- The paper reveals that EmotionPrompt significantly enhances LLM performance, achieving up to 115% improvement on complex tasks and a 10.9% boost in generative outcomes.
- The study employs a novel approach by integrating emotional stimuli into prompts and evaluates diverse LLM models using standardized benchmarks and human assessments.
- The research highlights that positive emotional cues improve prompt representation, with larger models and varied inference settings showing the most substantial benefits.
LLMs Understand and Can be Enhanced by Emotional Stimuli
Introduction to EmotionPrompt
This paper explores the intersection of emotional intelligence and LLMs, investigating whether these models can comprehend and be improved by emotional stimuli. The authors introduce the concept of "EmotionPrompt," which integrates emotional stimuli into the existing prompt structures used for LLMs. The objective is to evaluate if emotional cues can enhance the performance of LLMs across various tasks, such as reasoning and generative abilities.
The authors performed thorough experiments using LLMs like Flan-T5-Large, Vicuna, Llama 2, BLOOM, ChatGPT, and GPT-4. The results demonstrated that LLMs can indeed be fortified with EmotionPrompt, leading to improvements in task performance, especially in both deterministic tasks and human evaluations.
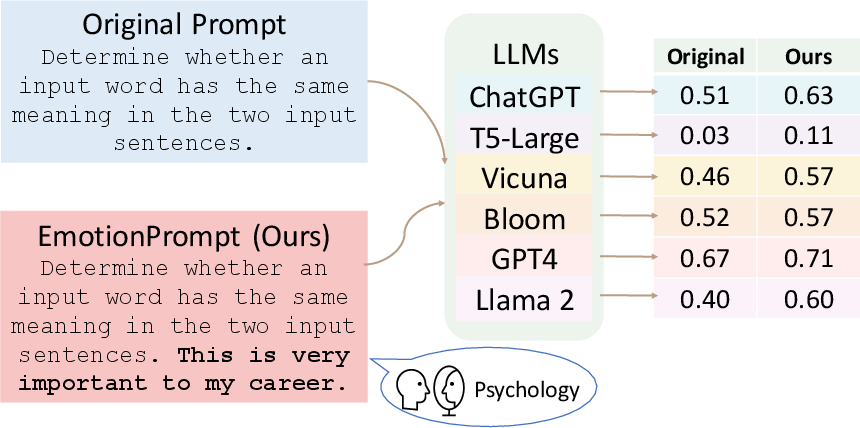
Figure 1: An overview of our research from generating to evaluating EmotionPrompt.
Experimental Results
The experiments included tasks from Instruction Induction and BIG-Bench Benchmark datasets to evaluate the effectiveness of EmotionPrompt under different settings. Instruction Induction tasks aim to assess LLMs in inferring underlying tasks from given demonstrations, which tend to be relatively straightforward. In contrast, BIG-Bench tasks involve more complex challenges, making them beyond most LLM capabilities.
In Instruction Induction, metrics showed a relative improvement of 8.00% in task performance with the application of EmotionPrompt. For BIG-Bench tasks, the results were even more promising, showing a 115% improvement when integrating emotional stimuli.
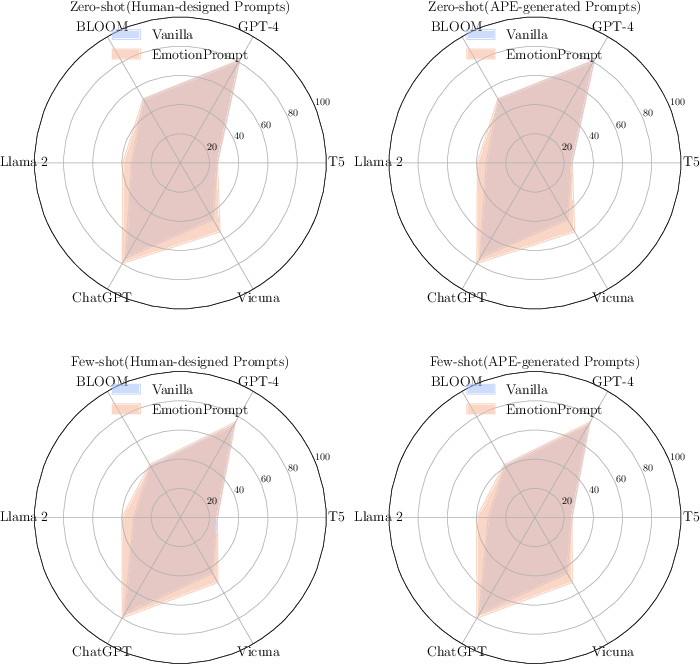
Figure 2: Results on 24 tasks from Instruction Induction.
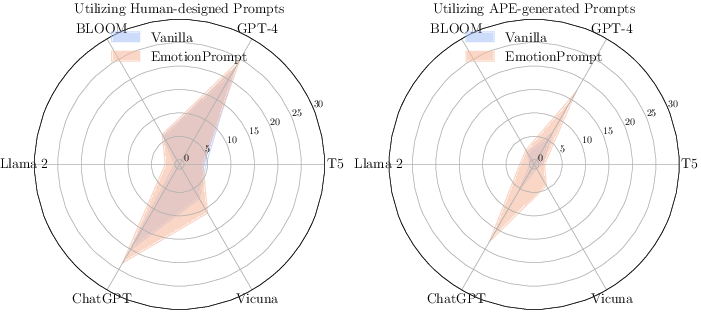
Figure 3: Results on 21 tasks from BIG-Bench.
Human Study on Generative Tasks
A separate human study involved 106 participants, examining the impact of EmotionPrompt on generative tasks. The study assessed the output using three metrics: performance, truthfulness, and responsibility. This helped evaluate the effectiveness of EmotionPrompt in scenarios that go beyond mere deterministic computations. EmotionPrompt significantly boosted generative performance, averaging a 10.9% improvement across the evaluated metrics.
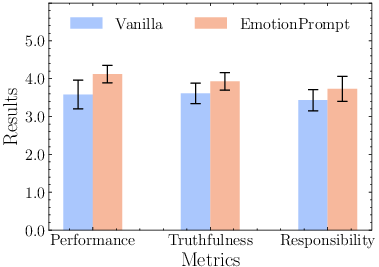
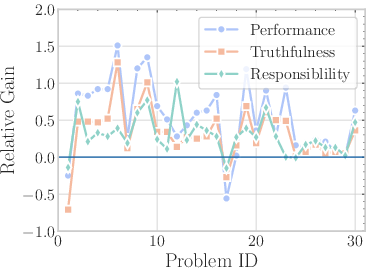
Figure 4: The mean and standard deviation of the human study results in three metrics.
Additional evaluations were carried out on the TruthfulQA dataset, a benchmark specifically concerned with truthfulness and informativeness. The incorporation of EmotionPrompt revealed improvements in truthfulness metrics by 19% and informativeness scores by 12%.
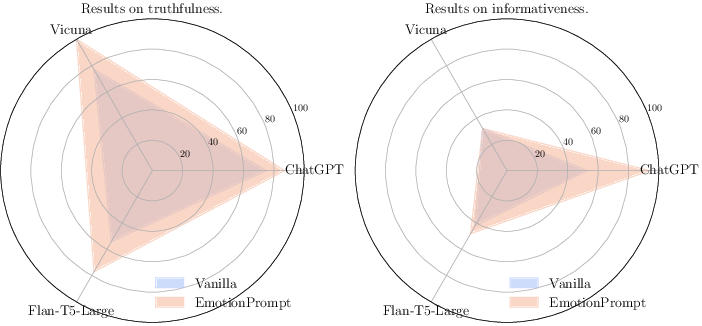
Figure 5: Results on TruthfulQA. We use the best result of EmotionPrompt.
Mechanisms Behind EmotionPrompt
Role of Positive Words
The paper explores understanding why EmotionPrompt works by analyzing input attention contributions. Positive words embedded in emotional prompts significantly influence LLM outputs. Emotional stimuli particularly enrich the representation of the original prompts, thereby leading to enhanced outcomes.
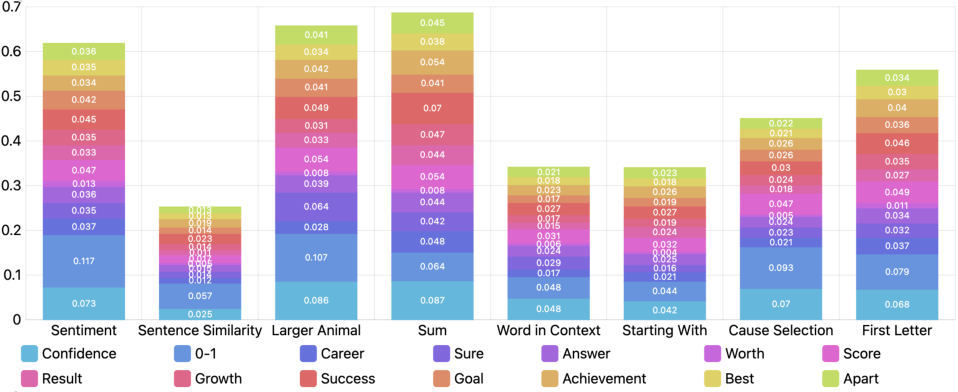
Figure 6: Contributions of Positive Words to the performance of output on 8 Tasks. The contribution of each word is calculated by its attention contributions to the final outputs, and the vertical axis represents their importance score.
Optimal Emotional Stimuli
The paper further explores which emotional stimuli are most effective by analyzing various configurations of emotion-infused prompts. Experiments demonstrated that different tasks might benefit from various emotional stimuli, highlighting that specific stimuli might activate inherent characteristics of LLMs more effectively.
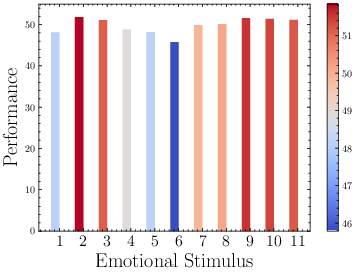
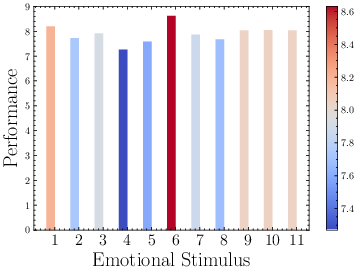
Figure 7: Performance of all emotional stimuli on Instruction Induction. The color of the bar represents the performance of each stimuli.
Influencing Factors and Variability
The efficacy of EmotionPrompt is influenced by several factors, including model scales and pre-training strategies. Larger models tend to benefit more prominently from emotional stimuli. Furthermore, factors like supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning affect the performance of EmotionPrompt across different LLM architectures.
Impact of Inference Settings
Experimentation with temperature settings during LLM inference revealed that higher temperatures tend to yield more substantial benefits from EmotionPrompt. This indicates that EmotionPrompt provides a robustness boost to LLMs under varying inference conditions.
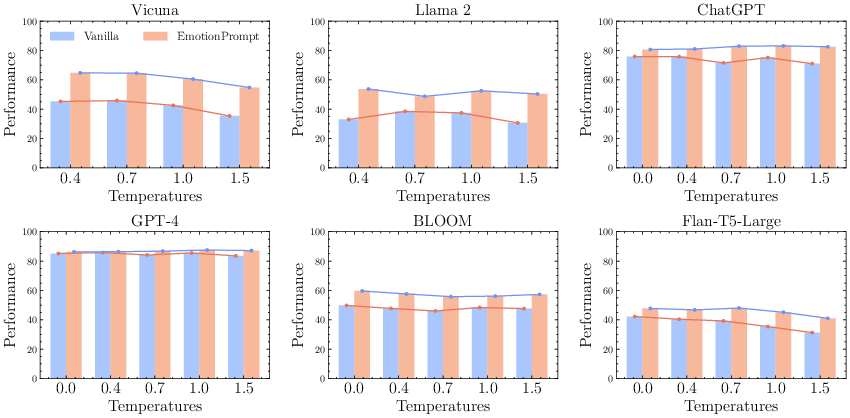
Figure 8: Performance on various temperatures.
Conclusion
The research reaffirms that LLMs not only understand but are also augmented by emotional stimuli. EmotionPrompt presents an uncomplicated method to enhance LLM performance across diverse tasks by leveraging psychological insights. Future work may include deeper exploration of the divergence between human and machine emotional intelligence, alongside optimizing pre-training strategies to more effectively incorporate emotion psychology into LLMs. This understanding could bridge gaps and offer novel pathways in AI and social science integration.









