Generative Job Recommendations with Large Language Model
Abstract: The rapid development of online recruitment services has encouraged the utilization of recommender systems to streamline the job seeking process. Predominantly, current job recommendations deploy either collaborative filtering or person-job matching strategies. However, these models tend to operate as "black-box" systems and lack the capacity to offer explainable guidance to job seekers. Moreover, conventional matching-based recommendation methods are limited to retrieving and ranking existing jobs in the database, restricting their potential as comprehensive career AI advisors. To this end, here we present GIRL (GeneratIve job Recommendation based on LLMs), a novel approach inspired by recent advancements in the field of LLMs. We initially employ a Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) strategy to instruct the LLM-based generator in crafting suitable Job Descriptions (JDs) based on the Curriculum Vitae (CV) of a job seeker. Moreover, we propose to train a model which can evaluate the matching degree between CVs and JDs as a reward model, and we use Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)-based Reinforcement Learning (RL) method to further fine-tine the generator. This aligns the generator with recruiter feedback, tailoring the output to better meet employer preferences. In particular, GIRL serves as a job seeker-centric generative model, providing job suggestions without the need of a candidate set. This capability also enhances the performance of existing job recommendation models by supplementing job seeking features with generated content. With extensive experiments on a large-scale real-world dataset, we demonstrate the substantial effectiveness of our approach. We believe that GIRL introduces a paradigm-shifting approach to job recommendation systems, fostering a more personalized and comprehensive job-seeking experience.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Explain it Like I'm 14
What is this paper about?
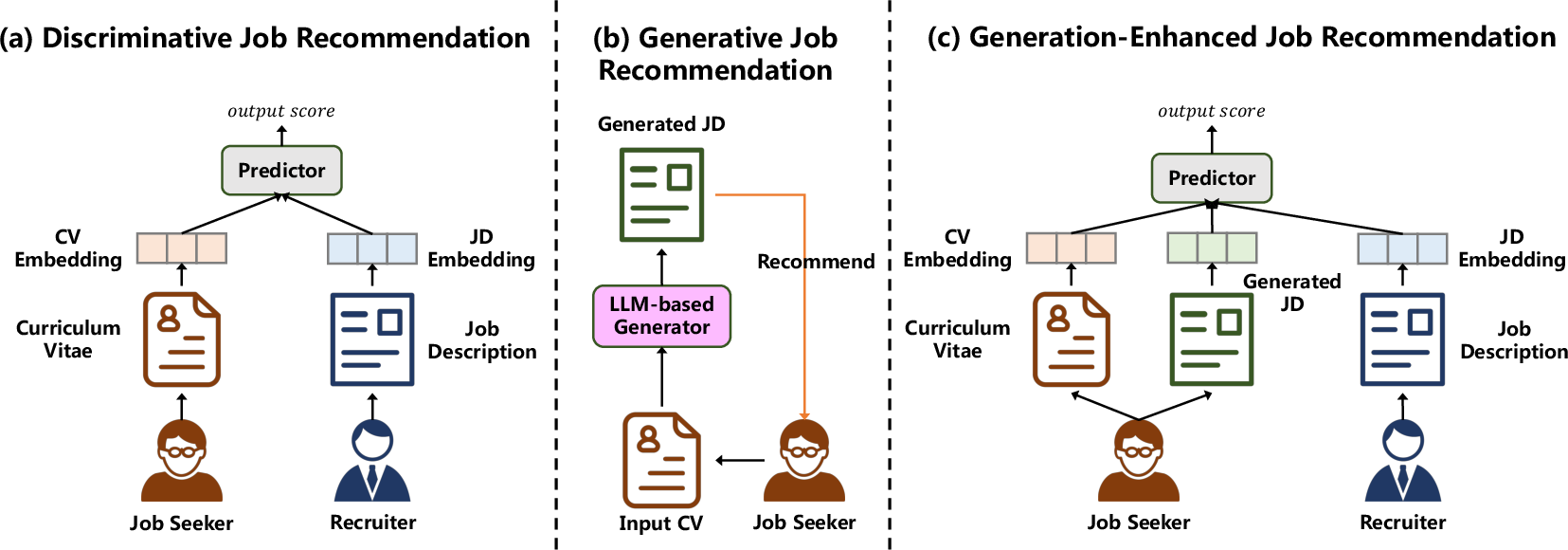
This paper introduces a new way to recommend jobs using large AI LLMs. Instead of only scoring how well a person’s resume (CV) matches existing job postings, the system, called GIRL (Generative job Recommendation based on LLMs), actually writes a custom job description (JD) for the job seeker based on their CV. This makes the recommendations more personal and easier to understand, and the generated text can also help improve traditional job-matching systems.
What are the goals of the research?
The researchers set out to:
- Create a job recommendation system that can generate a personalized job description for each job seeker, not just list jobs from a database.
- Make recommendations more explainable, so job seekers see why a job fits them.
- Align the generated job descriptions with real-world recruiter preferences (what employers are likely to want).
- Use the generated content to boost the accuracy of regular matching models that pair CVs with real job postings.
- Test whether their training approach (including supervised learning and reinforcement learning) improves results, and explore practical settings like the number of generated descriptions and performance on new users (cold start).
How did the researchers do it?
Think of the system as a very smart writer that learns to draft tailored job postings for you and then gets feedback to improve.
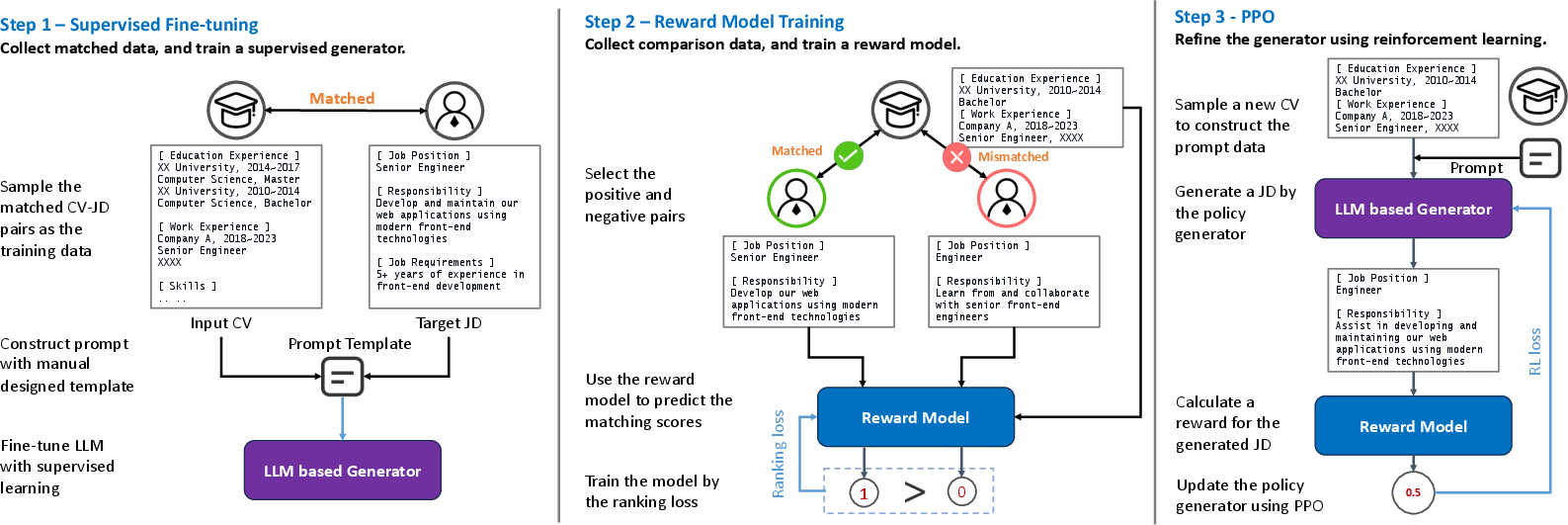
Step 1: Teach the model with examples (Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT)
- The model is shown many pairs of real CVs and their matched job descriptions.
- It learns to write a JD that fits a given CV, like a student learning from good examples.
- A “prompt” (instructions + the CV) tells the model what to write.
Step 2: Build a “judge” that scores matches (Reward Model)
- They train a smaller model to predict whether a CV and a JD are a good match (matched vs. mismatched based on recruiter feedback).
- This judge acts like a coach: it gives higher scores when the JD fits the CV well and lower scores when it doesn’t.
Step 3: Train with feedback (Reinforcement Learning with PPO)
- The main model generates job descriptions for CVs it hasn’t seen before.
- The judge scores these descriptions. The system adjusts the generator to make future outputs more aligned with what recruiters prefer.
- They use a method called PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization), which is a safe way of teaching the model step-by-step without letting it change too wildly. An analogy: it’s like practicing a sport with a coach who nudges you to improve a little at a time, instead of changing your entire technique at once.
Using generated JDs to improve regular recommendation models
- Traditional systems turn text (CV and real JD) into vectors (lists of numbers that represent meaning), then compute a match score.
- GIRL adds a third piece: the generated JD. This extra text helps bridge the “semantic gap” between how CVs and JDs are written.
- By feeding this generated JD into the traditional model, the match scores become more accurate.
What did they find?
- The generated job descriptions were better: Using ChatGPT as an evaluator, GIRL’s generated JDs beat other LLMs and also beat a simpler version that didn’t use reinforcement learning (called GIRL-SFT). The JDs were more detailed, more relevant to the CV, and easier to read.
- Better recommendations: When the generated JDs were added to traditional matching models, performance improved (higher AUC and lower LogLoss, which means more accurate predictions).
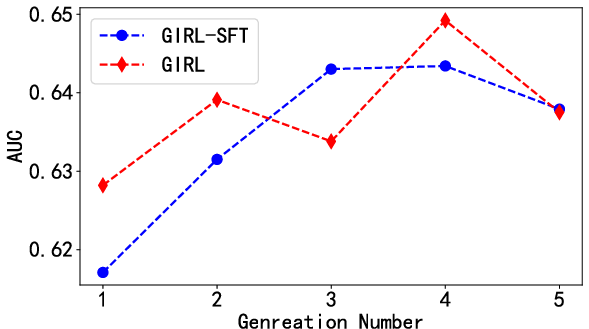
- Reinforcement learning helped: The full GIRL (with RL) outperformed the SFT-only version, showing that learning from recruiter-like feedback makes the generated content more useful.
- Smart use of multiple drafts: Generating several JDs and combining their information can help—up to a point. Too many drafts increase cost and can eventually hurt performance.
- Stronger for new users (cold start): GIRL’s improvements were even bigger when recommending jobs to job seekers who weren’t in the training data, which is a common real-world challenge.
Why does this matter?
Job seeking is personal and important. Traditional recommenders often act like black boxes: they say “this job matches you” without explaining why. GIRL writes a JD tailored to the person’s CV, helping them understand what kind of role fits them, what skills to highlight, and what responsibilities they might enjoy. It also gives recruiters and platforms better tools to match people to jobs more fairly and accurately.
Final thoughts: Implications and impact
- For job seekers: More personalized guidance and clearer explanations of suitable roles, almost like having an AI career advisor.
- For platforms: Improved matching accuracy, especially for new users with little history, and better trust through explainable recommendations.
- For the future: This approach could be extended to other recommendation areas (like courses, projects, or internships). As with any AI system, teams should watch out for biases in training data and protect privacy, but the results suggest a promising direction for more helpful, human-centered job recommendation systems.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.