- The paper introduces EasyEdit, a novel framework that efficiently updates LLMs with targeted knowledge edits to correct outdated or erroneous information.
- The methodology integrates modular components such as Editor, Method, and Trainer, enabling diverse editing strategies including memory-based, meta-learning, and locate-then-edit approaches.
- Experimental results on LLaMA 2 demonstrate improved reliability, generalization, and efficiency compared to traditional fine-tuning methods.
EasyEdit: An Easy-to-use Knowledge Editing Framework for LLMs
Introduction
The paper "EasyEdit: An Easy-to-use Knowledge Editing Framework for LLMs" presents a novel framework designed to address the limitations of LLMs associated with knowledge cutoff and fallacy issues. These issues arise because LLMs rely on data up to their last training point and can generate incorrect information due to outdated or noisy data sources. The framework introduced, EasyEdit, is structured to efficiently inject updated knowledge into LLMs and rectify undesired behaviors without adversely affecting unrelated data outputs. By supporting various knowledge editing methodologies, the framework aims to overcome the absence of a standard implementation practice in the domain, promoting widespread adoption and application.
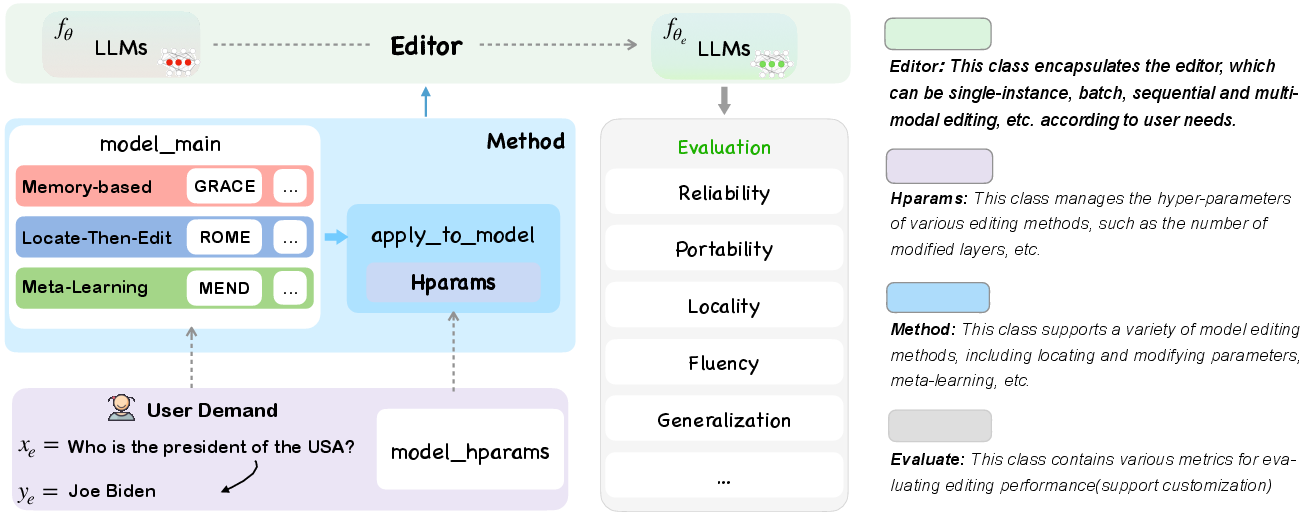
Figure 1: The overall architecture of EasyEdit. The main function is apply_to_model, which applies the selected editing method to the LLMs. The Editor serves as the direct entry point, receiving customized user inputs and outputs, and returning the edited weights. Please note that some methods may require pre-training of classifiers or hypernetworks through the Trainer (See §3.5).
Background and Framework Design
Traditional interventions like model fine-tuning or prompt augmentation manage to adjust the output of LLMs to some extent but often suffer from high computational costs and inefficient parameter updates. These methods can result in overfitting or limited generalization ability when confronted with small datasets. On the contrary, knowledge editing provides a more dynamic methodology for updating model parameters. This approach ensures more focused edits and preserves model performance across a broader input spectrum.
EasyEdit is architected to modularize various knowledge editing techniques and evaluate their effectiveness across diverse metrics, including Reliability, Generalization, Locality, and Portability. It supports a wide range of editing scenarios such as single or batch instance modifications and implements memory-based, meta-learning, and locate-then-edit methodologies. This modular setup enhances its assembly flexibility, allowing for new advancements to be incorporated without extensive restructuring.
Methodology
The EasyEdit framework integrates several primary functionality modules:
Evaluation Metrics
The framework employs several metrics to evaluate the impact of knowledge editing across LLMs:
- Reliability: Measures the accuracy on the modified instances.
- Generalization: Assesses the system's ability to correctly adjust a broad set of in-scope inputs.
- Locality: Ensures that out-of-scope outputs remain consistent with the base model.
- Portability: Examines the capacity to generalize edited knowledge to related concepts.
- Efficiency: Evaluates the resource consumption and runtime during the editing process.
Experimental Results
Using LLaMA 2 as the test subject, EasyEdit demonstrated significant improvements in incorporating factual updates without undermining the model's overall predictive capabilities. The tests, conducted on datasets like ZsRE, showcased how chosen knowledge editing methods outperformed traditional fine-tuning techniques across various metrics. Specifically, SERAC and IKE exhibited exceptional performance, with IKE showing strengths in in-context learning settings, albeit at a trade-off with locality. Other methods like MEND offered balanced accuracy while still maintaining high reliability.
Conclusion
EasyEdit establishes a pivotal platform for targeted and efficient LLM knowledge manipulation, facilitating both practical and research applications. This adaptability promises to enrich LLM usability in diverse contexts and advance the approach to dynamic knowledge updating. Moving forward, integrating multi-modal inputs and exploring editing personalities represent potential areas for further enhancement and study within the framework, paving the way for richer and more nuanced LLM applications.



