didn’t always use.
- Run-time mistakes: Tools that needed detailed configuration files could fail if GitAgent set a wrong path or time range.
Why is this important and what could it change?
This work shows that an AI can grow its abilities by installing and using new tools from GitHub—almost like adding apps to a phone—without a person guiding every step. That means:
- It could help people solve specialized problems more quickly, even if they don’t know how to install complicated software.
- It can learn from past attempts and from human fixes posted online, making it more robust over time.
- It points toward smarter, more independent AI assistants that handle diverse tasks across fields like finance, biology, chemistry, and image processing.
In the future, improving how the AI selects the right repository, handles errors, and understands messy documentation could raise success rates even more. If that happens, tools like GitAgent could become powerful helpers for students, researchers, and developers tackling complex projects.
Knowledge Gaps
Knowledge gaps, limitations, and open questions
Below is a concise list of concrete gaps and open questions that remain unresolved and can guide future research:
- External validity and scale: The evaluation uses 30 queries across 4 repositories; it is unclear how GitAgent performs across hundreds/thousands of heterogeneous repositories, languages, and domains (e.g., C/C++/Rust, robotics, distributed systems).
- Baselines and ablations: No comparison to existing agents (e.g., HuggingGPT, RestGPT, ToolLLM) or simple heuristics; no ablations to quantify the contribution of Issues/PRs exploration, hierarchical decomposition, or the Store phase.
- Objective metrics and reporting: Success criteria per task are not formally specified; wall-clock time, monetary cost, and standard deviations per phase are not reported (despite being mentioned), limiting reproducibility and interpretability.
- Semantic repository retrieval: The Search phase relies on name/topic search; the paper does not test code-aware/semantic retrieval (e.g., GitHub code search v2, learned code embeddings) or rankers that incorporate signals such as stars, maintenance frequency, and dependency health.
- Query-to-repo mapping benchmark: No public benchmark exists for mapping natural-language queries to appropriate repositories; constructing and releasing such a dataset would enable standardized evaluation.
- Reliability of Issues/PRs mining: The approach lacks methods to assess whether Issues/PRs are up-to-date, correct, or applicable; there is no mechanism to detect conflicting advice, stale fixes, or to verify learned solutions with tests.
- Verification and testing: The agent does not generate or run unit/integration tests to verify correct setup and application, nor does it use CI or reproducibility checks (e.g., pinning commit SHAs, dependency versions).
- Security and safety: There is no threat model or systematic safeguards for executing untrusted code (e.g., supply-chain attacks, dependency confusion, adversarial READMEs/Issues for prompt injection, network egress controls, secret handling, SBOM/SLSA scanning).
- Licensing and compliance: The paper does not address license compatibility, attribution, and redistribution of modified code or Docker images; compliance checks and policy enforcement are absent.
- Resource and hardware constraints: Handling repositories requiring GPUs/CUDA, specialized OS packages, or long build times is not evaluated; scheduling, timeouts, and fallback strategies are unspecified.
- Cost–performance optimization: Although token/API counts are reported, there is no study of wall-clock latency, dollar costs, or strategies like model cascading (small LLMs for routine steps), caching, and early-exit planning.
- Robustness to drift and updates: Repositories evolve; the system lacks mechanisms for version pinning, update detection, automatic revalidation, and patch management for stored Docker images.
- Storage and retrieval at scale: Storing per-repo Docker images may not scale; deduplication, garbage collection, versioning, and retrieval latency for large tool registries are not addressed.
- Multi-tool composition: The agent does not handle tasks requiring orchestration of multiple repositories/tools, environment isolation/merging, or conflict resolution across dependencies.
- Standardized tool interfaces: The paper stores “function descriptions” and experiences but does not define schemas for standardized wrappers (CLI/API contracts), adapter generation, or an extensible, queryable tool registry.
- Long-context log handling: The approach uses ad hoc regex for long logs; no general method (e.g., chunked summarization, retrieval-augmented parsing, log-structure learning) is proposed or evaluated.
- Determinism and reproducibility: Inference stochasticity degrades stability; no techniques like self-consistency, majority voting, or deterministic planning are explored to reduce variance.
- Human-in-the-loop policies: There is no strategy for when to seek clarifications, confirmations, or approvals (especially for risky actions), nor a cost-aware ask-vs-act policy.
- Learning across tasks: The benefit of stored experience E is not quantified on held-out, related tasks; methods for continual learning, knowledge consolidation, and retrieval-augmented reuse are untested.
- Failure detection and recovery: The system lacks automatic detection of misaligned repo selection, rollback to checkpoints, or dynamic switching to alternative repositories mid-execution.
- Rate limits and offline resilience: GitHub API rate limiting/outages are acknowledged but not mitigated; caching, backoff strategies, or offline mirrors are not evaluated.
- Internationalization: The agent’s ability to handle non-English queries/repos (and multilingual Issues/PRs) is untested; cross-lingual topic extraction and retrieval remain open.
- Dataset and artifact release: The paper does not indicate release of code, prompts, evaluation data, or stored images; without artifacts, independent replication is difficult.
- Success definition per phase: The Submit-based phase completion check is underspecified; clearer, measurable per-phase objectives and ground-truth outputs are needed for rigorous evaluation.
- Ethics and governance: Policies for rejecting unsafe tasks, handling sensitive data, and auditing actions/logs are not defined.
- Upstreaming fixes: The agent modifies local copies but does not propose mechanisms to create upstream PRs, manage forks, or engage maintainers—raising sustainability and maintenance questions.
- Handling missing/poor documentation: Beyond Issues/PRs, the agent does not leverage static code analysis, symbol/index graphs, or test discovery to infer entry points and configurations when README is insufficient.
- Retrieval evaluation bias: Precision@1 is measured on the same queries used to create stored repos; generalization to paraphrases, novel tasks within the same repo, and near-neighbor tasks is untested.
- Hyperparameter sensitivity: The impact of temperature, prompt design, and tool-calling policies on success, cost, and stability is not analyzed.
Practical Applications
Immediate Applications
Below are deployable use cases that leverage GitAgent’s four-phase workflow (Search → Setup → Apply → Store) and its “human experience learning” from GitHub Issues/PRs, along with sector alignment and feasibility notes.
- Software/IT (DevOps and IT Operations): Autonomous OSS integration and environment provisioning
- Use case: Automate discovery, setup (in Docker), and execution of open-source tools to accomplish internal tasks (e.g., data transformation, CLI utilities, model training) from a natural-language request.
- Potential products/workflows: “RepositoryOps” pipelines; internal agent that converts tickets into fully configured tool environments; cached Docker image store with function descriptions and execution recipes.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Reliable LLM (GPT‑class with function calling), GitHub API access, network connectivity, robust sandboxing (Docker + network egress rules), license checks, cost budgets for tokens and compute.
- Finance (Quant research assistance with Qlib)
- Use case: Analysts ask for a backtest or model comparison; the agent pulls Qlib, configures dependencies, writes the config, fetches data, runs experiments, and returns metrics/plots and transaction details.
- Potential products/workflows: “On-demand quant lab” assistant integrated with research notebooks and CI.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Market data access, compute resources, correct configuration of time ranges/paths, license compliance for datasets and repos.
- Healthcare/Bioinformatics (Variant calling with Sniffles)
- Use case: Bioinformatics teams provide long-read data; the agent provisions Sniffles, installs missing utilities, and executes SV calling pipelines end-to-end.
- Potential products/workflows: “Bioinformatics-on-demand” agent for ad hoc or peak workloads; reproducible pipeline snapshots.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Secure handling of PHI, file format compatibility (e.g., BAM/CRAM), HPC/cluster integration, audit logs, and sandboxing beyond Docker as needed.
- Chemistry (Retrosynthetic planning with AiZynthFinder)
- Use case: Chemists request synthesis routes; the agent auto-installs dependencies (e.g., RDKit), loads models, runs retrosynthesis, and returns candidate routes.
- Potential products/workflows: Bench scientist assistant; LIMS integrations for route documentation and inventory cross-checks.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Availability of chemistry toolchains (RDKit), model files, GPU/CPU as required, licensing for cheminformatics packages.
- Digital Media (Photo restoration with Bringing-Old-Photos-Back-to-Life)
- Use case: Users upload images; the agent retrieves and fixes the correct Dockerfile from PRs/Issues, builds the environment, and restores photos automatically.
- Potential products/workflows: “Restore my photos” concierge; batch pipelines for archives/museums.
- Assumptions/dependencies: GPU availability for inference, correct CUDA/cuDNN versions, stable dependency resolution, storage for large images.
- Education & Research (Reproducibility and lab automation)
- Use case: Students and researchers request “run this repo/paper code”; the agent builds the environment, executes experiments, and stores a reproducible Docker image and runbook.
- Potential products/workflows: Course/lab “reproducibility bot”; departmental registry of agent-verified research tool images.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Access to code/data, campus compute quotas, network access to GitHub, instructor approval for auto-execution of third-party code.
- MLOps/Prototyping (Rapid tool onboarding and reuse)
- Use case: Teams trial multiple open-source ML repos; the agent sets up and runs benchmarks, logs outcomes, and stores best-performing tool images and metadata for future reuse.
- Potential products/workflows: “Self-expanding plugin store” for ML components; CI hooks that automate environment setup and smoke tests.
- Assumptions/dependencies: GPUs/CPUs as needed, policy for running external code, registry management for stored images.
- Enterprise Knowledge Management (Persistent, searchable internal tool catalog)
- Use case: Build an internal, searchable catalog of “agent-ready” Docker images with function descriptions and lessons learned from Issues/PRs to accelerate repeated tasks.
- Potential products/workflows: Tool knowledge base; retrieval-first execution (“Precision@1” retrieval to bypass fresh search).
- Assumptions/dependencies: Metadata schema, RBAC for stored images, indexing and search infrastructure, policy on image retention and updates.
Long-Term Applications
These require further R&D to improve reliability, safety, standardization, and scale beyond the paper’s current 69.4% average success rate.
- Enterprise-Grade Agent Platform (Continuous, safe tool expansion across an organization)
- Vision: A compliance-aware agent that continuously discovers, evaluates, integrates, and monitors OSS tools, with automated testing, license scanning, and rollback.
- Potential products/workflows: “Agent governance layer” with automated license checks, SBOMs, vulnerability scanning, and human-in-the-loop approvals.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Advanced semantic search for GitHub (beyond topic search), policy and legal frameworks, higher success rates in repository selection and execution, mature sandboxing (e.g., gVisor/Firecracker), auditability.
- Public Sector & Policy (Open science and grant reproducibility auditing)
- Vision: Agencies deploy agents to validate the executability of code/artifacts in grant proposals and publications, improving reproducibility and transparency.
- Potential products/workflows: Reproducibility scorecards; standard submission format for “agent-executable” research artifacts.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Community standards for metadata and environments, controlled access to datasets, policy acceptance, legal clarity around auto-execution of third-party code.
- Security & Compliance Automation (Dynamic analysis of OSS with human experience mining)
- Vision: Agents that learn from Issues/PRs to patch exploitable misconfigurations, test fixes in sandboxes, and recommend secure defaults before adoption.
- Potential products/workflows: “Compliance copilot” for OSS intake, license compatibility checks, provenance tracking.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Integration with SCA/SAST/DAST tools, hardened sandboxes, curated knowledge extraction from Issues/PRs with trust/risk scoring.
- Agent-Ready Tool Ecosystem (Standardization and marketplace)
- Vision: A registry of “agent-ready” repositories with machine-readable function descriptions, setup recipes, and validated Docker images to accelerate integration.
- Potential products/workflows: Marketplace with reputation/quality metrics; automated badges signaling “agent compatibility.”
- Dependencies/assumptions: Community adoption of metadata standards, curation incentives, hosting and verification infrastructure.
- Robotics (Autonomous integration of ROS/OSS packages on robots)
- Vision: On-device agents that fetch and configure ROS packages from GitHub to accomplish new tasks (e.g., perception, navigation) with safety constraints.
- Potential products/workflows: “Robot task onboarding” agent; simulation-first validation pipelines.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Real-time constraints, deterministic builds, safety certification, offline mirrors, strict resource and permission controls.
- Edge/IoT and Offline Settings (Resource-aware autonomous tool deployment)
- Vision: Agents that prefetch, cache, and execute tools under tight compute/network constraints, with adaptive model/tool selection.
- Potential products/workflows: “Edge agent cache” with lightweight images and delta updates; bandwidth-aware workflows.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Compact images, robust caching, fallback semantics for intermittent connectivity, hardware-specific optimizations.
- IDE/CI Integration (Code-to-experiment assistants)
- Vision: Developer/analyst copilots that not only suggest code but also provision and run external repos in CI/CD, report results, and persist validated environments.
- Potential products/workflows: “Run-and-validate” buttons in IDE; CI stages that instrument the Search–Setup–Apply–Store loop.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Plugin ecosystems, secure CI runners, approval workflows for running third-party code.
- Knowledge Graphs of OSS Practice (Experience mining at scale)
- Vision: Aggregate and structure lessons from Issues/PRs across repos into a knowledge graph to boost agent reasoning for setup, bug fixing, and usage patterns.
- Potential products/workflows: “Troubleshooting oracle” for agents; cross-repo analogical reasoning for fixes.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Robust NLP pipelines, GitHub rate limits, deduplication and quality control, provenance tracking.
- Sector-Specific Auto-Labs (Healthcare, Finance, Chemistry)
- Vision: Turnkey “auto-labs” where domain experts articulate a goal and agents assemble and run tailored pipelines (e.g., clinical genomics QC, risk modeling, retrosynthesis screening), with storage/reuse of validated environments.
- Potential products/workflows: Regulated “clinical agent” frameworks; audit-ready experiment registries.
- Dependencies/assumptions: Regulatory approvals (HIPAA/GDPR, GxP), validated toolchains, explainability and traceability, domain-specific data access agreements.
Notes on feasibility across all applications:
- Reliability: Current average success rate (69.4%) implies the need for human-in-the-loop oversight for critical tasks.
- Cost: Token and API usage can be high; caching and retrieval (Store→Search) are key for cost control.
- Security: Running arbitrary code requires strict isolation, network controls, and monitoring; Docker alone may be insufficient.
- Legal: OSS license compliance and data governance must be enforced; policies for auto-execution should be explicit.
- Infrastructure: GPU/CPU availability, dataset access, and stable network/GitHub API quotas are required for smooth operation.
Glossary
- Action-observation sequence: The alternating process where an agent takes an action and receives an observation from the environment, forming the basis of its decision trajectory. "Such an action-observation sequence forms a trajectory of the agent to accomplish the query."
- Backtesting: The evaluation of a trading strategy using historical data to assess performance before real-world deployment. "This file encompasses a range of parameters including dataset settings, model hyperparameters, and backtesting parameters."
- Command-Line Interface: A text-based interface for interacting with software by typing commands and options. "Well-developed repositories provide clear entry for allowing straightforward applications (e.g., Command-Line Interface)."
- Docker environment: An isolated, containerized runtime that encapsulates software and its dependencies for secure, reproducible execution. "Furthermore, to ensure security measures, the repository is cloned into a docker environment, and all subsequent commands are executed within this isolated environment."
- Docker image: A versioned, portable snapshot of a containerized environment used to create Docker containers. "Specifically, the execution environment will be stored in a docker image so if a similar query comes, the agent can retrieve this repository and restore it to apply directly."
- Dockerfile: A text specification file containing build instructions to create a Docker image. "Conversely, for repositories such as Bringing-Old-Photos-Back-to-Life, although it provides an official dockerfile to build the execution environment, there exist some bugs in it."
- Function Calling feature: An LLM API capability that structures and executes tool or function calls via model outputs. "All actions including API callings, command executions, and agent operations (e.g., summarization) are implemented based on the Function Calling feature\footnote{https://openai.com/blog/function-calling-and-other-api-updates} of GPT-4."
- Germline: Genetic variations present in reproductive cells and inheritable across generations. "Sniffles is a structural variant caller for long-read sequencing, which can be used to detect SVs on germline, somatic, and population-level for PacBio."
- GitHub Issues/PRs API: The interface for programmatically querying GitHub Issues and Pull Requests to retrieve discussions and fixes. "It then judges the relevance of these Issues/PRs to determine their relevance and applicability to the current problem sequentially."
- Hierarchical task decomposition: A planning strategy that breaks a complex task into phases, subtasks, and actions. "GitAgent employs a hierarchical task decomposition strategy to achieve tool extension from GitHub."
- Long_Context_Process subtask: A procedure for extracting key information from lengthy outputs using programmatic parsing. "In some cases, extensive output (e.g., lengthy execution logs) often ensues and thus the agent needs to go to the Long_Context_Process subtask which writes a Python program (e.g., regular expressions) to extract critical information from the lengthy file."
- Long-read sequencing: DNA sequencing technology that produces longer reads, aiding structural variant detection. "Sniffles is a structural variant caller for long-read sequencing, which can be used to detect SVs on germline, somatic, and population-level for PacBio."
- PacBio: A sequencing platform by Pacific Biosciences known for long-read genomics data. "Sniffles is a structural variant caller for long-read sequencing, which can be used to detect SVs on germline, somatic, and population-level for PacBio."
- Precision@1: An information retrieval metric indicating whether the top-ranked result is correct. "The effectiveness of this retrieval process was quantitatively measured using the metric Precision@1, with the results detailed in Table~\ref{tab:retrieval}."
- Pull Requests (PRs): Proposed code changes in a repository, typically reviewed and discussed before merging. "As GitHub provides Issues and Pull Requests~(PRs) which contains human practice experience, GitAgent can resort to Issues and PRs to learn how human practitioners solve problems (e.g., bugs) during the tool extension."
- Quantitative investment: An approach to investing that uses mathematical models and data-driven strategies. "Qlib~\footnote{https://github.com/microsoft/qlib} is a quantitative investment platform for Quant researchers to conduct quantitative investment experiments."
- Retrosynthetic planning: A chemistry method that plans synthetic routes by iteratively breaking a target molecule into simpler precursors. "AiZynthFiner~\footnote{https://github.com/MolecularAI/aizynthfinder} is a toolkit for retrosynthetic planning in the chemistry domain."
- Semantic search API: A search interface that retrieves results based on meaning rather than exact keyword matches. "As GitHub lacks the semantic search API, we resort to the topic search API."
- Somatic: Genetic variations occurring in non-reproductive cells, not inherited by offspring. "Sniffles is a structural variant caller for long-read sequencing, which can be used to detect SVs on germline, somatic, and population-level for PacBio."
- Structural variant caller: A bioinformatics tool that detects large-scale genomic rearrangements like insertions, deletions, and duplications. "Sniffles~\footnote{https://github.com/fritzsedlazeck/Sniffles} is a structural variant caller for long-read sequencing, which can be used to detect SVs on germline, somatic, and population-level for PacBio."
- System prompt: The initial instruction or context provided to an agent/LLM that guides its behavior for a task. "where refers to the agent, refers to the system prompt of the agent."
- Temperature: A sampling parameter that controls randomness in LLM outputs; higher values increase variability. "We implement our GitAgent based on the gpt-4-32k version~\footnote{Version in 2023-12-08} of GPT-4~\citep{openai2023gpt4} with $0.6$ temperature."
- Topic search API: A GitHub search interface for finding repositories labeled with specific topics. "As GitHub lacks the semantic search API, we resort to the topic search API."
- Trajectory: The complete sequence of states, actions, and observations an agent follows to solve a task. "Such an action-observation sequence forms a trajectory of the agent to accomplish the query."
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.