- The paper demonstrates a novel IQAtesting framework that transforms GUI testing into a Q&A task using LLMs.
- It employs dual-loop processes for GUI context extraction and functionality-aware memory prompting to guide testing.
- The approach outperforms baselines by achieving 75% activity coverage, 66% code coverage, and uncovering 53 unknown bugs.
Overview of the Paper
The paper "Make LLM a Testing Expert: Bringing Human-like Interaction to Mobile GUI Testing via Functionality-aware Decisions" (2310.15780) addresses the critical need for efficient automated GUI testing of mobile applications. It introduces a novel framework, termed {IQAtesting}, that leverages LLMs to perform automated testing by iteratively interacting with mobile applications. This approach formulates the GUI testing problem as a question-answer task, exploiting LLMs to generate human-like interactions and guide the exploration process.
Methodology
Motivation and Challenges
Automated GUI testing is indispensable for ensuring app quality, especially with the proliferation of mobile applications. Traditional approaches, including learning-based techniques, suffer from low coverage and inadequate generalization, largely due to their reliance on vast amounts of training data and limited semantic understanding of app functionalities. By harnessing the capabilities of LLMs, which have demonstrated success in understanding and generating natural language, this paper proposes to bridge these gaps by transforming GUI testing into a conversational task akin to a Q&A session.
Proposed Framework: {IQAtesting}
The {IQAtesting} framework consists of a dual-loop process involving both GUI context extraction and functionality-aware memory prompting. The GUI context extraction identifies macro-level app information, page-specific GUI details, and micro-level widget information, all derived from app manifest files and view hierarchy data. Utilizing linguistic patterns, these components are encoded into prompts for LLM input.
A significant innovation in the framework is the functionality-aware memory mechanism. This mechanism records detailed interactive testing information, stores the functionality-level progress, and formulates prompts that guide the LLM in reasoning about long-term goals and operations. This approach allows the LLM to produce actionable steps that comprehensively test app functionalities.

Figure 1: Overview of {IQAtesting} process illustrating the component extraction and prompting mechanisms.
Results and Evaluation
The effectiveness of {IQAtesting} is rigorously evaluated on a dataset of 93 Android applications across various categories. It significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving 75% activity coverage and 66% code coverage, marking a 32% improvement over the best baseline. Importantly, the framework detects 31% more bugs at a faster rate, including 53 previously unknown bugs in Google Play apps, with 35 of these confirmed and fixed.
Numerical Results
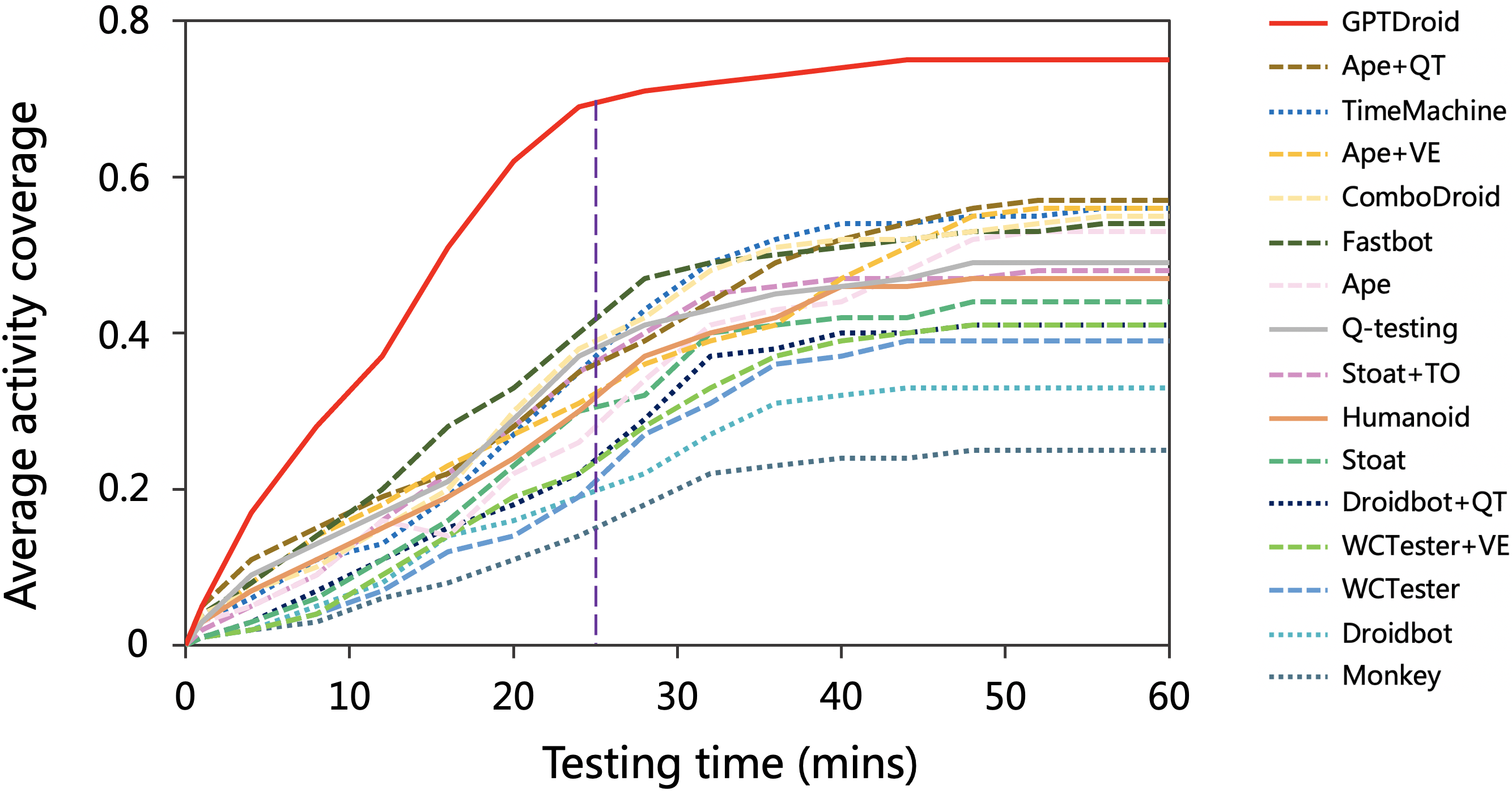
Figure 2: Activity coverage with varying time demonstrating superior performance of {IQAtesting}.

Figure 3: Bug detection with varying time showcasing faster detection rates compared to baselines.
Ablation Studies
The paper also presents insightful ablation studies that elucidate the contributions of different components within the framework. The GUI context extraction and functionality-aware memory mechanisms are critical for achieving high coverage and effective bug detection, highlighting their indispensable role in the framework's overall performance.
Implications and Future Directions
The results demonstrate substantial practical implications for software engineering, particularly in automated testing and quality assurance. The novel use of LLMs to conduct functionality-aware reasoning provides a promising direction for further research in human-like interaction modeling for software testing tasks.
Future developments could explore more advanced prompt engineering techniques and the integration of open-source LLM fine-tuning to enhance performance in this and related domains. The adaptability of {IQAtesting} to continuously evolving app functions and its ability to uncover latent bugs establish it as a pioneering approach in automated GUI testing.
Conclusion
The paper succeeds in establishing a comprehensive framework that revolutionizes mobile GUI testing by applying LLMs as interactive testers, thereby overcoming limitations of coverage and generalization found in traditional methods. The research opens new avenues for advancing automated software testing, offering significant gains in efficiency and reliability in app quality assurance.
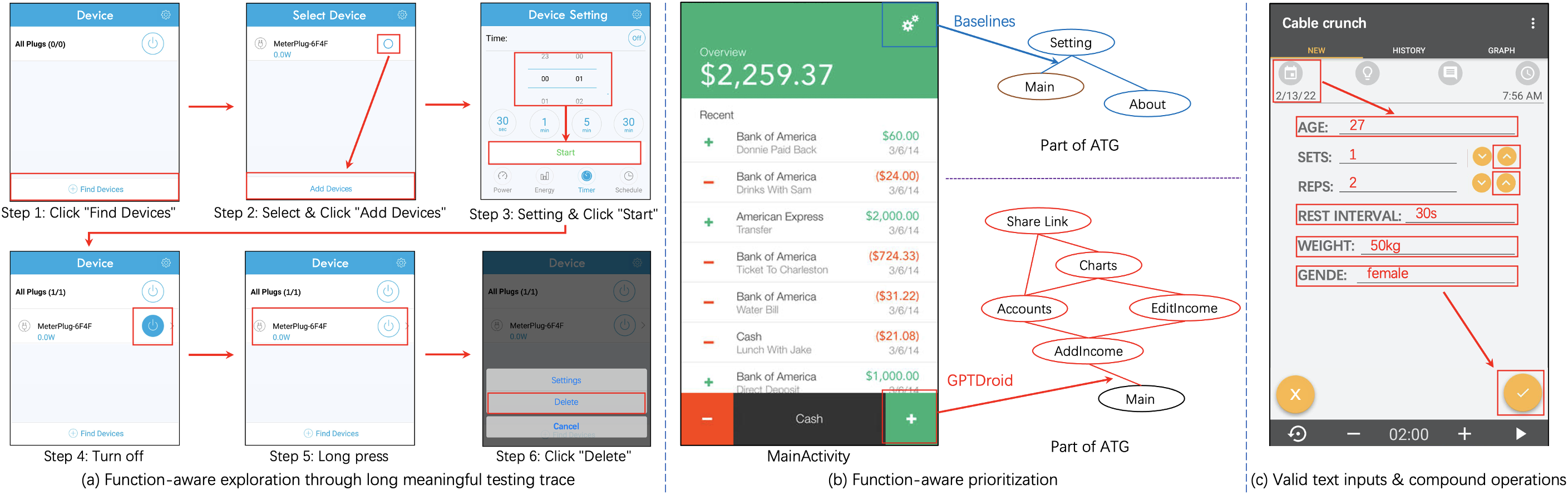
Figure 4: Examples of insights gained from experiments, providing clarity on the testing advantages of {IQAtesting}.



