nnSAM: Plug-and-play Segment Anything Model Improves nnUNet Performance (2309.16967v3)
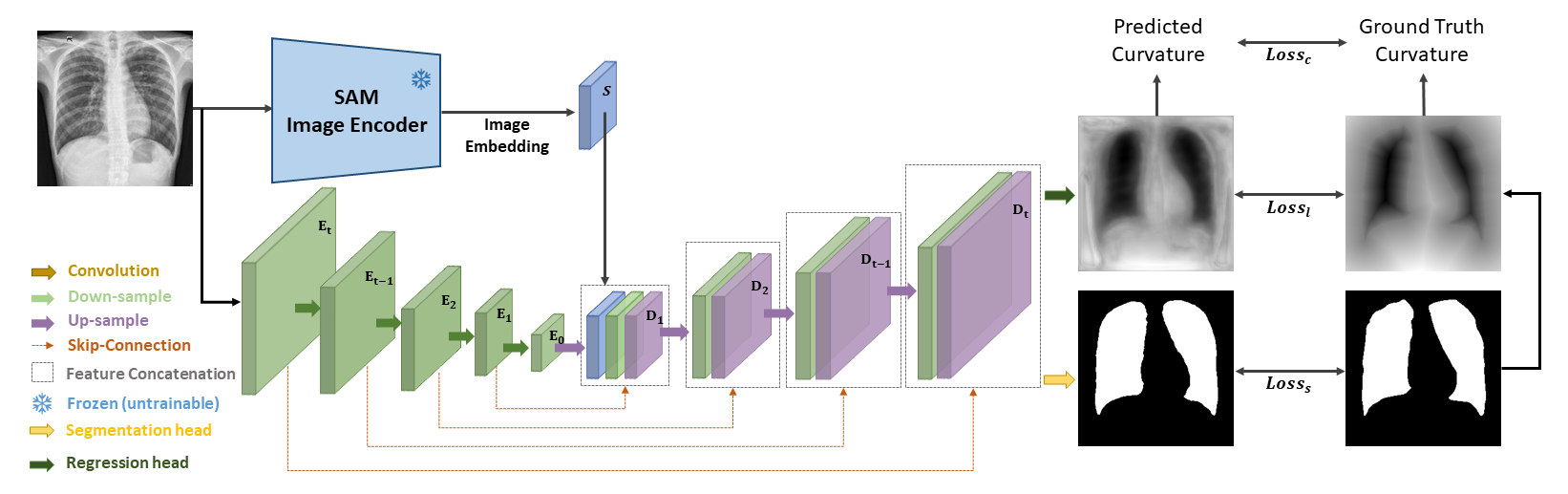
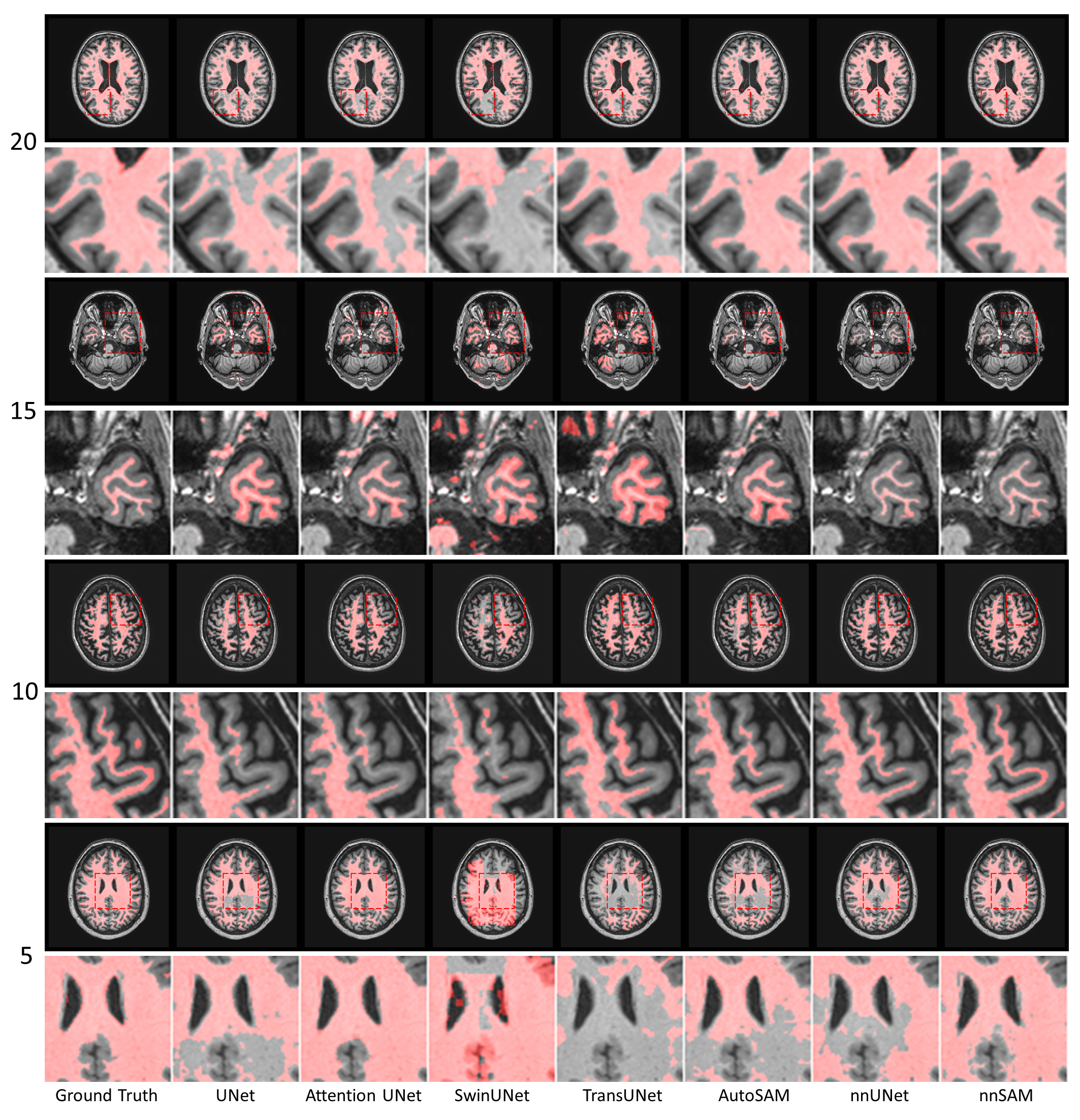
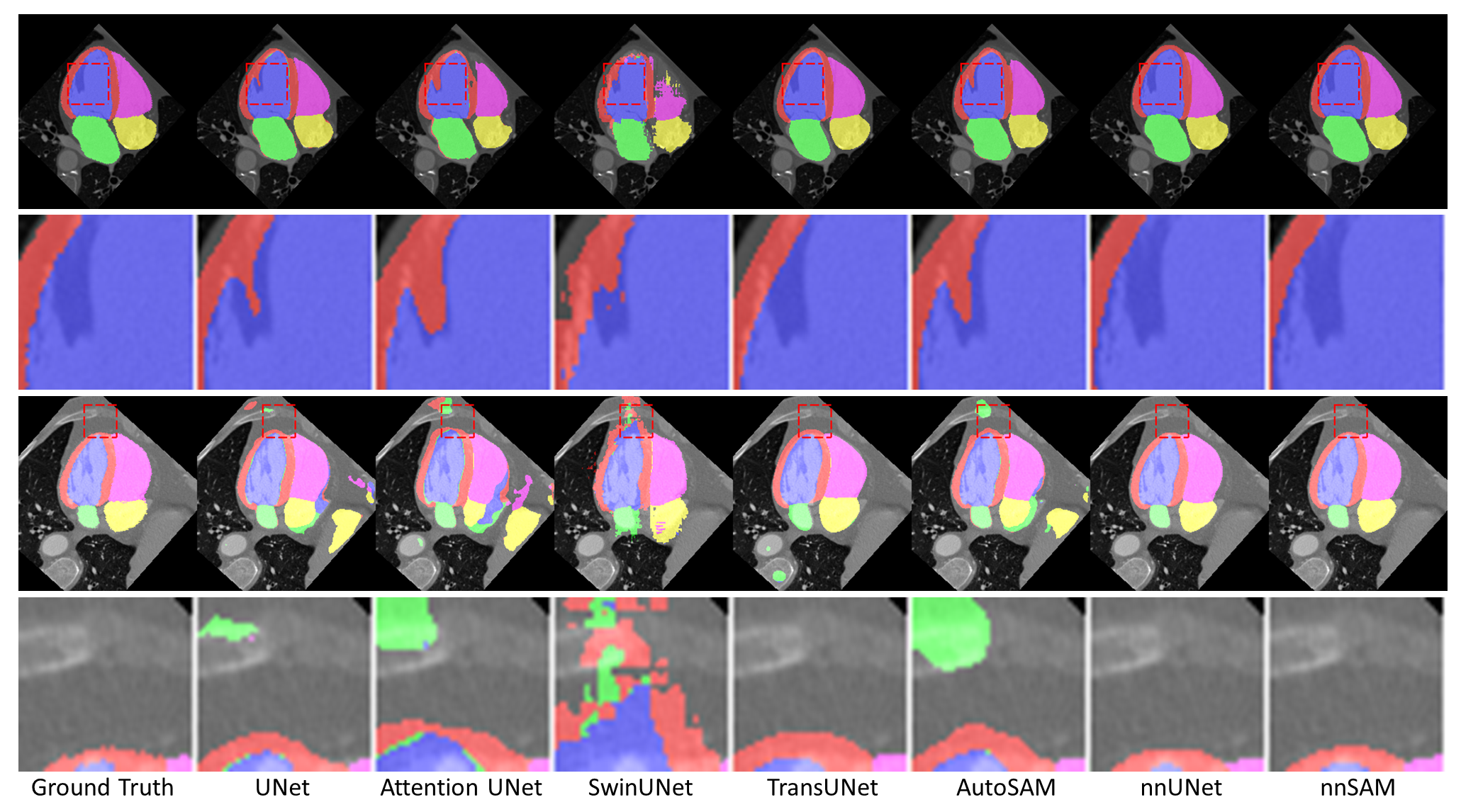
Abstract: Automatic segmentation of medical images is crucial in modern clinical workflows. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) has emerged as a versatile tool for image segmentation without specific domain training, but it requires human prompts and may have limitations in specific domains. Traditional models like nnUNet perform automatic segmentation during inference and are effective in specific domains but need extensive domain-specific training. To combine the strengths of foundational and domain-specific models, we propose nnSAM, integrating SAM's robust feature extraction with nnUNet's automatic configuration to enhance segmentation accuracy on small datasets. Our nnSAM model optimizes two main approaches: leveraging SAM's feature extraction and nnUNet's domain-specific adaptation, and incorporating a boundary shape supervision loss function based on level set functions and curvature calculations to learn anatomical shape priors from limited data. We evaluated nnSAM on four segmentation tasks: brain white matter, liver, lung, and heart segmentation. Our method outperformed others, achieving the highest DICE score of 82.77% and the lowest ASD of 1.14 mm in brain white matter segmentation with 20 training samples, compared to nnUNet's DICE score of 79.25% and ASD of 1.36 mm. A sample size study highlighted nnSAM's advantage with fewer training samples. Our results demonstrate significant improvements in segmentation performance with nnSAM, showcasing its potential for small-sample learning in medical image segmentation.
- A review of deep-learning-based medical image segmentation methods. Sustainability, 13(3):1224, 2021.
- Deep learning in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Medical physics, 46(1):e1–e36, 2019.
- U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1505.04597, 2015.
- Gt u-net: A u-net like group transformer network for tooth root segmentation. In Machine Learning in Medical Imaging: 12th International Workshop, MLMI 2021, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2021, Strasbourg, France, September 27, 2021, Proceedings 12, pages 386–395. Springer, 2021.
- Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306, 2021.
- Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 39(6):1856–1867, 2019.
- Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.05537, 2021.
- nnu-net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nature Methods, 17(2):203–211, 2020.
- Segment anything. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02643, 2023.
- Faster segment anything: Towards lightweight sam for mobile applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.14289, 2023.
- Segment anything model for medical image analysis: an experimental study. Medical Image Analysis, 89:102918, 2023.
- Segment anything in medical images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.12306, 2023.
- An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929, 2020.
- Tinyvit: Fast pretraining distillation for small vision transformers. In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 68–85. Springer, 2022.
- Evaluation of algorithms for multi-modality whole heart segmentation: an open-access grand challenge. Medical image analysis, 58:101537, 2019.
- Cf distance: a new domain discrepancy metric and application to explicit domain adaptation for cross-modality cardiac image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 39(12):4274–4285, 2020.
- Autosam: Adapting sam to medical images by overloading the prompt encoder. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06370, 2023.
- Agmb-transformer: Anatomy-guided multi-branch transformer network for automated evaluation of root canal therapy. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 26(4):1684–1695, 2021.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.