- The paper reveals that generative AI can boost personalized educational interactions through tailored feedback while risking passive information consumption.
- It employs analysis of LLMs to illustrate how personalized prompts and metacognitive strategies can enhance active learning.
- Findings suggest integrating AI literacy and critical thinking workshops to counteract over-reliance on automated responses in education.
Generative AI in the Classroom: Can Students Remain Active Learners?
The incorporation of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI), particularly LLMs, into educational settings presents both pronounced opportunities and palpable risks. This paper addresses the dual role of GAI as both a catalyst for enhanced learning experiences and a potential obstacle to active learning. The analysis recognizes the potential of LLMs in education while highlighting the pivotal role of active learning strategies and metacognitive skills.
Opportunities for Active Learning
Enhancing Pedagogical Interactions
GAI offers a significant potential to transform educational environments by facilitating more personalized and adaptive learning experiences. LLMs can be employed to design pedagogical interactions that stimulate deeper cognitive processing and foster student engagement. Prior work demonstrates that LLMs, such as GPT-3, enhance students' curiosity and facilitate the formulation of more intricate questions during comprehension tasks by providing prompts to clarify uncertainties. Furthermore, LLMs can introduce dialogic opportunities and authentic problem scenarios that are crucial for nurturing critical thinking capabilities. Their interactive nature allows for educational activities that position students as collaborators or educators themselves, fostering essential metacognitive skills necessary for evaluating and monitoring learning processes.
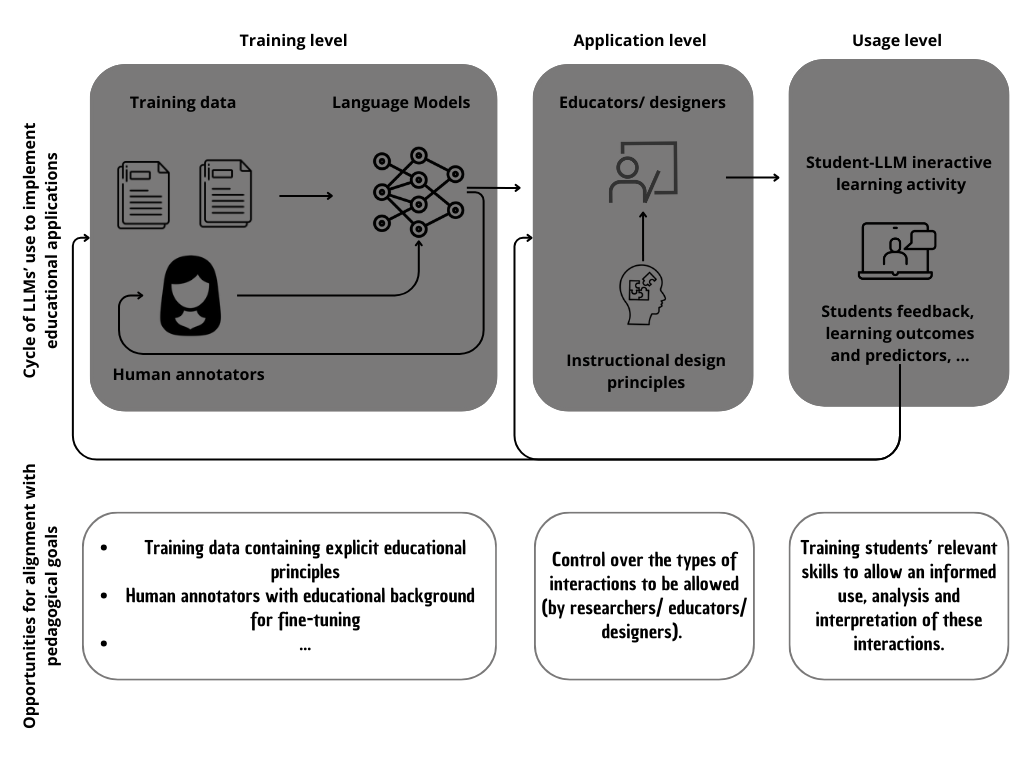
Figure 1: Life-cycle of LLMs usage in educational applications and opportunities for alignment with pedagogical goals.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Another strength of LLMs lies in providing tailored pedagogical guidance that includes feedback on cognitive performance and recommendations for metacognitive strategies. This personalized feedback can help students develop accurate mental models and optimize their learning strategies to achieve educational goals effectively. The successful integration of LLMs requires targeted design interventions focused on enhancing the pedagogical transparency of these models to maximize their learning potential.
Challenges to Active Learning
While GAI facilitates access to information, it also poses the risk of students becoming passive recipients of knowledge rather than active seekers. The convenience of instant information access through LLMs might diminish students' intrinsic motivation to engage in exploratory behaviors, such as formulating questions or engaging in active inquiry. This reliance on LLMs for quick information retrieval could undermine students' ability to associate cognitive success with effortful learning strategies.
Impediments to Critical Thinking
A critical challenge arises from the fact that LLMs may not adequately convey uncertainty, potentially leading students to misinterpret the model's authority and knowledge. Such interactions might foster an overestimation of students’ comprehension and the capabilities of LLMs, thereby stunting the development of critical analysis skills. Overconfidence in the model’s output and a lack of critical reflection on the veracity of information can lead to the adoption of misguided information, which is difficult to correct.
To counteract these challenges, it is imperative to promote GAI literacy and enhance students' metacognitive skills. This involves educating students on the operational mechanisms of LLMs, including their strengths and weaknesses, highlighting common misconceptions, and demonstrating the models' limitations in terms of reasoning or contextual understanding. Moreover, equipping students with effective prompting strategies can foster an environment conducive to active learning. Educators and designers should also be trained to implement GAI in ways that promote pedagogically sound interactions that encourage student inquiry.
Encouraging Critical Engagement
To foster critical engagement and control over their learning processes, students need opportunities to evaluate their understanding actively and adjust their cognitive approaches. This necessitates the development of critical-thinking skills that rely heavily on metacognitive awareness. Training interventions focusing on metacognitive skills, such as monitoring and self-regulation, are crucial for helping students navigate and utilize GAI effectively.
Conclusion
Generative AI holds immense promise for revolutionizing educational landscapes by addressing challenges such as personalization and resource constraints. However, this requires a concerted effort from educators, AI specialists, and learners to ensure that GAI supports rather than impedes active learning. By advancing metacognitive training and promoting GAI literacy, students can be empowered to harness the full potential of these technologies while maintaining control over their learning processes and outcomes.


