- The paper introduces a hierarchical agent design combining a proficient LLM for intention reasoning with a lightweight LLM for rapid action execution, achieving significantly lower latency.
- The paper details a two-stage reasoning process in its Slow Mind and real-time action execution via Fast Mind, ensuring robust human-AI collaboration.
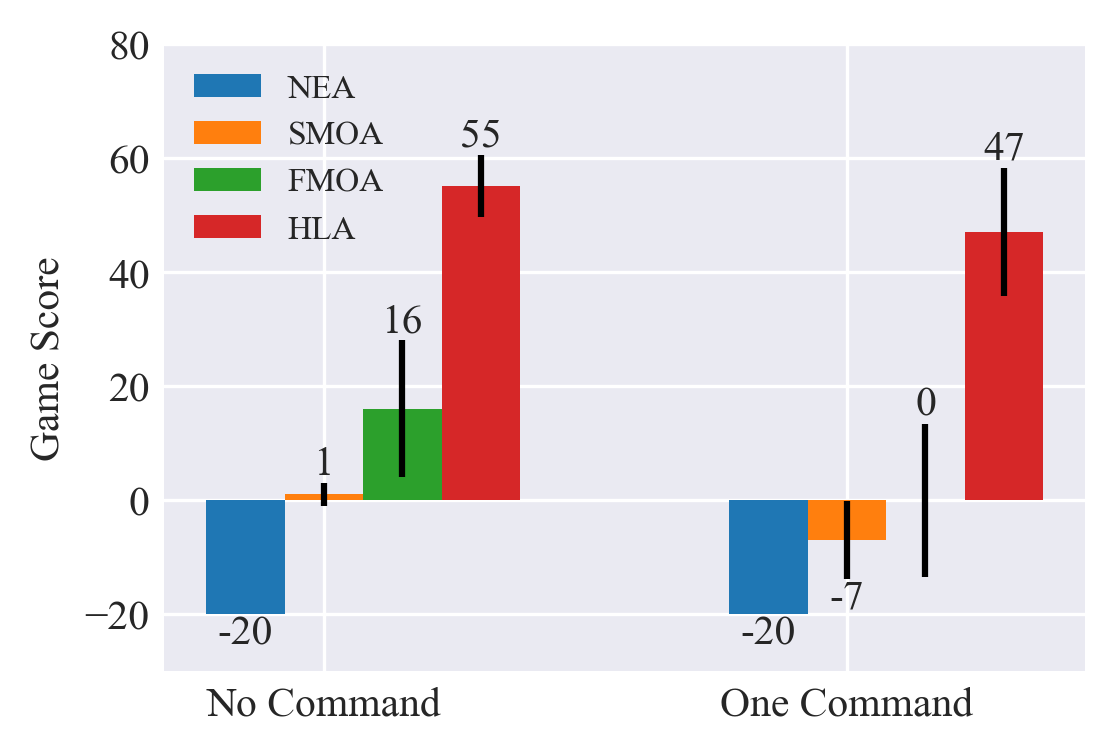
- Human studies and benchmarks in Overcooked demonstrate approximately 50% higher game scores and enhanced real-time responsiveness compared to baseline models.
LLM-Powered Hierarchical Language Agent for Real-time Human-AI Coordination
This paper introduces a Hierarchical Language Agent (HLA) designed to facilitate real-time human-AI coordination, particularly in interactive environments like the Overcooked game. The core innovation lies in a hierarchical architecture that integrates a proficient LLM for high-level reasoning with a lightweight LLM and a reactive policy for rapid action execution. This approach addresses the limitations of traditional LLM-based agents, which often suffer from high inference latency, making them unsuitable for real-time applications.
HLA Architecture
The HLA framework (Figure 1) is structured into three key modules:
- Slow Mind: A proficient LLM (GPT-3.5) responsible for interpreting human commands, maintaining context through command history, and generating natural language responses. This module focuses on intention reasoning and language-based communication.
- Fast Mind: A lightweight LLM (Llama2-13B-chat) that translates interpreted commands into high-level actions, referred to as "macro actions." This module aims to provide real-time responsiveness while adhering to human instructions.
- Executor: A reactive policy implemented as pre-defined scripts that convert macro actions into atomic actions, enabling the agent to interact with the environment at a high frequency.
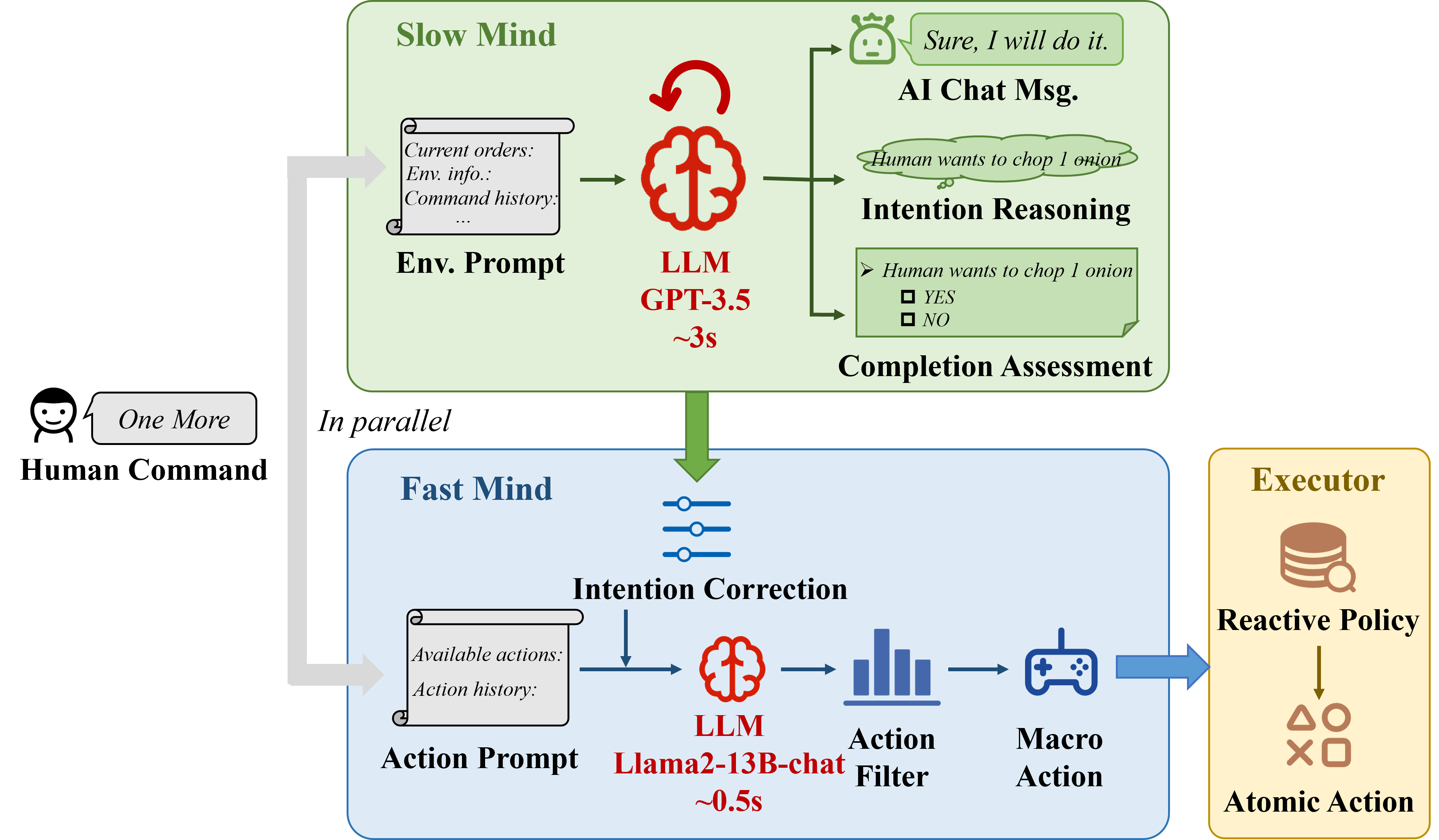
Figure 1: Framework of {Hierarchical Language Agent}, including a {Slow Mind} for intention reasoning and language interaction, a {Fast Mind} for macro actions generation, and an {Executor} to execute atomic actions.
The {Slow Mind} employs a two-stage design (Figure 2). In the first stage, the {Intention Reasoning Stage}, infers human intention given the command and command history when the human issues a new command. The second stage, {Chat }, periodically checks command completion and generates reply messages to the human partner based on the inferred intention.
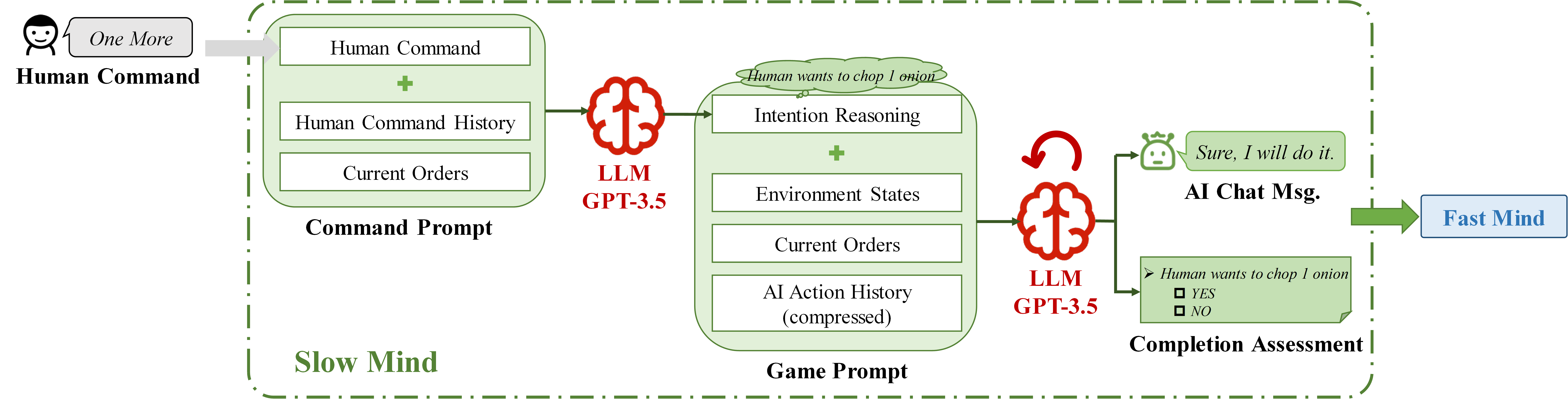
Figure 2: Workflow of {Slow Mind}. {Slow Mind} employs a two-stage design. It reasons human intention according to human commands in the first stage, then generates chat message and performs completion assessment periodically in the second stage.
The {Fast Mind} (Figure 3) is empowered by a lightweight LLM (quantized version of Llama2-13B-chat). To better ground human commands into moves, {Fast Mind} works with {Slow Mind} cooperatively with a conditional prompt mechanism. Lastly, {Fast Mind} avoids sub-optimal moves with an action-filtering mechanism.
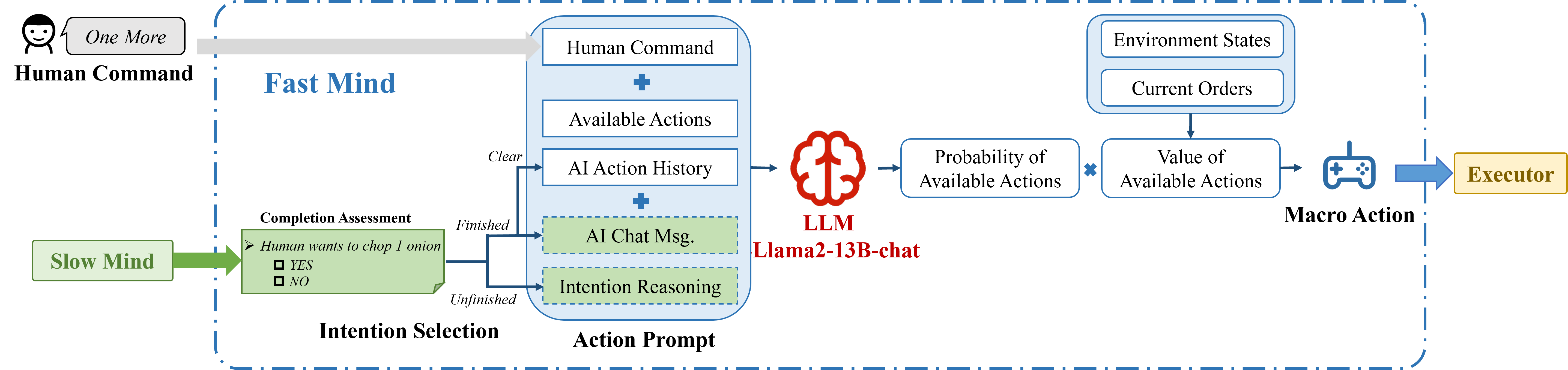
Figure 3: Workflow of {Fast Mind}. {Fast Mind} is empowered by a lightweight LLM. It works with {Slow Mind} cooperatively with a conditional prompt mechanism and avoids sub-optimal moves with an action-filtering mechanism.
Experimental Evaluation
The HLA was evaluated in the Overcooked environment, enhanced with language-based communication capabilities. The experiments focused on assessing the agent's real-time responsiveness, command reasoning abilities, and overall cooperation with human players.
Three baseline agents were used for comparison:
- Slow-Mind-Only Agent (SMOA): Lacks the {Fast Mind} and relies solely on the proficient LLM for action generation.
- Fast-Mind-Only Agent (FMOA): Removes the {Slow Mind}, using only the lightweight LLM for action planning without intention reasoning.
- No-Executor Agent (NEA): Eliminates the {Executor}, requiring the {Fast Mind} to directly control atomic actions.
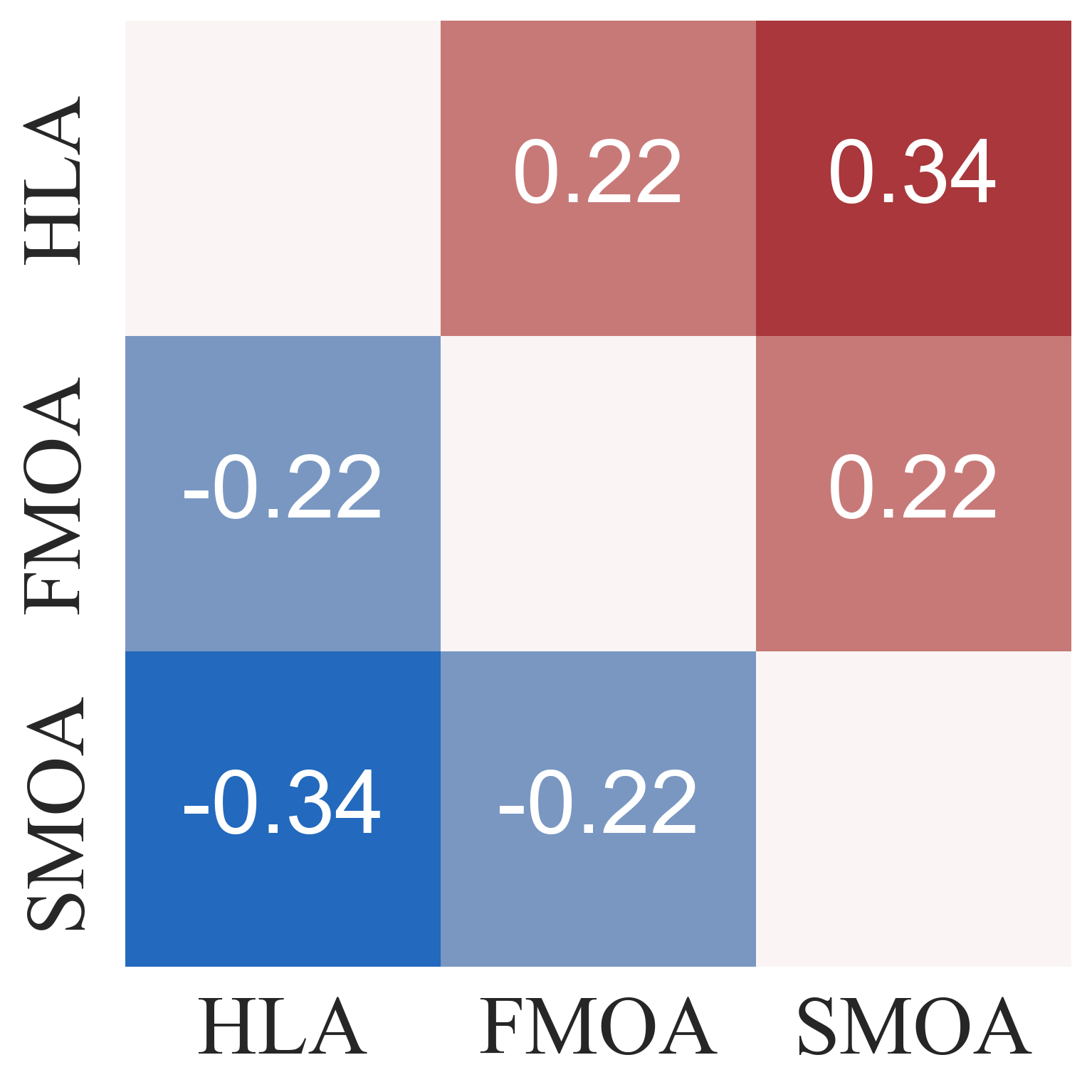
Key Findings
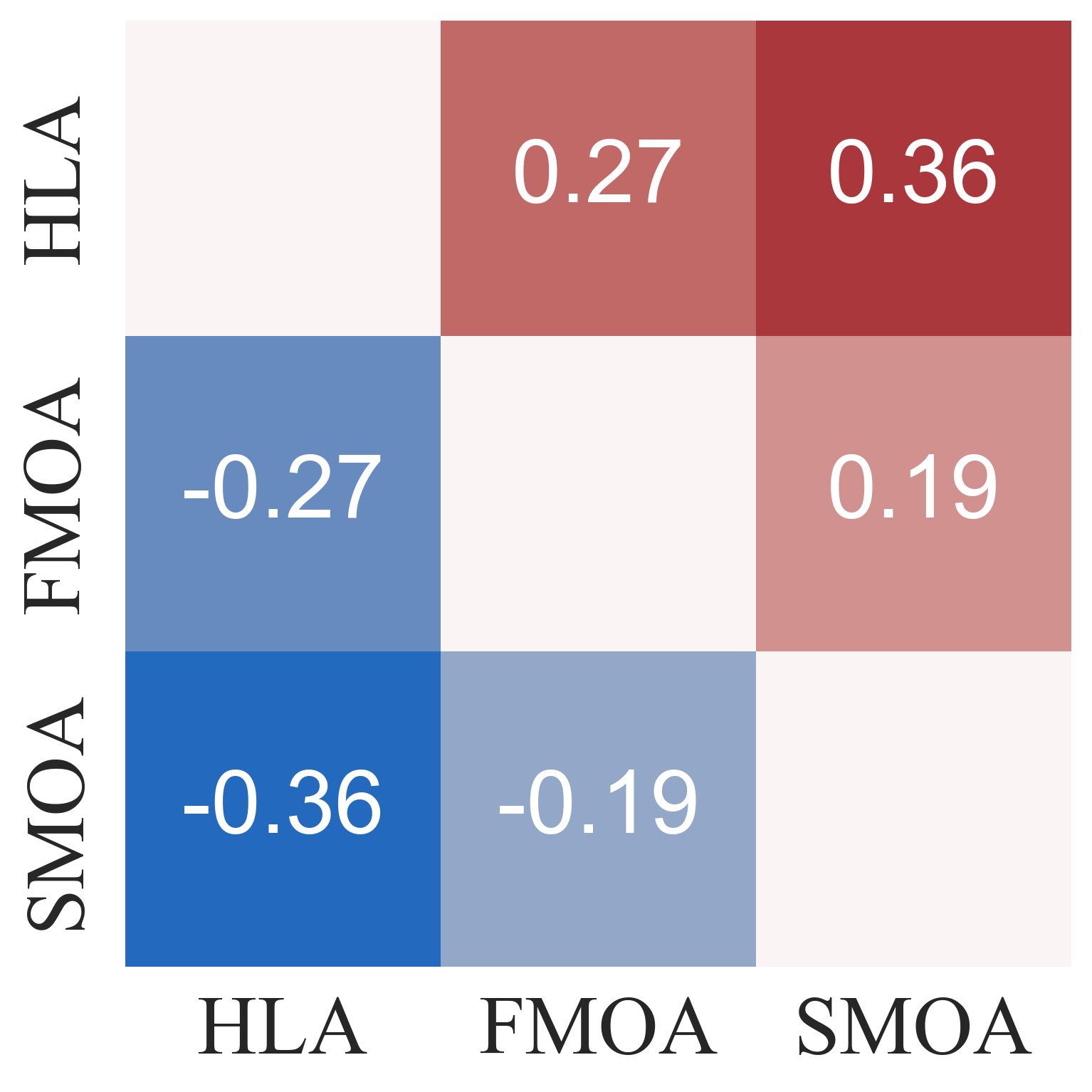
Figure 5: Comm. Accuracy.
Implications and Future Directions
The HLA framework presents a promising approach to building AI agents that can effectively collaborate with humans in real-time interactive environments. The hierarchical architecture, which combines the reasoning capabilities of LLMs with the speed of reactive policies, offers a viable solution to the latency challenges associated with traditional LLM-based agents.
The paper suggests several potential avenues for future research:
- Substituting GPT-3.5 with more advanced models like GPT-4 in the {Slow Mind} to further enhance semantic analysis and command understanding.
- Replacing the scripted executor with a learned policy trained through goal-conditioned reinforcement learning to improve low-level execution performance and reduce reliance on manual scripting.
- Explore the use of different LLMs with different sizes to optimize the performance.
Conclusion
The HLA framework represents a significant step towards achieving seamless human-AI coordination in real-time environments. By integrating high-level reasoning with rapid action execution, HLA enables AI agents to effectively understand, respond to, and collaborate with human partners in dynamic and interactive tasks. The experimental results and human studies provide strong evidence for the effectiveness of the hierarchical design and highlight the potential of HLA for a wide range of real-world applications.