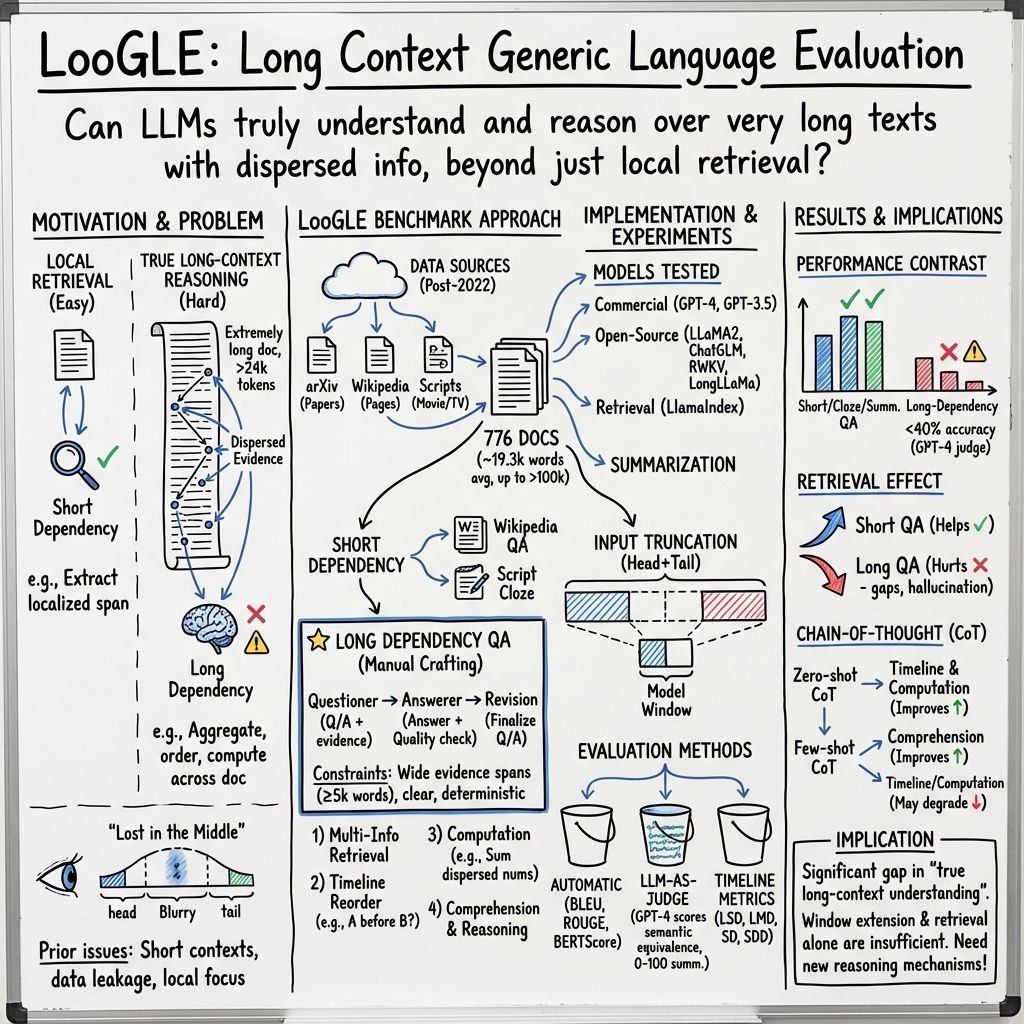
- The paper introduces LooGLE as a benchmark that rigorously evaluates LLM capabilities on texts with over 24,000 tokens focusing on long dependency tasks.
- Methodology includes curated long dependency questions and comparative evaluations of eight LLMs, revealing commercial models outperform open-sourced ones on long-context tasks.
- Findings reveal that LLMs excel at short tasks but struggle with long dependencies, indicating a need for improved evaluation techniques in extended context comprehension.
LooGLE: Can Long-Context LLMs Understand Long Contexts?
LLMs exhibit remarkable proficiency across various language tasks, albeit usually within a constrained context window size. This limitation has catalyzed research endeavors to bolster LLMs’ capabilities in understanding extended contexts, prompting the creation of long-sequence benchmarks that address prior datasets' insufficiencies. Traditional datasets fall short with their relatively brief context lengths compared to the potential of modern LLMs, and often encounter data leakage issues due to outdated documents, focusing predominantly on short dependency tasks rather than demanding long dependency tasks.
Introduction to LooGLE
The paper introduces "LooGLE," a Long Context Generic Language Evaluation benchmark crafted to assess LLMs' long context understanding. It features documents postdating 2022 with over 24,000 tokens and incorporates 6,000+ questions spanning diverse domains. Human annotators meticulously ensured high-quality question-answer pairs, cross-validating over 1,100 long dependency questions. Evaluations on eight advanced LLMs on LooGLE unveiled critical observations: commercial models consistently surpassed open-sourced counterparts, LLMs managed short tasks adeptly yet faltered at intricate long dependency tasks, and in-context learning imparted only marginal improvements. Notably, retrieval-based techniques substantially benefited short question-answering, while modifications in transformer architectures or positional encoding minimally affected comprehension of extensive contexts.
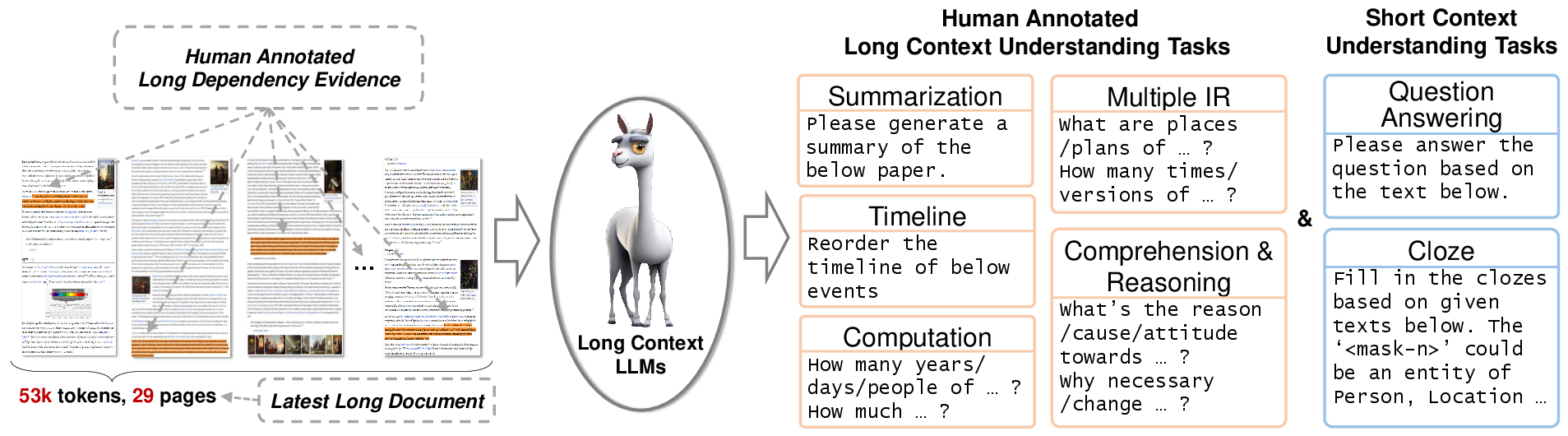
Figure 1: The LooGLE benchmark for long context understanding.
Limitations of Current Datasets
The expansion of traditional benchmarks often includes short texts and outdated content, potentially skewing LLM evaluations due to pre-training data overlap. Moreover, current benchmarks predominantly comprise short dependency tasks, insufficient to rigorously assess LLMs' capabilities in piecing together evidence from various document sections for comprehensive answers—denoting the essence of long dependency tasks.
Features of LooGLE Benchmark
LooGLE addresses these deficits with ultra-long realistic documents averaging 19,367 words, eliminating distribution biases. It encompasses cross-domain generic data from sources like arXiv, Wikipedia, and entertainment scripts, reinforcing its comprehensive nature. The benchmark includes manually curated long dependency tasks alongside seven major evaluation tasks specifically engineered to test both short and long dependency comprehension.

Figure 2: Long dependency QA tasks.
Evaluation of Long-Context Understanding
The benchmark facilitated a comparative analysis of eight LLMs renowned for extending context comprehension. The findings suggested superior performance for models with larger context windows, though a significant dip was noted in long dependency tasks, underscoring a pressing need for enhanced long-context understanding efficacy among LLMs. The performances were evaluated using various metrics, including GPT-4 as a judge to mitigate inherent semantic expression and format correlational deficiencies found in automatic evaluation techniques.
Current State and Future Prospects
Commercial LLMs like GPT-4 displayed superior overall proficiency across both short and long context evaluations, while open-sourced models lagged behind, substantiating the gap in development capabilities. Retrieval mechanisms were specifically less effective in tasks demanding an understanding of long dependency due to their reliance on contextual learning and reasoning beyond surface-level retrieval.

Figure 3: An overview performance of LLMs on \dataset for long context understanding.
Conclusion
This research presented the LooGLE benchmark, pointing towards the pronounced challenges faced by LLMs in tackling long dependency comprehension. While current models exhibit adeptness in handling short context tasks, significant opportunities exist to enhance their adeptness in long dependency comprehension—facilitating real-world application scenarios involving extensive text. The insights gleaned from this paper provide a vital reference for future research focused on true long context understanding, leveraging LooGLE as a cornerstone benchmark for advancing LLM capabilities in this domain.