- The paper introduces a novel latent diffusion method that unifies multi-view texturing using a single Depth-to-Image network and MultiDiffusion.
- It leverages spherical harmonic latent texture mapping and GAN inversion to ensure consistent textures across diverse 3D mesh views.
- Quantitative evaluations using CLIP-Score and FID indicate improved fidelity and text-prompt alignment over traditional methods.
"Consistent Mesh Diffusion" Essay
The paper "Consistent Latent Diffusion for Mesh Texturing" presents an innovative approach to generating consistent 3D textures from text prompts using a novel method that leverages latent diffusion processes. This approach resolves the challenge of creating a uniform texture across different viewing angles, which has been a significant limitation in prior mesh texturing methods. The authors propose utilizing a single Depth-to-Image diffusion network alongside MultiDiffusion, producing consistent textures efficiently.
Methodology
The proposed methodology utilizes a combination of MultiDiffusion and spherical harmonic latent texture mapping to ensure consistency across multiple views of a 3D mesh. The process begins with the application of a Depth-to-Image diffusion model to generate initial textures. The transformation into a latent texture map allows the incorporation of spherical harmonics, which adds view-dependent variation, enhancing the visual quality without compromising consistency.
Key to the method is the use of consistent latent diffusion, which unifies multiple diffusion paths into a single cohesive output. This unification is achieved by averaging noise across multiple views during diffusion, ensuring that textural details remain consistent regardless of viewing perspective. This represents a departure from prior work, which often displayed inconsistency due to varying projections and heuristics used in stitching images together.
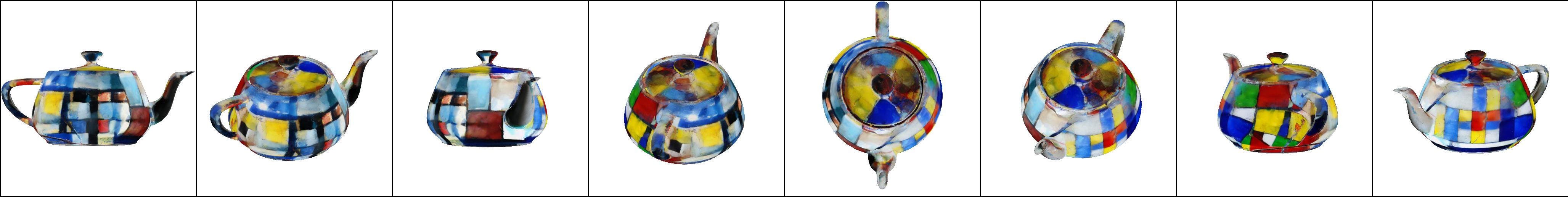
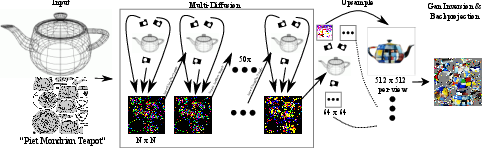

Figure 1: Multi-Diffusion Mesh Texturing. Textures are generated from a mesh with a UV parameterization and a text prompt using multi-diffusion processes.
The methodology also incorporates GAN inversion techniques to maintain consistency post-diffusion. By fine-tuning latent space variables rather than image space, the approach minimizes inconsistencies that stem from the pixel-level variations in the generated texture.
Quantitative and Qualitative Results
The researchers evaluate the method's performance using both CLIP-Score and Frechet Inception Distance (FID) across a dataset of 30 meshes. The results demonstrate a significant improvement over prior methods like TEXTure in terms of both fidelity and text-prompt alignment. The method achieves a median CLIP-Score that is competitive with state-of-the-art, as well as lower FID values, suggesting higher fidelity to base diffusion model outputs.
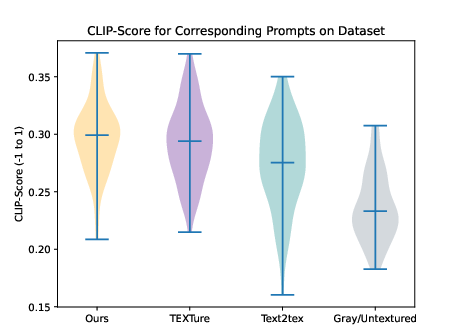
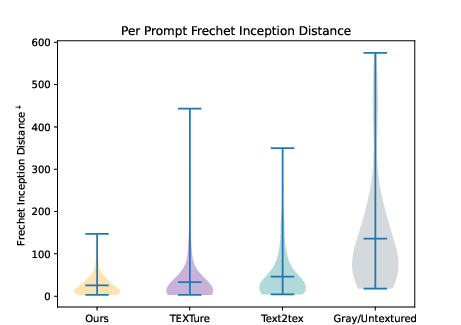
Figure 2: CLIP-Score comparisons highlight the method's competitive text-prompt similarity across diverse meshes.
The study provides exhaustive qualitative comparisons, exhibiting more visually appealing and seamless texturing results across different prompts and mesh geometries.
Implementation Details
The approach can be implemented efficiently requiring approximately five minutes per mesh on an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 GPU. This efficiency is achieved through the use of the MultiDiffusion framework, which allows for fast texture generation while maintaining high consistency and quality.
Pseudocode for consistent latent diffusion and mesh texturing algorithms are provided, offering a comprehensive guide for implementation. Critical parameters such as guidance scale, texture map sizes, and camera viewpoints are systematically ablated to optimize texturing outcomes.
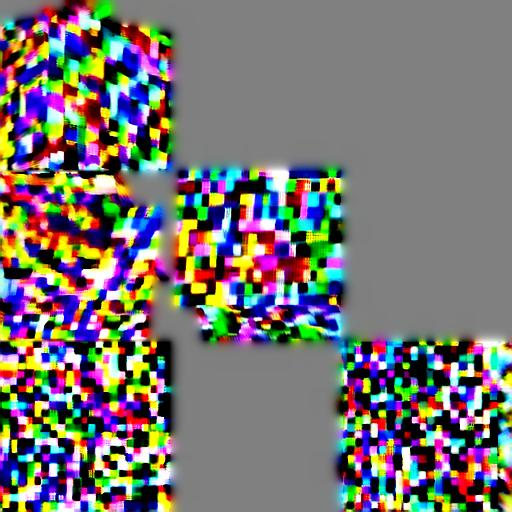

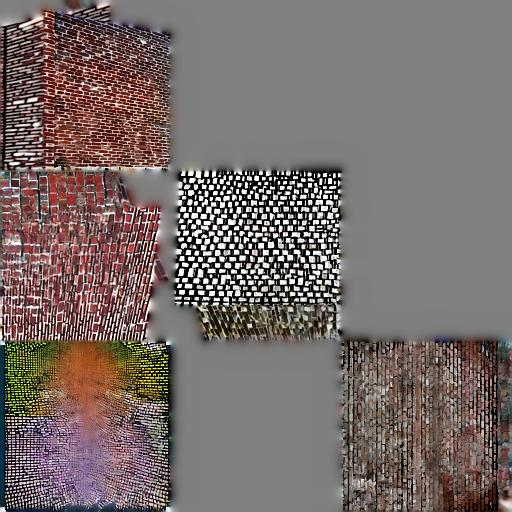
Figure 3: Latent UV parameterization ablation demonstrates the importance of texture size in achieving quality output.
Limitations and Future Directions
Despite its advancements, the method faces limitations such as the multi-Janus problem, where different views generate inconsistent faces. Additionally, the ambiguity in text prompts can sometimes lead to varied outputs. Addressing these challenges could involve more precise control over text prompt specifications and enhancing the diffusion process to handle multiple potential outcomes from a single prompt.
Future work might explore integrating more intricate 3D priors into the diffusion process or extending this methodology to cover more complex geometries and real-world applications, such as gaming and virtual reality assets.
Conclusion
"Consistent Latent Diffusion for Mesh Texturing" provides a robust solution to the longstanding problem of consistent texturing across 3D meshes. By merging multi-view diffusion paths, the approach not only enhances texture fidelity but also significantly reduces the computational burden associated with traditional methods. The research lays the groundwork for further advancements in generative modeling and 3D content creation, with promising applications in various digital fields.