- The paper presents Kernel Density Matrices (KDMs) that extend traditional density matrices to RKHS for unified modeling of discrete and continuous probabilities.
- It employs both non-parametric and parametric approaches to enable accurate density estimation and probabilistic inference within deep models.
- Experiments show competitive performance in bidirectional classification, conditional generation, and handling label proportions under weak supervision.
Kernel Density Matrices for Probabilistic Deep Learning
The paper "Kernel Density Matrices for Probabilistic Deep Learning" introduces Kernel Density Matrices (KDMs) as a novel mechanism to represent joint probability distributions of continuous and discrete random variables. By extending the concept of density matrices from quantum mechanics into a reproducible kernel Hilbert space (RKHS), the authors provide a differentiable framework for density estimation, inference, and sampling, integrated naturally with deep neural models.
Introduction to Kernel Density Matrices (KDM)
Conceptual Framework
The notion of density matrices from quantum mechanics is pivotal in representing quantum states, incorporating both classical and quantum uncertainties. Density matrices are Hermitian, positive-semidefinite, and act within the Hilbert space representing the quantum system's state space. This research extends density matrices to RKHS, creating Kernel Density Matrices (KDMs) to unify discrete and continuous probability distributions for applications in machine learning.
Density Matrices
A density matrix ρ can be expressed as:
ρ=∑iNpi∣ψi⟩⟨ψi∣
where pi are probabilities associated with states ∣ψi⟩. Extending this to RKHS permits application to various machine learning tasks.
Implementation of KDMs
Discrete and Continuous KDMs
Discrete KDMs utilize kernels like the cosine kernel, suitable for finite dimension RKHS, to represent categorical distributions. Continuous KDMs employ radial basis kernels such as the Gaussian kernel, fulfilling necessary conditions for density representation.
Probabilistic Training
Non-Parametric Density Estimation
Based on Kernel Density Estimation (KDE), non-parametric density estimation using KDMs ensures convergence in probability for continuous probability distributions.
Parametric Density Estimation
Parametric estimation involves maximizing likelihoods, representing a flexible approach to adapt the kernel parameters for training data.
Joint Densities and Inference
Inference using KDMs revolves around transforming input distributions to output distributions, maintaining expressiveness, compositionality, and reversibility—mimicking quantum measurement operations applied in classical machine learning contexts.
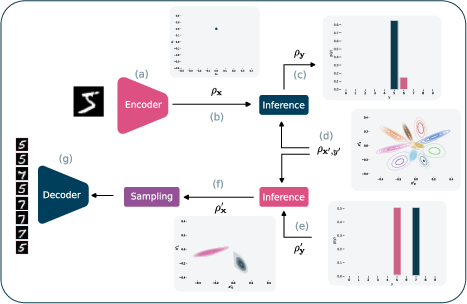
Figure 1: Classification and generation with KDMs. The encoder maps input samples into a latent space, projected as a KDM, facilitating inference with model parameters.
Experiments
Bidirectional Classification and Conditional Generation
Figure 1 illustrates a classifier enhanced by KDM inference modules, transitioning seamlessly between classification and conditional generation. KDM models show performance on par with conventional deep learning models, with added versatility in data generation.
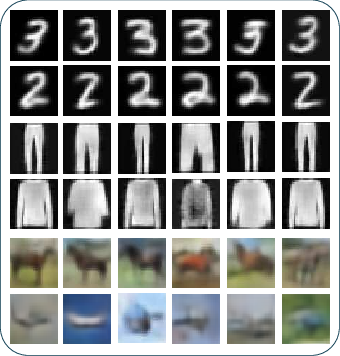
Figure 2: Conditional image generation from Mnist, Fashion-Mnist, and Cifar-10 using the KDM conditional generative model, each row corresponds to a different class.
Learning with Label Proportions
The second experiment showcases KDMs in handling label proportions, demonstrating its adaptability to weakly supervised learning scenarios. KDM's probabilistic modeling of bag uncertainties achieves competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art LLP algorithms.
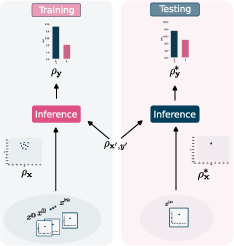
Figure 3: KDM model for classification with label proportions. Model receives bags of instances during training, representing uncertainty effectively.
Conclusion
The paper introduces Kernel Density Matrices as a robust framework for probabilistic deep learning, capable of integrating density matrices into machine learning models efficiently. This contributes significantly to both theoretical and practical aspects of AI, offering new pathways in quantum machine learning applications and inviting future exploration in KDM-centric methodologies.
The versatility of KDMs in various AI applications—spanning from data inference to conditional generation—highlights the potential for further research into broader machine learning contexts and tools leveraging quantum-inspired principles.




