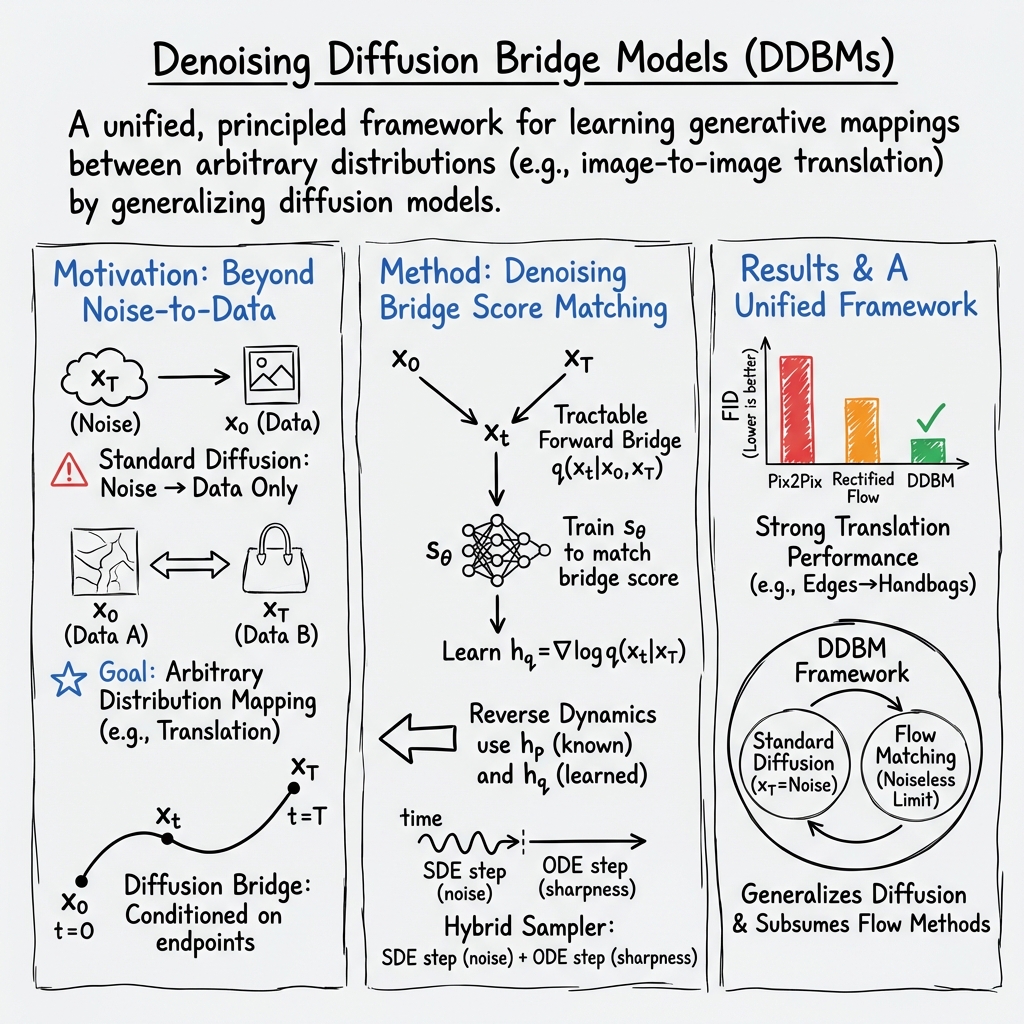
Denoising Diffusion Bridge Models
Abstract: Diffusion models are powerful generative models that map noise to data using stochastic processes. However, for many applications such as image editing, the model input comes from a distribution that is not random noise. As such, diffusion models must rely on cumbersome methods like guidance or projected sampling to incorporate this information in the generative process. In our work, we propose Denoising Diffusion Bridge Models (DDBMs), a natural alternative to this paradigm based on diffusion bridges, a family of processes that interpolate between two paired distributions given as endpoints. Our method learns the score of the diffusion bridge from data and maps from one endpoint distribution to the other by solving a (stochastic) differential equation based on the learned score. Our method naturally unifies several classes of generative models, such as score-based diffusion models and OT-Flow-Matching, allowing us to adapt existing design and architectural choices to our more general problem. Empirically, we apply DDBMs to challenging image datasets in both pixel and latent space. On standard image translation problems, DDBMs achieve significant improvement over baseline methods, and, when we reduce the problem to image generation by setting the source distribution to random noise, DDBMs achieve comparable FID scores to state-of-the-art methods despite being built for a more general task.
- Stochastic interpolants: A unifying framework for flows and diffusions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08797, 2023.
- Building normalizing flows with stochastic interpolants. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023. URL https://openreview.net/forum?id=li7qeBbCR1t.
- A note on the inception score. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.01973, 2018.
- Diffusion schrödinger bridge with applications to score-based generative modeling. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34:17695–17709, 2021.
- Inversion by direct iteration: An alternative to denoising diffusion for image restoration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.11435, 2023.
- Simulation of conditioned diffusion and application to parameter estimation. Stochastic Processes and their Applications, 116(11):1660–1675, 2006.
- Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34:8780–8794, 2021.
- Joseph L Doob and JI Doob. Classical potential theory and its probabilistic counterpart, volume 262. Springer, 1984.
- Generative adversarial nets. In NIPS, 2014.
- Simulating diffusion bridges with score matching. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.07243, 2021.
- Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30, 2017.
- Classifier-free diffusion guidance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.12598, 2022.
- Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33:6840–6851, 2020.
- Imagen video: High definition video generation with diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.02303, 2022.
- simple diffusion: End-to-end diffusion for high resolution images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.11093, 2023.
- Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 1125–1134, 2017.
- A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 4401–4410, 2019.
- Elucidating the design space of diffusion-based generative models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.00364, 2022.
- Variational diffusion models. Advances in neural information processing systems, 34:21696–21707, 2021.
- Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. 2009.
- Bbdm: Image-to-image translation with brownian bridge diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1952–1961, 2023.
- Flow matching for generative modeling. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023. URL https://openreview.net/forum?id=PqvMRDCJT9t.
- I22{}^{2}start_FLOATSUPERSCRIPT 2 end_FLOATSUPERSCRIPTsb: Image-to-image schrödinger bridge. arXiv, 2023.
- Flow straight and fast: Learning to generate and transfer data with rectified flow. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.03003, 2022a.
- Let us build bridges: Understanding and extending diffusion generative models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.14699, 2022b.
- Dpm-solver: A fast ode solver for diffusion probabilistic model sampling in around 10 steps. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.00927, 2022a.
- Dpm-solver++: Fast solver for guided sampling of diffusion probabilistic models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.01095, 2022b.
- SDEdit: Guided image synthesis and editing with stochastic differential equations. In International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022.
- Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 8162–8171. PMLR, 2021.
- Scalable diffusion models with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 4195–4205, 2023.
- Stefano Peluchetti. Non-denoising forward-time diffusions.
- Stefano Peluchetti. Diffusion bridge mixture transports, schr\\\backslash\" odinger bridge problems and generative modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.00917, 2023.
- Multisample flow matching: Straightening flows with minibatch couplings. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14772, 2023.
- Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with clip latents. ArXiv, abs/2204.06125, 2022.
- Diffusions, Markov processes and martingales: Volume 2, Itô calculus, volume 2. Cambridge university press, 2000.
- High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 10684–10695, 2022.
- Palette: Image-to-image diffusion models. ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference Proceedings, 2021.
- Progressive distillation for fast sampling of diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.00512, 2022.
- Applied stochastic differential equations, volume 10. Cambridge University Press, 2019.
- Guided proposals for simulating multi-dimensional diffusion bridges. 2017.
- Diffusion schr\\\backslash\" odinger bridge matching. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.16852, 2023.
- Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 2256–2265. PMLR, 2015.
- Aligned diffusion schr\\\backslash\" odinger bridges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11419, 2023.
- Denoising diffusion implicit models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.02502, 2020a.
- Generative modeling by estimating gradients of the data distribution. Advances in neural information processing systems, 32, 2019.
- Score-based generative modeling through stochastic differential equations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.13456, 2020b.
- Dual diffusion implicit bridges for image-to-image translation. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022.
- Inequivalence of nonequilibrium path ensembles: the example of stochastic bridges. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 2015(12):P12008, 2015.
- Simulation-free schr\\\backslash\" odinger bridges via score and flow matching. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.03672, 2023a.
- Improving and generalizing flow-based generative models with minibatch optimal transport. In ICML Workshop on New Frontiers in Learning, Control, and Dynamical Systems, 2023b.
- DIODE: A Dense Indoor and Outdoor DEpth Dataset. CoRR, abs/1908.00463, 2019. URL http://arxiv.org/abs/1908.00463.
- Cédric Villani. Optimal transport: Old and new. 2008.
- Fast sampling of diffusion models with exponential integrator. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.13902, 2022.
- The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In CVPR, 2018.
- Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pages 2242–2251, 2017.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Glossary
- Brownian Bridge: A stochastic process conditioned to start and end at specified points, often used as a baseline bridge between endpoints. Example: "constructs a Brownian Bridge for direct iteration"
- Classifier guidance: A technique that modifies the generative dynamics using gradients from a classifier to steer samples toward desired outputs. Example: "Due to the probability flow ODE's resemblance with classifier-guidance"
- Denoising Diffusion Bridge Models (DDBMs): The proposed framework that learns to map between two endpoint distributions by reversing a diffusion bridge using learned scores. Example: "we propose Denoising Diffusion Bridge Models (DDBMs)"
- Denoising score-matching: A training objective that learns the score (gradient of log-density) by matching a tractable conditional score with additive noise. Example: "we take inspiration from denoising score-matching"
- Diffusion bridge: A diffusion process conditioned on both its start and end points, used to interpolate between endpoints. Example: "we consider a reverse-time perspective of diffusion bridges"
- Diffusion process: A stochastic process defined by an SDE that gradually perturbs data, commonly used in generative modeling. Example: "constructing a diffusion process"
- Doob's h-function: The function used in Doob’s h-transform to condition a Markov process on an endpoint, effectively reweighting paths. Example: "reliant on Doob's -function"
- Doob's h-transform: A method to condition a diffusion process to hit a desired endpoint by modifying its drift using an h-function. Example: "via Doob's -transform"
- Drift (SDE): The deterministic component of an SDE that dictates the average rate of change of the process. Example: "is vector-valued drift function"
- Entropic optimal transport: An optimal transport formulation regularized by entropy, yielding smooth couplings and tractable algorithms. Example: "learn an entropic optimal transport between two probability distributions"
- Euler–Maruyama step: A numerical method for simulating SDEs by discretizing time and adding appropriate stochastic increments. Example: "take an Euler-Maruyama step"
- Flow-matching: A training paradigm that learns a vector field to match a reference flow transporting one distribution to another. Example: "ODE based flow-matching methods"
- Frechet Inception Distance (FID): A metric comparing distributions of generated and real images using features from an Inception network. Example: "as measured by FID"
- Heun steps: A second-order Runge–Kutta (improved Euler) method used to integrate ODEs more accurately than Euler steps. Example: "used for Heun steps"
- Iterative Markovian Fitting: An iterative procedure proposed for bridge matching that alternates updates to fit Markovian dynamics between distributions. Example: "Bridge-Matching~\citep{shi2023diffusion} proposes to use Iterative Markovian Fitting"
- Iterative Proportional Fitting (IPF): An iterative scaling algorithm used to solve regularized optimal transport problems like Schrödinger Bridges. Example: "proposes Iterative Proportional Fitting (IPF) to tractably solve Sch\"odinger Bridge (SB) problems"
- Kolmogorov backward equation: A partial differential equation that describes the evolution of expected future values and characterizes transition densities backward in time. Example: "satisfies the Kolmogorov backward equation"
- LPIPS: A perceptual similarity metric comparing deep feature distances between images to assess visual similarity. Example: "as measured by LPIPS~\citep{zhang2018perceptual}"
- Optimal transport (OT): The problem of transporting mass from one distribution to another with minimal cost, forming a basis for transport-based generative models. Example: "optimal transport"
- OT-Flow-Matching: A method that fits an ODE’s velocity field to implement (often straight-line) optimal transport between distributions. Example: "OT-Flow-Matching"
- Predictor–corrector sampler: A sampling scheme that alternates stochastic (predictor) and deterministic (corrector) updates to improve SDE sampling quality. Example: "predictor-corrector sampler"
- Probability flow ODE: A deterministic ODE whose marginals match those of a corresponding SDE, allowing ODE-based generation. Example: "an equivalent deterministic process called the probability flow ODE"
- Rectified Flow: A flow-based approach that learns straight-line (or simplified) transport paths between distributions for efficient generation. Example: "Rectified Flow~\citep{liu2022flow}"
- Reverse SDE: The time-reversed stochastic differential equation used to transform noise into data by following reverse-time dynamics. Example: "the above reverse SDE"
- Schrödinger Bridge (SB): The entropy-regularized optimal transport problem of finding a stochastic process that interpolates between two endpoint distributions. Example: "Schr\"odinger Bridge and models"
- Score (of a distribution): The gradient of the log-density with respect to the input; used to guide reverse-time dynamics in diffusion models. Example: "learns the score of the diffusion bridge"
- Score-matching loss: An objective that fits a model to the score by minimizing squared error between predicted and true (or tractable) scores. Example: "score-matching loss"
- Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR): The ratio of signal power to noise power at a given diffusion time, often governing training and sampling schedules. Example: "signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)"
- Stochastic differential equation (SDE): An equation describing the evolution of a random process with both drift and diffusion terms. Example: "the following SDE"
- Stochastic interpolants: Randomized interpolation paths between distributions used to unify or generalize flow- and diffusion-based models. Example: "stochastic interpolants \citep{albergo2023building}"
- Transition kernel: The conditional distribution describing how a stochastic process moves from one time to another. Example: "the transition kernel "
- Variance Exploding (VE) bridge: A diffusion-bridge instantiation based on a VE diffusion (noise level increases with time), used for translation. Example: "VE bridge (left)"
- Variance Preserving (VP) bridge: A diffusion-bridge instantiation based on a VP diffusion (variance preserved via suitable drift), used for translation. Example: "VP bridge (right)"
- Wiener process: A standard Brownian motion used as the noise driving term in SDEs. Example: "is a Wiener process"
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.