- The paper presents a snippet-level anomalous attention mechanism that refines feature extraction for weakly-supervised video anomaly detection.
- It introduces a three-module architecture combining temporal embedding, focused attention, and multi-branch supervision to optimize anomaly localization.
- Experiments on UCF-Crime and XD-Violence demonstrate competitive performance, achieving 86.19% AUC and 84.23% AP with RGB-Audio fusion.
Weakly-Supervised Video Anomaly Detection with Snippet Anomalous Attention
The paper "Weakly-Supervised Video Anomaly Detection with Snippet Anomalous Attention" presents an innovative approach to tackle the challenges associated with video anomaly detection (VAD) in a weakly supervised setting. By introducing a snippet-level anomalous attention mechanism, this paper overcomes several limitations of existing methods that heavily rely on preparatory labels or overlook informative snippet-level features. This essay provides a detailed discussion on the methodologies proposed in the paper and their implications in advancing the field of VAD.
Introduction and Background
Weakly-supervised video anomaly detection (WS-VAD) is a challenging task due to its reliance on coarsely annotated video-level labels and lack of frame-wise labeling. Existing approaches primarily fall into two categories based on their methodology: one-stage Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) techniques and two-stage self-training strategies. The former focuses on selecting and using the most representative features, while the latter creates and refines pseudo labels. However, these methods are susceptible to sub-optimal performance due to their respective limitations in feature representation and noise management.
Proposed Methodology
The proposed framework in the paper is structured around a three-module design:
- Temporal Embedding Unit: This module integrates global and local dependencies to effectively model video features.
- Anomalous Attention Unit: A novel attention mechanism is introduced to focus on snippet-level anomalous features. This attention is not driven by video-level supervision but by its anomaly-specific characteristics, ensuring a more granular and precise anomaly identification.
- Multi-branch Supervision Module: This component leverages anomaly-specific attention to detect challenging snippets, thereby exploring anomaly completeness without heavy dependence on the most discriminative snippets.

Figure 1: Comparisons with the existing approaches.
The framework fundamentally addresses the weaknesses of traditional WS-VAD approaches by emphasizing snippet-level feature significance, supported by soft attention and multi-branch supervision. Moreover, an optimization process enhances the anomalous attention's precision through guide and norm constraints.
Experimental Results
The paper exhaustively validates the proposed method through experiments on widely-recognized datasets, namely UCF-Crime and XD-Violence. These tests demonstrate that the proposed model performs competitively with MOSAIC and existing state-of-the-art methodologies, especially in contexts with dispersed anomalous distributions. For instance, the model achieves an AUC of 86.19% on the UCF-Crime dataset and an AP of 84.23% on XD-Violence with RGB-Audio fusion, showcasing its efficacy in managing complex real-world scenarios.
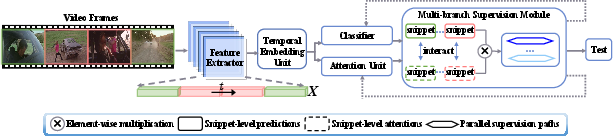
Figure 2: The proposed method consists of three primary modules for feature encoding, anomaly detection, and anomaly completeness modeling.
Methodological Implications
The primary contribution of the proposed method is its shift towards snippet-level attentiveness, complementing global video context with refined local anomaly specifications. This allows the handling of anomalies that are subtle and temporally sparse effectively. The introduction of multi-branch supervision allows the model to avoid reliance on potentially biased discriminative snippets and instead emphasizes a broader aspect of anomaly detection, resulting in improved localization accuracy.
Future Work
This work opens several avenues for future exploration. Improving the granularity and reliability of snippet attention by experimenting with alternative norm and guide mechanisms offers a promising path. Additionally, investigating alternative fusion strategies for multi-modal scenarios could further improve detection accuracy. Furthermore, scaling this approach to real-time applications is a critical step toward broader adoption in surveillance and safety software solutions.
Conclusion
"Snippet Anomalous Attention" presents a significant advance in WS-VAD by capitalizing on snippet-level anomalous features and utilizing a robust supervision mechanism. Through this, the paper establishes a formidable state-of-the-art in detecting and localizing anomalies within untrimmed video environments. The approach promises enhanced anomaly detection and paves the way for further research refining snippet-level focus and anomaly-specific attention mechanisms. As WS-VAD continues to evolve, incorporating such detailed attention insights is key to overcoming challenges associated with computational efficiency and real-world applicability.
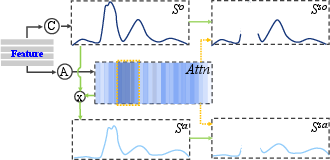
Figure 3: Qualitative results of anomaly detection performance on XD-Violence and UCF-Crime dataset.
This work is poised as a cornerstone for developing more nuanced approaches to video anomaly detection, setting a precedent for algorithms that adeptly balance computational efficiency with detection precision and accuracy.


