ClinicalGPT: Large Language Models Finetuned with Diverse Medical Data and Comprehensive Evaluation (2306.09968v1)
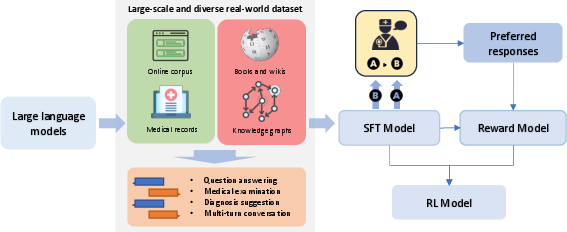
Abstract: LLMs have exhibited exceptional performance on various NLP tasks, leveraging techniques such as the pre-training, and instruction fine-tuning. Despite these advances, their effectiveness in medical applications is limited, due to challenges such as factual inaccuracies, reasoning abilities, and lack grounding in real-world experience. In this study, we present ClinicalGPT, a LLM explicitly designed and optimized for clinical scenarios. By incorporating extensive and diverse real-world data, such as medical records, domain-specific knowledge, and multi-round dialogue consultations in the training process, ClinicalGPT is better prepared to handle multiple clinical task. Furthermore, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation framework that includes medical knowledge question-answering, medical exams, patient consultations, and diagnostic analysis of medical records. Our results demonstrate that ClinicalGPT significantly outperforms other models in these tasks, highlighting the effectiveness of our approach in adapting LLMs to the critical domain of healthcare.
- Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805, 2018.
- Aligning books and movies: Towards story-like visual explanations by watching movies and reading books. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pages 19–27, 2015.
- Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 21(1):5485–5551, 2020.
- Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in neural information processing systems, 33:1877–1901, 2020.
- Palm: Scaling language modeling with pathways. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.02311, 2022.
- Lamda: Language models for dialog applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.08239, 2022.
- Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:27730–27744, 2022.
- Christian Baumgartner. The potential impact of chatgpt in clinical and translational medicine. Clinical and translational medicine, 13(3), 2023.
- Tyler Cowen. The ai revolution in medicine: Gpt-4 and beyond. 2023.
- Foundation models for generalist medical artificial intelligence. Nature, 616(7956):259–265, 2023.
- On the dangers of stochastic parrots: Can language models be too big? In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM conference on fairness, accountability, and transparency, pages 610–623, 2021.
- Multi-scale attentive interaction networks for chinese medical question answer selection. IEEE Access, 6:74061–74071, 2018.
- What disease does this patient have? a large-scale open domain question answering dataset from medical exams. Applied Sciences, 11(14):6421, 2021.
- Meddialog: Two large-scale medical dialogue datasets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03329, 2020.
- Webgpt: Browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.09332, 2021.
- Learning to summarize with human feedback. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33:3008–3021, 2020.
- Bloom: A 176b-parameter open-access multilingual language model, 2023.
- Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09685, 2021.
- Zero: Memory optimizations toward training trillion parameter models. In SC20: International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, pages 1–16. IEEE, 2020.
- Glm-130b: An open bilingual pre-trained model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.02414, 2022.
- Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models, 2023.
- Bloom: A 176b-parameter open-access multilingual language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.05100, 2022.
- Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 311–318, 2002.
- Chin-Yew Lin. Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Text summarization branches out, pages 74–81, 2004.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.