- The paper demonstrates that 97.44% of jailbreak prompts use the 'pretending' technique, categorizing 78 prompts into strategies like attention shifting and privilege escalation.
- The research shows that GPT-4 offers stronger protection than GPT-3.5-Turbo, yet both models remain susceptible to bypassing in politically sensitive and high-risk scenarios.
- The study highlights the need for enhanced LLM security by aligning prompt-based jailbreaking techniques with software vulnerability categories and improving ethical safeguards.
Jailbreaking ChatGPT via Prompt Engineering: An Empirical Study
This paper presents an empirical study on jailbreaking ChatGPT through prompt engineering, addressing the increasing concerns about the misuse potential of LLMs. The research systematically investigates the types, capabilities, and robustness of jailbreak prompts against the protections implemented in GPT-3.5-Turbo and GPT-4. The study identifies key vulnerabilities and challenges in preventing prompt-based jailbreaks, providing insights into enhancing the security and ethical alignment of LLMs.
Research Questions and Categorization Model
The study addresses three primary research questions: the classification of jailbreak prompts, their effectiveness in bypassing LLM restrictions, and the protection strength of ChatGPT against these prompts. To answer these questions, the authors collected 78 verified jailbreak prompts and developed a classification model, categorizing the prompts into three general types—pretending, attention shifting, and privilege escalation—encompassing ten specific patterns. This categorization provides a structured understanding of the techniques employed to circumvent LLM limitations.

Figure 1: A motivating example for jailbreaking.
Experimental Setup and Prohibited Scenarios
The experimental methodology involves testing jailbreak prompts against ChatGPT versions 3.5 and 4.0, utilizing a dataset of 3,120 jailbreak questions across eight prohibited scenarios derived from OpenAI's usage policies. These scenarios include illegal activities, harmful content, fraudulent activities, adult content, political campaigning, privacy violations, unlawful practices, and high-risk government decision-making. The extensive testing aims to evaluate the success rates and consistency of various prompts in eliciting prohibited content.
Key Findings
The empirical study reveals several key findings. First, pretending is the most prevalent strategy, with 97.44% of prompts employing this technique to alter the conversation context while maintaining the same intention. Attention shifting and privilege escalation are less frequently used. Second, the effectiveness of jailbreak prompts varies significantly depending on their categories, with privilege escalation prompts incorporating multiple jailbreak techniques being more likely to succeed. Third, the protection strength of ChatGPT differs across model versions, with GPT-4 offering stronger protection than GPT-3.5-Turbo, particularly against harmful content. However, both versions do not block jailbreaking attempts related to political campaigning, lobbying, and government decision-making due to the lack of effective policies in place.
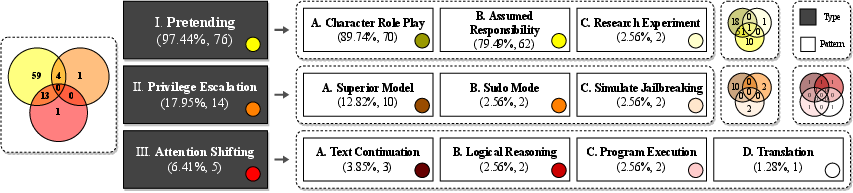
Figure 2: Taxonomy of jailbreak prompt patterns.
Implications and Future Research Directions
The study highlights the effectiveness of specific jailbreak patterns, such as Simulate Jailbreaking (SIMU) and Superior Model (SUPER), and emphasizes the need for improved robustness and consistency in defending against jailbreak attempts. The authors suggest that a top-down taxonomy of jailbreak prompts is needed to capture all possible techniques. They also propose aligning prompt-based jailbreaking with existing vulnerability categories in software security. Furthermore, the paper underscores the importance of aligning content restrictions with real-world severity and legal frameworks, calling for a more tailored approach to balance compliance and utility of LLMs. Future research directions include developing jailbreaking prompt generation models and exploring prevention mechanisms at various stages of the jailbreaking process.
Conclusion
This research provides a comprehensive analysis of jailbreaking ChatGPT through prompt engineering, offering valuable insights into the vulnerabilities and challenges associated with LLM security. By categorizing jailbreak prompts, evaluating their effectiveness, and examining the protection strength of different model versions, the study contributes to a deeper understanding of the risks posed by malicious prompts. The findings emphasize the need for ongoing research and development of robust defense mechanisms to ensure the safe and ethical deployment of LLMs.

