- The paper introduces NUDGE, which employs neurally-guided symbolic abstraction to derive interpretable logic policies.
- It combines differentiable forward reasoning with an actor-critic framework to optimize rule weights effectively.
- Experimental results demonstrate superior performance and adaptability compared to traditional neural and logic-based methods.
Interpretable and Explainable Logical Policies via Neurally Guided Symbolic Abstraction
Introduction
This paper presents a novel approach in neuro-symbolic reinforcement learning (RL) that addresses the interpretability and explainability challenges posed by traditional deep RL methods. The method, termed Neurally Guided Differentiable Logic Policies (NUDGE), integrates symbolic logic with neural guidance to produce interpretable and explainable policies using logical rules. The approach begins by leveraging trained neural network-based agents to guide the search for candidate-weighted logic rules. These rules are then refined and optimized using differentiable logic within an actor-critic framework.

Figure 1: Overview of NUDGE. Given a state, NUDGE computes the action distribution using relational state representation and differentiable forward reasoning. NUDGE provides interpretable and explainable policies.
Methodology
NUDGE combines differentiable forward reasoning with neurally-guided symbolic abstraction to create logical policies. The system consists of two main modules: policy reasoning and policy learning.
Policy Reasoning: This entails converting raw input states into logical representations. The reasoning step involves three sequential processes:
- Relational Perception: Raw input states are transformed into a set of probabilistic atoms.
- Differentiable Forward Reasoning: Weighted action rules are applied to the probabilistic logical representation to deduce actions.
- Action Selection: The final distribution over possible actions is computed, yielding interpretable and actionable outputs.
Policy Learning: This involves using neurally-guided symbolic abstraction to refine the action rules. A pretrained neural policy guides the search for a promising ruleset. These candidate rules are optimized for weights via the critic of an actor-critic agent.
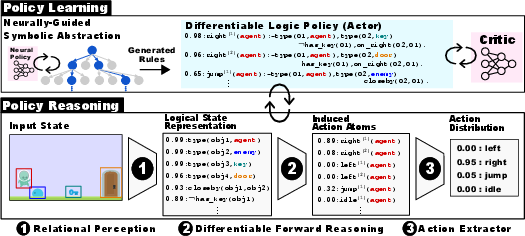
Figure 2: NUDGE-RL. Policy Reasoning and Learning process illustration.
Experimental Evaluation
The performance of NUDGE was evaluated on various environments, showcasing its superiority over purely neural or logic-based systems. It was tested against existing baselines, including Neural PPO and previous logic-based methods without symbolic abstraction.
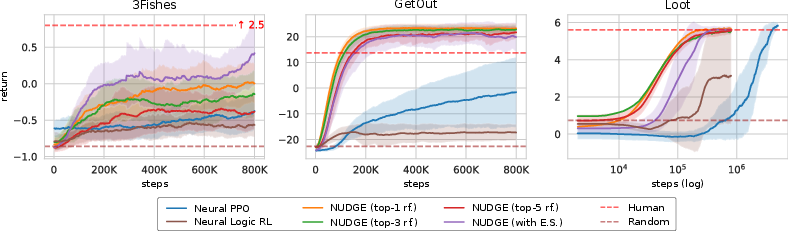
Figure 3: NUDGE outperforms neural and logic baselines in three logic environments.
- Performance: NUDGE outperformed existing neural and logic baselines in logic-oriented environments, such as GetOut, 3Fishes, and Loot. It demonstrated faster convergence and reduced variance in returns.
- Adaptability: The versatility of NUDGE was further highlighted as it adapted effectively to environmental changes without requiring retraining or fine-tuning.
- Interpretability and Explainability: NUDGE's policies were represented as sets of weighted logic rules, making them interpretable. The system could explain the relevance of individual inputs using gradient-based attribution methods, an advantage over traditional neural networks which tend to provide less coherent explanations.
Implications and Future Work
The implications of NUDGE are significant for developing RL agents that require both robustness and transparency in decision-making processes. Importantly, NUDGE's ability to produce interpretable rules and explanations can enhance the user's understanding of agent behavior, particularly in sensitive and complex domains.
Future work could focus on refining the language used for generating predicates and entities, potentially through predicate invention or automatic discovery. The integration of NUDGE with explanatory interactive learning and causal RL also presents interesting research avenues. Given its strength in distilling logical rules, NUDGE might help reduce the reliance on complex and opaque neural networks in favor of more interpretable architectures.
Conclusion
NUDGE represents a significant stride towards creating reinforcement learning agents that are both interpretable and explainable. By leveraging the strengths of neural networks for initial guidance and logic-based rules for policy formation, NUDGE provides an effective framework capable of addressing the challenges of transparency and adaptability in RL applications. The research demonstrates that by combining neural and symbolic approaches, it is possible to achieve performance without sacrificing interpretability, paving the way for future developments in neuro-symbolic AI.


