- The paper introduces a novel MTD-GPT model that integrates reinforcement learning and GPT for multi-task decision-making at unsignalized intersections.
- The methodology captures expert trajectories using PPO enhanced with attention mechanisms, transforming them into tokenized sequences for GPT training.
- Simulation results indicate that smaller GPT models adapt better to diverse intersection scenarios, improving safety and traffic efficiency.
MTD-GPT: A Multi-Task Decision-Making GPT Model for Autonomous Driving at Unsignalized Intersections
Introduction
This paper presents the development of the Multi-Task Decision-Making Generative Pre-trained Transformer (MTD-GPT) model to address challenges in autonomous driving, specifically at unsignalized intersections. Autonomous vehicles (AVs) must safely execute multiple tasks—such as left turns, straight driving, and right turns—in complex intersection environments. The authors have leveraged reinforcement learning (RL) alongside the sequence modeling capabilities of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) to handle these diverse tasks concurrently.
In autonomous driving, decision-making at intersections is a complex problem due to the interaction dynamics with human-driven vehicles and the need to adapt to unpredictable traffic patterns. Traditional rule-based models are insufficient due to their limited flexibility and often unrealistic assumptions inherent in game theory-based methods.
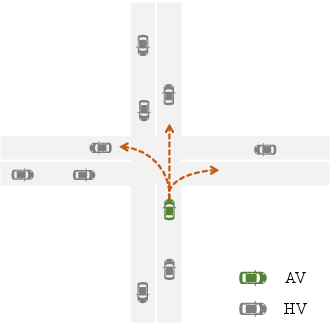
Figure 1: The intersection scenario for multi-task decision-making in our research.
Methodology
Training Pipeline
The MTD-GPT model benefits from a robust training pipeline designed to integrate RL with sequence modeling for multi-task scenarios. This pipeline involves training single-task RL experts using the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm enhanced with attention mechanisms. Expert trajectories are then captured in a simulated environment to develop a comprehensive, mixed multi-task dataset. This dataset serves as the foundation for offline GPT training.
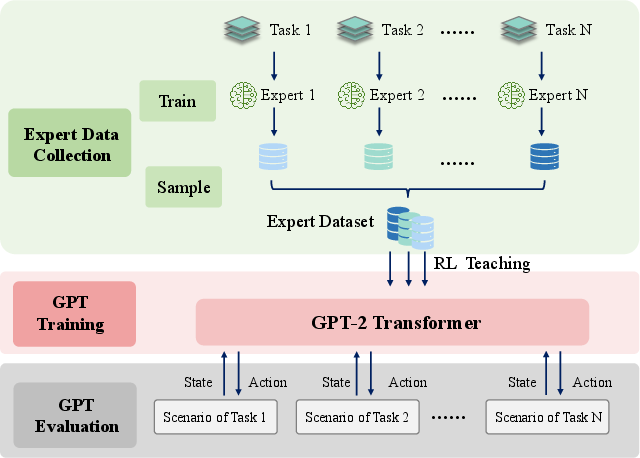
Figure 2: The Training Pipeline for our MTD-GPT.
Expert Data Collection and GPT Model
The process of expert data collection is essential for the subsequent training phases. For each defined task (left turn, straight, right turn), RL experts are trained to optimize high-level decision-making actions using a PID controller to simulate real vehicle dynamics.
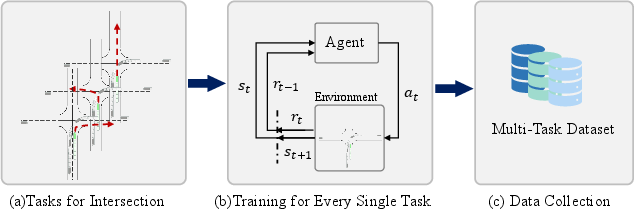
Figure 3: The process of the data sample for offline training.
Offline GPT training abstracts decision-making as sequence modeling. The transformation of state-action-reward data from experts into tokens allows the GPT model to learn effectively through an autoregressive approach. This method exploits the architectural benefits of GPT-2, using multi-layer perceptrons (MLP), positional encodings, and self-attention mechanisms to predict action decisions.
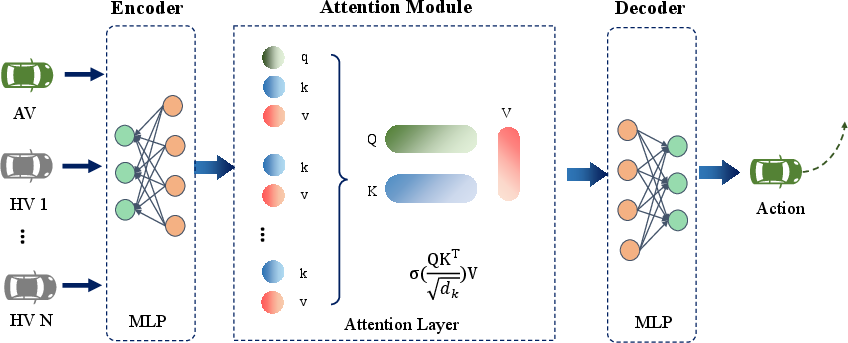
Figure 4: The policy network with attention layer.
Simulation and Evaluation
The performance of MTD-GPT is assessed by simulating various tasks within an OpenAI Gym-based environment. Metrics such as training loss, action error, and task success rates are used to evaluate different models with varying parameter scales. Notably, the smaller GPT models demonstrate superior adaptability, perhaps avoiding overfitting typically seen in larger models.
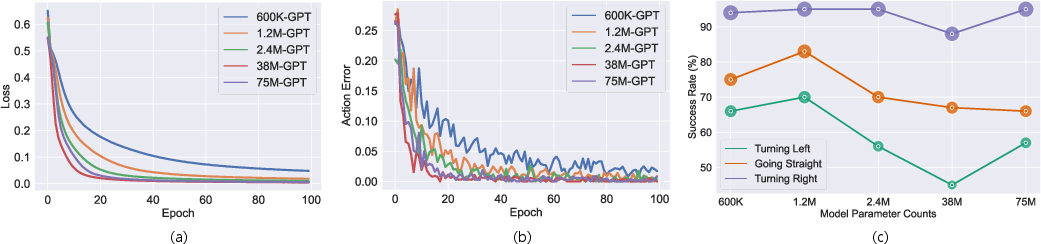
Figure 5: The performance of GPT with different parameter counts: (a) training loss, (b) training action error, (c) the success rate on different testing tasks.
MTD-GPT's efficacy in multi-task decision-making surpasses that of single-task RL experts, reinforcing its capacity to generalize across tasks effectively.
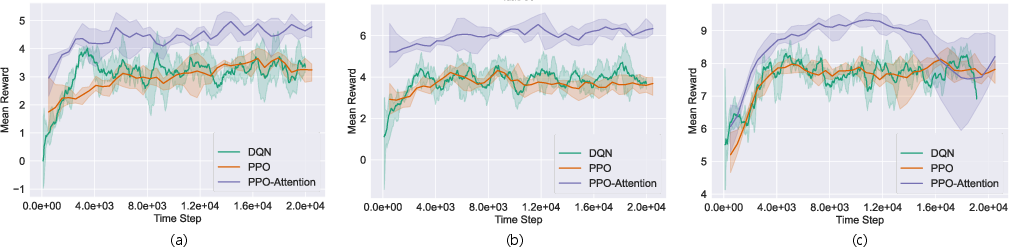
Figure 6: The performance comparison between RL Experts (PPO-Attention) and other baselines:(a) turning left task, (b) going straight task, (c) turning right task.
Case Analysis
Analyses of specific intersection scenarios reveal varying decision-making strategies employed by MTD-GPT models with different scales. Models exhibit distinct behavioral styles ranging from aggressive to conservative, impacting safety and traffic efficiency.
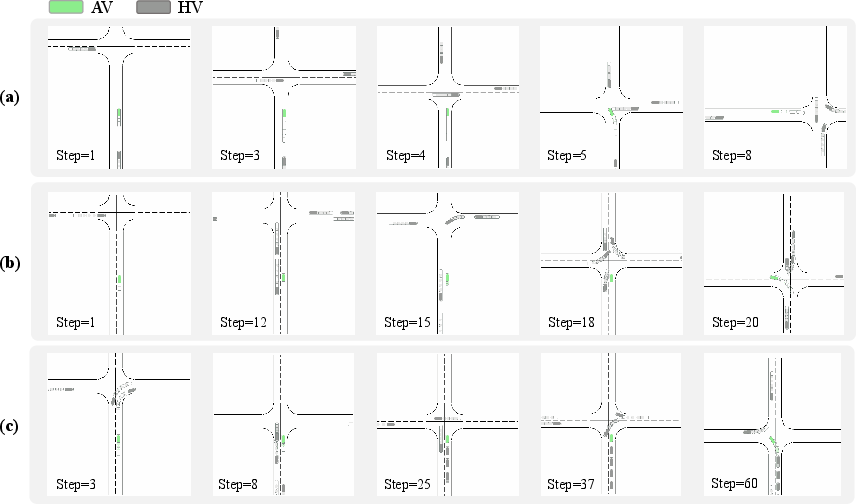
Figure 7: Three cases of turning left task from different models: (a) Case 1 from GPT with 600K parameters, (b) Case 2 from GPT with 1.2M parameters, (c) Case 3 from GPT with 75M parameters.
Conclusions
This research demonstrates the capability of the MTD-GPT model to perform multi-task decision-making in complex autonomous driving scenarios, achieving performance comparable or superior to single-task RL models. Future work aims to enhance the model’s generalization for broader traffic scenarios, including utilizing natural driving data and integrating Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) strategies. The continued evolution of GPT-driven architectures promises significant advancements in safe and efficient autonomous vehicle interactions at intersections.








