EIPE-text: Evaluation-Guided Iterative Plan Extraction for Long-Form Narrative Text Generation (2310.08185v1)
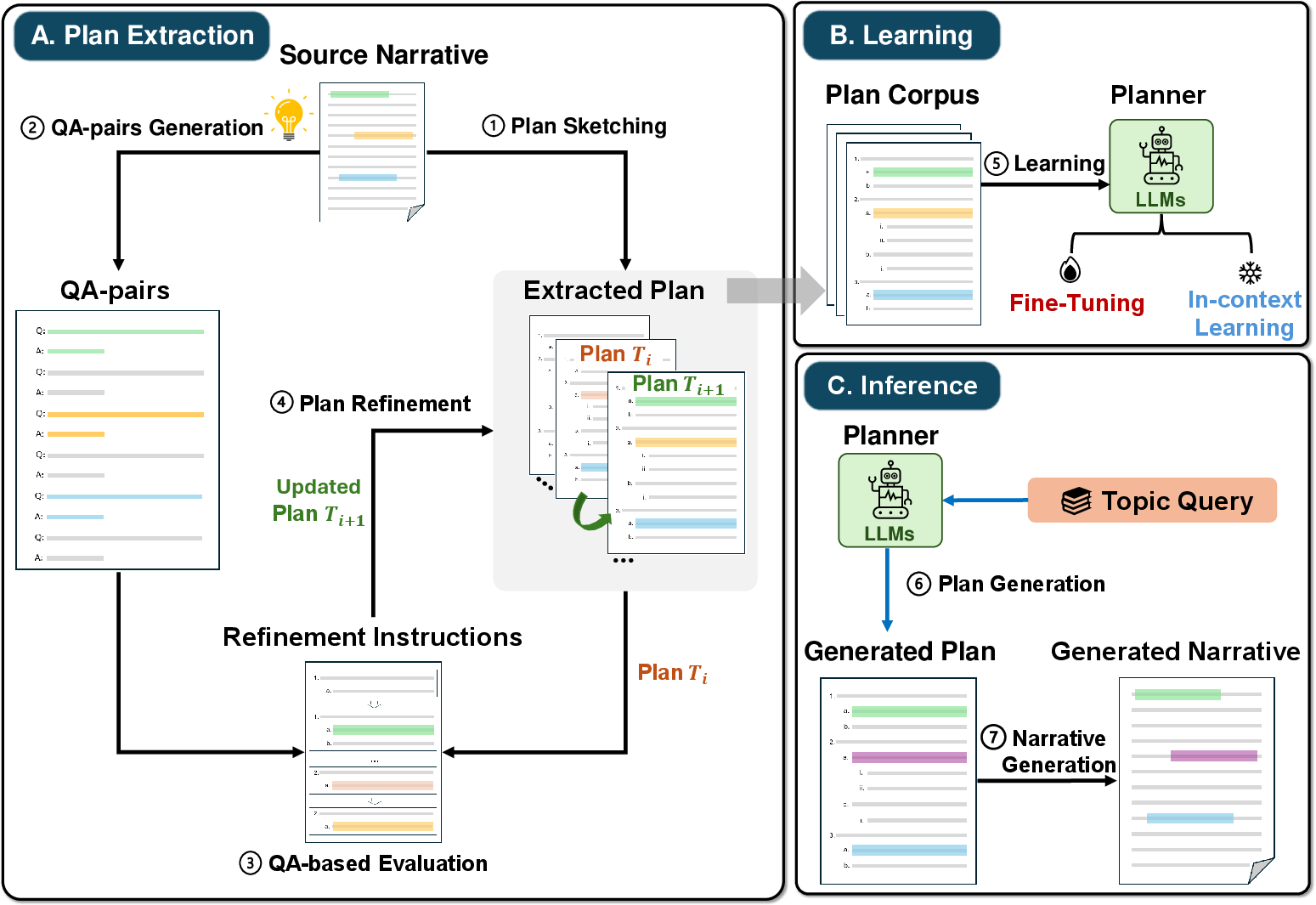
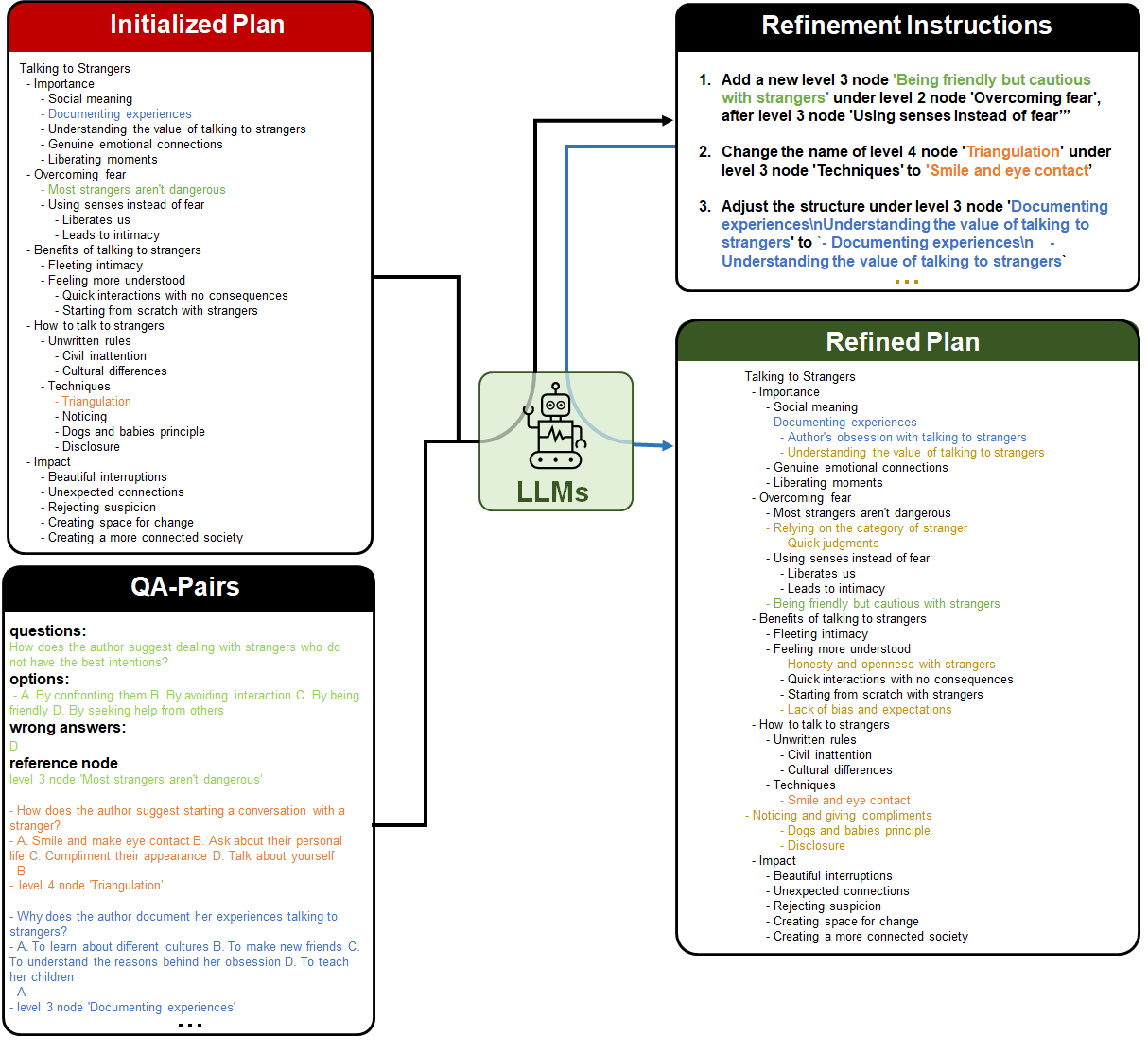
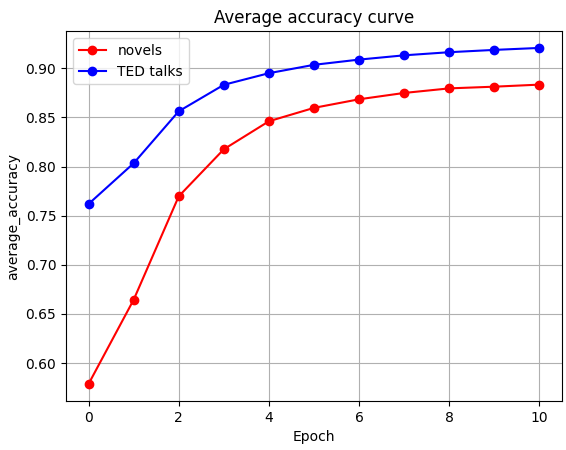
Abstract: Plan-and-Write is a common hierarchical approach in long-form narrative text generation, which first creates a plan to guide the narrative writing. Following this approach, several studies rely on simply prompting LLMs for planning, which often yields suboptimal results. In this paper, we propose a new framework called Evaluation-guided Iterative Plan Extraction for long-form narrative text generation (EIPE-text), which extracts plans from the corpus of narratives and utilizes the extracted plans to construct a better planner. EIPE-text has three stages: plan extraction, learning, and inference. In the plan extraction stage, it iteratively extracts and improves plans from the narrative corpus and constructs a plan corpus. We propose a question answer (QA) based evaluation mechanism to automatically evaluate the plans and generate detailed plan refinement instructions to guide the iterative improvement. In the learning stage, we build a better planner by fine-tuning with the plan corpus or in-context learning with examples in the plan corpus. Finally, we leverage a hierarchical approach to generate long-form narratives. We evaluate the effectiveness of EIPE-text in the domains of novels and storytelling. Both GPT-4-based evaluations and human evaluations demonstrate that our method can generate more coherent and relevant long-form narratives. Our code will be released in the future.
- Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4.
- A survey on evaluation of large language models.
- Talebrush: sketching stories with generative pretrained language models. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pages 1–19.
- Hierarchical neural story generation. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 889–898, Melbourne, Australia. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Strategies for structuring story generation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 2650–2660, Florence, Italy. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Content planning for neural story generation with aristotelian rescoring. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 4319–4338, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Long text generation by modeling sentence-level and discourse-level coherence. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 6379–6393, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. In International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Haozhe Ji and Minlie Huang. 2021. DiscoDVT: Generating long text with discourse-aware discrete variational transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 4208–4224, Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Coauthor: Designing a human-ai collaborative writing dataset for exploring language model capabilities. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pages 1–19.
- Gpteval: Nlg evaluation using gpt-4 with better human alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.16634.
- Co-writing screenplays and theatre scripts with language models: Evaluation by industry professionals. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pages 1–34.
- Generating high-quality and informative conversation responses with sequence-to-sequence models. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 2210–2219, Copenhagen, Denmark. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models.
- DOC: Improving long story coherence with detailed outline control. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 3378–3465, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Re3: Generating longer stories with recursive reprompting and revision. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 4393–4479, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Plan-and-write: Towards better automatic storytelling. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, volume 33, pages 7378–7385.
- Wordcraft: story writing with large language models. In 27th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, pages 841–852.
- Recurrentgpt: Interactive generation of (arbitrarily) long text.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.