- The paper presents LLMiner, which autonomously mines QA pairs from domain texts to enhance chatbot training.
- It leverages chain-of-thought reasoning and GPT-4 generated seed data to fine-tune LLaMa-7b, reducing reliance on human curation.
- Experimental results demonstrate improved performance in responding to domain-specific queries compared to conventional methods.
A Self-enhancement Approach for Domain-specific Chatbot Training via Knowledge Mining and Digest
The paper "A Self-enhancement Approach for Domain-specific Chatbot Training via Knowledge Mining and Digest" presents an innovative methodology to enhance LLMs with domain-specific expertise by leveraging autonomous knowledge mining. This process aims to address the challenges LLMs face in answering intricate and knowledge-intensive queries specific to various domains.
Introduction
The authors begin by acknowledging the significant role LLMs have played in advancing natural language understanding and generation. Despite their strengths, LLMs struggle with domain-specific knowledge-intensive queries due to conventional training methodologies that inadequately address complex information retrieval. The paper proposes a novel approach — LLMiner — that autonomously extracts Question-Answer (QA) pairs from domain-specific texts using chain-of-thought reasoning. This is coupled with conversational datasets to fine-tune LLMs, thereby enhancing their domain-specific conversational abilities.
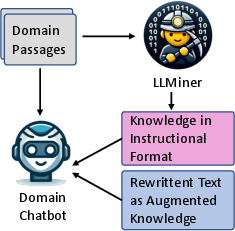
Figure 1: Illustration of the LLMiner approach for enhancing LLMs as domain-specific chatbots.
Methodology
Preparing Seed Data with GPT-4
The methodology begins with curating a corpus of 600 instances where each passage is assessed for significance (Figure 2). This involves prompting GPT-4 to analyze the importance of selected sentences, generate questions based on these analyses, and articulate answers for the proposed questions. This process substitutes human intervention using GPT-4, aiding the development of a behavior cloning model for knowledge mining.
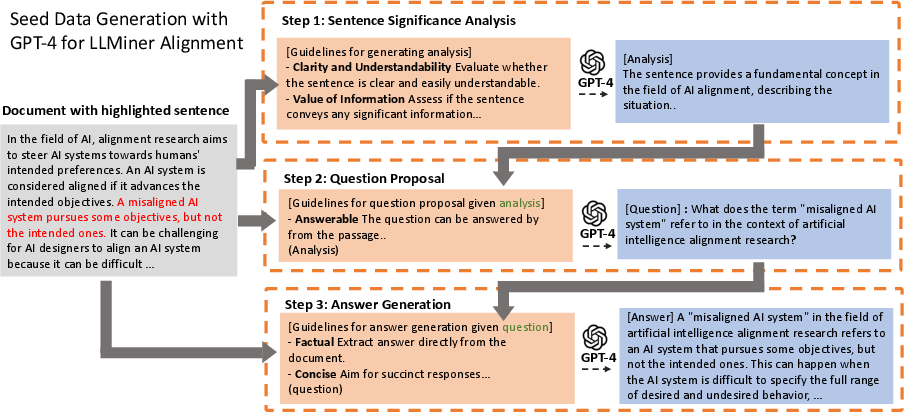
Figure 2: LLMiner Training Data Collection: Given a passage, GPT-4 analyzes, questions, and answers about the emphasized sentence, generating seed data for behavior cloning.
Training for Model Alignment
The training of LLMiner is structured to align with the task by fine-tuning LLaMa-7b using simplified prompts to simulate GPT-4’s generative capabilities. This alignment is critical for mitigating the computational overheads and detailed prompt requirements inherent in large-scale GPT-4 inferencing.
Inference with LLMiner
The inference stage involves processing each passage sentence-by-sentence, using LLMiner to produce knowledge in instructional formats which enrich the original text corpus (Figure 3). These instructional formats enhance the chatbot’s ability to retrieve and apply domain-specific knowledge effectively.
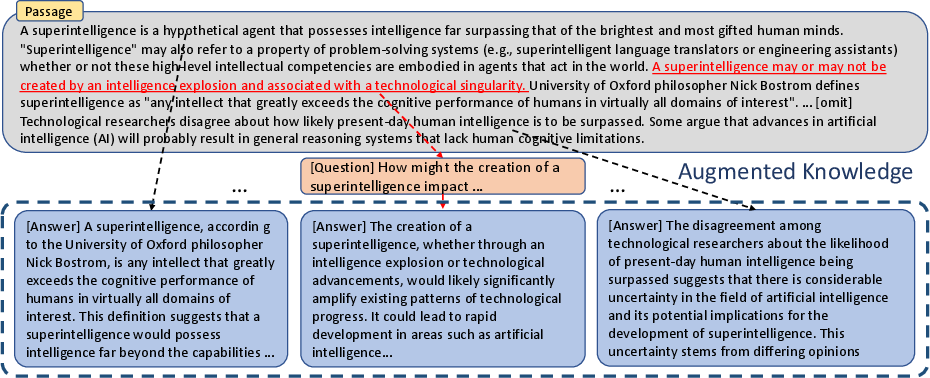
Figure 3: Knowledge Augmentation of the Original Passage: Minded answers enrich the understanding of the original passage.
Domain-Specific Corpus Collection
A robust methodology for domain corpus collection is outlined, employing GPT-4 to propose related Wikipedia titles, followed by relevance filtering using additional GPT-4 prompts. The culmination of this process is a well-curated domain-specific corpus, supplemented with annotator-generated queries and reference answers independent of the corpus (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Example illustrating the utility of chain-of-thought (COT) analysis in extracting comprehensive knowledge from a passage.
Chatbot Training Methodology
The training incorporates diverse data types to bolster the chatbot's domain expertise:
- Raw domain-specific texts
- Conversation datasets from OpenAssistant
- QA pairs mined by LLMiner
- Text augmentations providing diverse perspectives on domain knowledge, enhancing the comprehension quality (Figure 5).
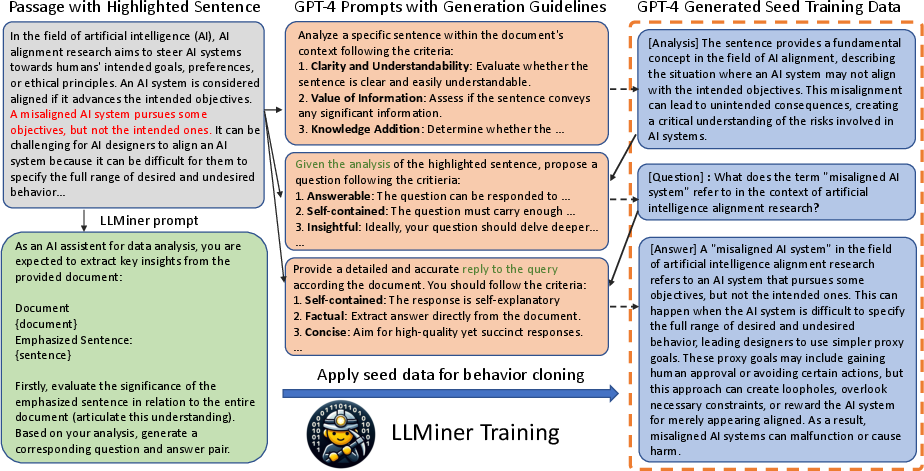
Figure 5: LLMiner Training Pipeline: Fine-tuning of a smaller LLM to mimic GPT-4's responses efficiently.
Experimental Results
Empirical validations demonstrate LLMiner's superior performance in mining QA pairs compared to models lacking chain-of-thought processes. The chatbot trained using LLMiner's augmentations offers marked improvement in addressing domain-specific queries. The incorporation of mined QA data and textual augmentations provides significant advantages over conventional baseline models (Table displayed).
Conclusion
This research outlines an effective method for transforming LLMs into domain-specific knowledge miners, demonstrating substantial enhancements in understanding and responding to complex queries. LLMiner's self-enhancement capabilities showcase the progression toward autonomous knowledge integration, paving the way for continuous adaptation and growth in dynamic AI landscapes.
Future Work
Further exploration into optimizing the ratio of mixed training data and expanding LLMiner's applications to various industrial domains holds promise for advancing domain specialization in AI conversational systems.






