- The paper demonstrates that ChatGPT can automatically extract critical patient data from clinical notes to streamline trial enrollment.
- The paper employs zero-shot and few-shot prompting techniques, achieving query performance that often surpasses traditional human-generated methods on metrics like nDCG@10 and R-Precision.
- The paper underscores the potential of integrated AI systems to enhance recruitment accuracy while addressing vital data privacy and ethical concerns in healthcare.
Utilizing ChatGPT to Enhance Clinical Trial Enrollment
Advancements in AI, specifically in NLP applications such as ChatGPT, present opportunities to expedite and refine clinical trial enrollment processes. The paper "Utilizing ChatGPT to Enhance Clinical Trial Enrollment" explores the integration of ChatGPT into these processes, aiming to improve patient recruitment efficiency by leveraging AI's ability to interpret and generate relevant information from unstructured clinical notes.
Introduction to Clinical Trial Enrollment Challenges
Clinical trials play an essential role in validating new medical interventions. However, the enrollment process can suffer delays due to challenges in identifying suitable participants, which directly impacts the trial's validity and generalizability. Presently, identifying eligible patients often hinges upon EHR-derived data, including clinical notes and laboratory reports, which require significant human effort for interpretation.
The paper proposes a solution that utilizes ChatGPT to automatically extract patient-related data from clinical notes and formulate queries to identify compatible clinical trials. By automating this step, the model reduces manual labor and potential human error, thereby streamlining the initial phases of the trial enrollment.
The Role of EHRs and NLP in Trial Enrollment
Historically, EHRs have been instrumental in improving recruitment rates by providing detailed patient data. Despite their potential, shortcomings in research-specific EHR modules limit optimization in trial recruitment. ChatGPT, with its advanced NLP capabilities, provides a method to bridge these gaps and ensure the efficient extraction of complex medical information.
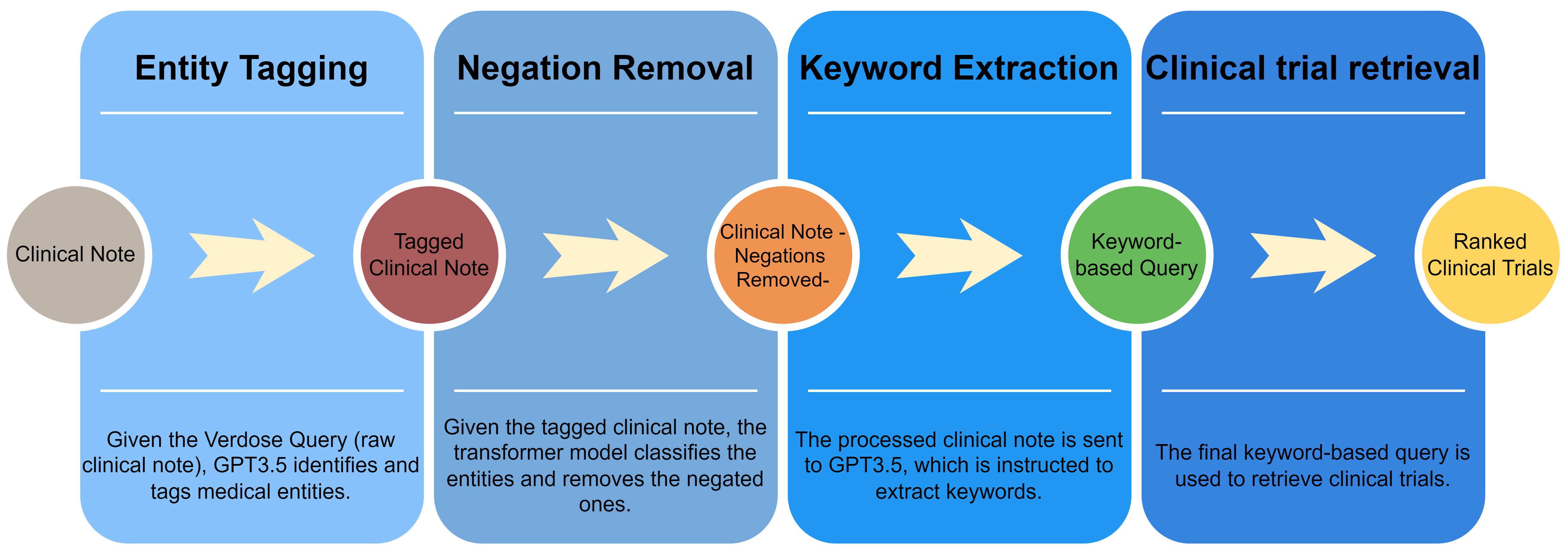
Figure 1: Combining ChatGPT with a negation classification model.
The paper explores different prompting techniques, including zero-shot and few-shot prompting for extracting relevant medical information. With various systems roles defined, the study evaluated generic and domain-specific applications of these prompts. It revealed that specific guidance significantly affects the quality of extracted keywords or concepts.
Experimental Setup and Outcomes
Using benchmark datasets such as TREC Clinical Trials, experiments demonstrated ChatGPT's effectiveness in outperforming human-generated queries concerning trial retrieval metrics, encompassing nDCG@10 and R-Precision. Enhanced prompts yielded competitive performance in identifying eligible trials against baseline EHR-driven methodologies.
Observations on Query Generation Efficacy
The study found that ChatGPT-generated queries could match or surpass traditional human query performance in trial eligibility detection. Importantly, it identified that setting a domain-specific role within ChatGPT, augmented by detailed task descriptions, contributed to improved extraction accuracy.
Implications for Integrated AI Systems
Applying ChatGPT in clinical trial enrollment has transformative potential in reducing direct risks to patients by ensuring precise and rapid data processing. Although promising, the implementation of such AI systems should prioritize data privacy and ethical considerations, adhering to HIPAA standards while enhancing service quality.
Future Directions in Research
Future investigations could refine prompt methodologies further to address nuances such as negation detection and semantic drift in keyword extraction. Additionally, empirical studies should explore the integration of neural re-rankers to improve post-retrieval phases, ensuring both robustness and adaptability in diverse clinical scenarios.
Conclusion
Utilizing ChatGPT to automate elements of clinical trial enrollment presents significant advantages, predominantly in efficiency and accuracy. This paper delineates methods to capitalize on ChatGPT's linguistic capabilities, underlining its potential to revolutionize patient recruitment in clinical trials while influencing broader AI adoption in healthcare systems.


