- The paper introduces an innovative framework that improves RIR estimation via a novel integration of RQ-VAE and axial transformers.
- It employs discrete representation learning and autoregressive token generation to synthesize perceptually accurate RIRs from reference audio.
- Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in Log Spectral Distance and subjective similarity scores compared to conventional methods.
Yet Another Generative Model For Room Impulse Response Estimation
Introduction
The task of estimating Room Impulse Responses (RIRs) is critical for a wide range of acoustic applications, including speech recognition and speech enhancement. Conventional estimation methods employ an encoder and a generator to analyze reference audio and synthesize RIRs. This paper introduces an innovative framework that leverages an alternative generator architecture to enhance RIR estimation performance.
Proposed Framework
Discrete Representation Learning with RQ-VAE
The foundation of the proposed method involves training a Residual-Quantized Variational Autoencoder (RQ-VAE) to encode RIRs into a discrete latent token space. This autoencoder converts a single-channel RIR into a time-frequency representation with Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT), embedding features into a latent space that uses residual quantization. The quantized indices facilitate an efficient generative model by encapsulating complex RIR characteristics into discrete elements.
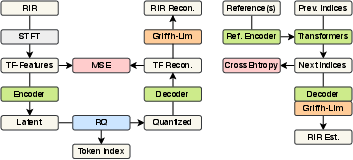
Figure 1: The proposed method (left: codebook learning with RQ-VAE, right: RIR estimation via conditional token generation).
To synthesize RIRs, the paper employs axial transformers for autoregressive token generation across three dimensions: frequency, time, and quantization depth. Various decoding strategies are proposed to manage sequence length and computational complexity. The generation of token indices is conditioned on reference audio features, transforming RIR estimation into a conditional task suitable for a range of acoustic scenarios, including blind estimation and acoustic matching.

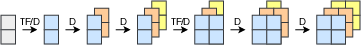
Figure 2: Token generation strategies with axial transformers.
Experimental Results
Evaluation Metrics
The paper evaluates its model using both objective and subjective metrics, such as Log Spectral Distance (LSD), Energy Decay Relief (EDR), and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) for key acoustic parameters like reverberation time (T30) and Direct-to-Reverberant Ratio (DRR).
The proposed framework demonstrates superior performance across various metrics compared to existing methods. Specifically, the use of RQ-VAE and autoregressive transformers results in significant improvements in LSD and subjective similarity scores in blind RIR estimation. The transfer of RIR characteristics is effectively achieved, indicating the model's ability to generate perceptually accurate RIRs that align closely with real-world reverberations.
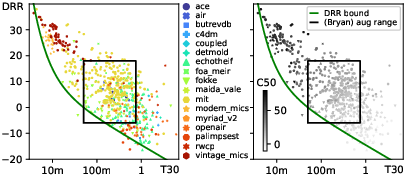
Figure 3: Reverberation parameter statistics of the IR datasets.
Conclusion
The development of this generative model for RIR estimation marks a significant advancement in acoustic signal processing. The paper's innovative use of RQ-VAE for discrete representation learning combined with axial transformers for efficient token generation provides a robust framework for diverse RIR estimation tasks, including standard blind estimation and acoustic matching. Future research avenues could explore the refinement of autoregressive modeling strategies and extend the framework for broader acoustic applications such as acoustic scene transfer.
This research underscores the potential for increased model expressiveness and computational efficiency in RIR estimation, paving the way for further enhancements in the field of acoustic modeling.






