- The paper introduces SBM-AE, which decouples unimodal representations and employs denoising score matching to fuse latent spaces for improved conditional generation.
- It empirically demonstrates monotonic improvements in conditional FID and cross-modal coherence on Extended PolyMNIST and CelebAMask-HQ datasets.
- The model overcomes quality decay seen in traditional multimodal VAEs, enabling scalable and robust generation even with missing modalities.
Score-Based Multimodal Autoencoders: A Technical Analysis
Introduction and Motivation
The increasing complexity and heterogeneity of multimodal datasets necessitate generative models that can synthesize and infer high-fidelity, coherent outputs across modalities. Conventional Multimodal VAEs, while conceptually appealing, suffer substantial quality degradation as the number of modalities increases [daunhawer2022on]. The "Score-Based Multimodal Autoencoder" (SBM-AE) paradigm addresses these fundamental limitations by decoupling unimodal representations and leveraging score-based modeling to learn joint priors over the concatenated latent spaces. This framework preserves unimodal generative quality while enforcing stronger cross-modal coherence and scalability.
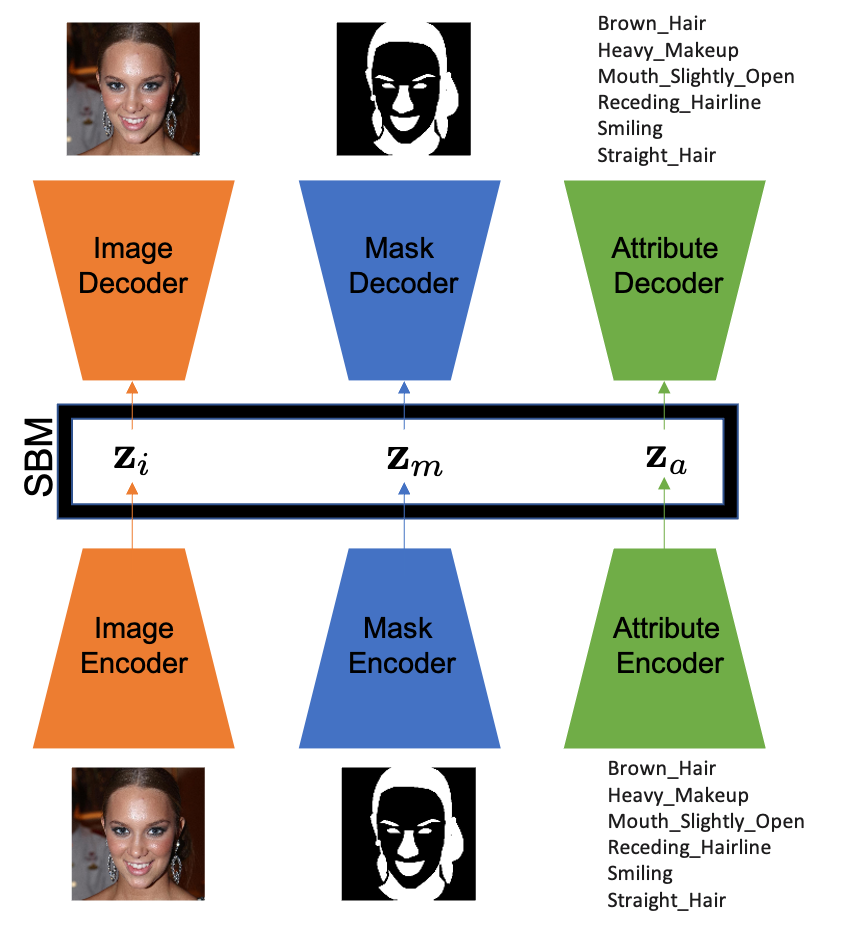
The SBM-AE framework is composed of independently trained unimodal VAEs (or deterministic RAEs), each encoding modality-specific information into latent vectors. These latent vectors are then used to fit a joint score-based model (SBM) via denoising score matching:
The variational lower bound is decomposed over modalities, regularizing each encoder via an isotropic Gaussian prior. In the second stage, the SBM fits a joint prior over all latents to maximize multimodal coherence, using variants of denoising score matching robust to high-dimensional spaces. Conditional inference leverages Langevin dynamics, efficiently sampling missing modalities given observed ones.
SBM-AE advances over prior art in the following ways:
- It circumvents the need for intractable joint posterior modeling (Product/Mixture of Experts, MoPoE [mopoe]), which scale poorly and lose sample quality with many modalities.
- Unlike mixture-based VAEs and hierarchical multimodal VAEs [wolff2022hierarchical], SBM-AE guarantees monotonic improvements in conditional generative fidelity as more modalities are observed, in contradiction to the empirically observed performance decay of predecessors [daunhawer2022on].
- It is robust to missing modalities and supports weak supervision, suggesting flexibility for real-world multimodal applications.
Experimental Validation: Extended PolyMNIST
The framework is empirically validated on Extended PolyMNIST (ten modalities) and CelebAMask-HQ. For PolyMNIST:
- SBM-VAE and SBM-RAE models consistently maintain generative quality with increasing modalities, measured by conditional Fréchet Inception Distance (FID).
- Baseline multimodal VAEs (MVAE, MMVAE, MoPoE, MMVAE+, MVTCAE) exhibit degradation in generative fidelity as modalities are incrementally conditioned.



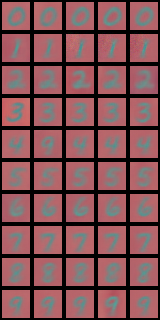
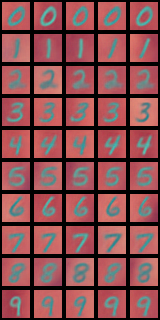
Figure 2: Visual samples generated by SBM-VAE highlight preservation of diversity and crispness in conditional outputs.
Conditional FID results demonstrate monotonic quality improvement for SBM-AE as more modalities are observed, whereas baselines show contradictory quality decay, violating the expectation of information gain.
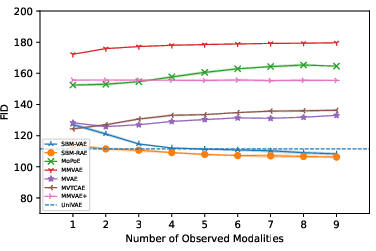
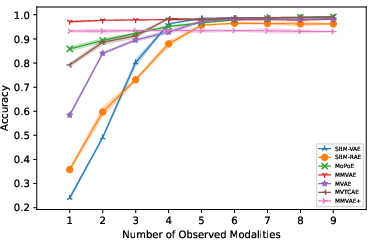
Figure 3: Conditional FID plot reveals that SBM-AE uniquely achieves reduced FID with increased conditional modalities.
Coherence is evaluated using a classifier, confirming superior cross-modal consistency for SBM-AE models in unconditional settings.
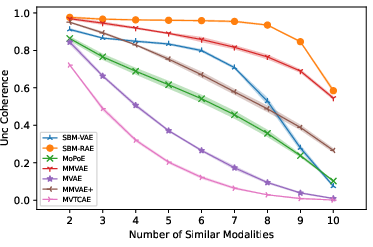
Figure 4: Unconditional generation coherence increases with the number of modalities, showing SBM-AE's scalability.
Scalability analysis confirms that conditional and unconditional metrics remain stable as the number of modalities increases, reinforcing SBM-AE's suitability for large multimodal datasets.
Experimental Validation: CelebAMask-HQ
On CelebAMask-HQ (images, masks, attributes):
- SBM-AE substantially outperforms baselines in unconditional and conditional FID, particularly for the image modality, achieving FID as low as 84 (SBM-VAE) versus 144 (MoPoE).
- Mask and attribute generation F1 scores are competitive, with MoPoE showing modest strengths on non-image modalities.
- Augmenting SBM-AE with DiffuseVAE further reduces FID to 25, approaching diffusion model quality.






Figure 5: SBM-VAE output retains multimodal constraints, with visually consistent synthesized images given mask and attribute conditioning.
Unconditional generation across all modalities confirms the model's capacity for coherent synthesis without observed input.
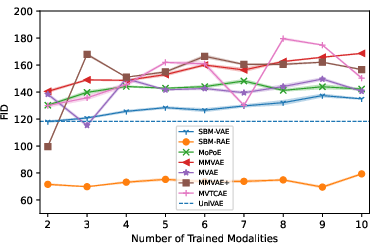
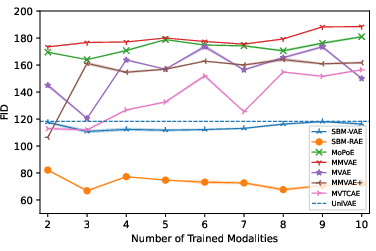
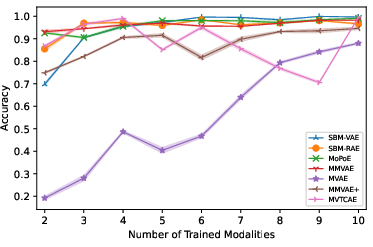
Figure 6: SBM-AE maintains low FID scores when scaling the number of training modalities, marking its computational efficiency and quality robustness.
Numerical Results and Contradictory Claims
The paper presents strong numerical evidence that, contrary to prior multimodal VAEs, the proposed SBM-AE framework guarantees a monotonic quality increase as more conditional modalities are specified, as measured by FID and classifier-based coherence. The unconditional coherence metric shows 84.5% alignment across nine modalities, exceeding all compared baselines.
Further, augmenting SBM-VAE with DiffuseVAE attains state-of-the-art image FID, suggesting the potential of SBM-AE to match cutting-edge generative models (e.g., diffusion models) in multimodal domains.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
The principal theoretical implication is the feasibility of joint score-based priors to model cross-modal dependencies without joint VAE ELBO construction, resolving a central limitation in scaling multimodal generative models. Practically, SBM-AE unlocks more reliable synthesis, inference, and filling in of missing modalities for applications in vision-language, medical data, and multi-view learning.
In future directions, SBM-AE encourages exploration of more expressive score-based networks, weakly-supervised settings, and hybridization with high-fidelity diffusion models for further improvement in multimodal sample quality and scalability.
Conclusion
Score-Based Multimodal Autoencoders offer a principled solution to the persistent quality and coherence problems of multimodal VAEs. By decoupling modality-specific encoders and fusing their latents using denoising score matching, SBM-AE delivers robust, scalable inference and synthesis—both conditional and unconditional—across diverse modalities. The empirical results robustly contradict the prior trend of quality decay with additional modalities, paving the way for advanced multimodal generative modeling with strong potential for future research and application (2305.15708).