- The paper introduces the StructGPT framework that iteratively reads and reasons over structured datasets to enhance LLM performance.
- It employs specialized interfaces for knowledge graphs, tables, and databases, achieving notable improvements such as a 72.6% Hits@1 in KGQA tasks.
- Error analysis and case studies underscore the framework’s potential for refining prompt design and scaling LLM applications in real-time systems.
StructGPT: A General Framework for LLM Reasoning over Structured Data
Introduction
The paper "StructGPT: A General Framework for LLM to Reason over Structured Data" (2305.09645) introduces StructGPT, a framework designed to enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs when dealing with structured data. The work addresses the inherent challenge that LLMs face due to their pretraining on unstructured text, which limits their capability to understand and reason over structured datasets like knowledge graphs (KGs), tables, and databases (DBs). The research proposes an Iterative Reading-then-Reasoning (IRR) approach utilizing specialized interfaces for data interaction.
Framework Overview
The StructGPT framework incorporates an iterative procedure called invoking-linearization-generation, designed to disentangle the processes of reading and reasoning, thereby allowing LLMs to focus on reasoning tasks. The procedure begins with invoking interfaces to extract targeted information, followed by linearizing this information into a textual format digestible by LLMs, and culminating in a generation phase where the model synthesizes this information to produce answers or executable queries.
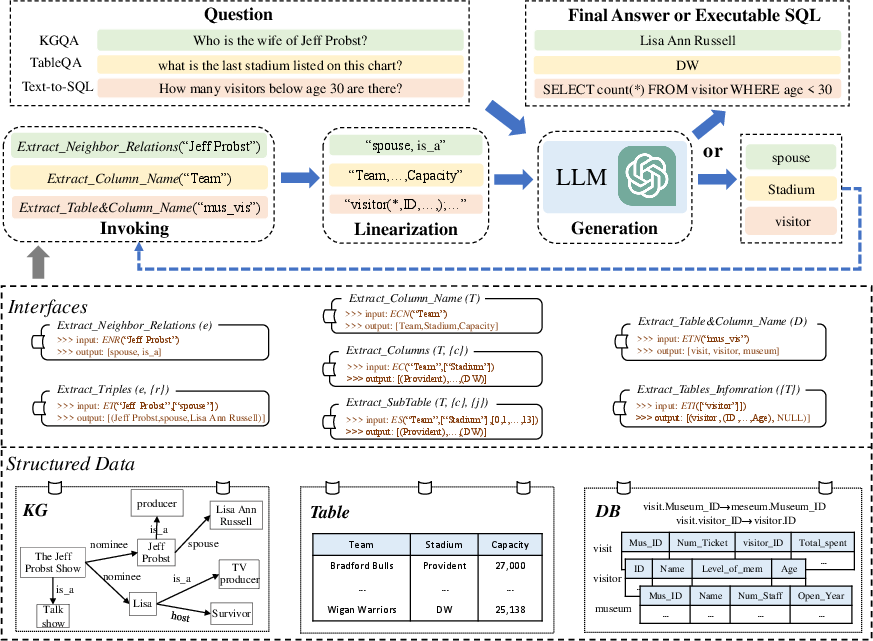
Figure 1: The overview of the proposed iterative reading-then-reasoning approach.
Interfaces for Structured Data
The paper details interfaces tailored for three types of structured data:
- Knowledge Graphs (KGs): Interfaces enable the extraction of neighboring relations and triples related to an entity, facilitating multi-hop reasoning.
- Tables: Interfaces allow for column and sub-table extraction, simplifying the process of isolating relevant data.
- Databases (DBs): Interfaces aid in accessing table structures, columns, and foreign key information to form executable SQL queries.
These specialized interfaces reduce the complexity of direct manipulation of structured data, focusing LLMs' efforts on high-level reasoning tasks.
Experimental Results
StructGPT was tested on tasks across KG-based QA, TableQA, and Text-to-SQL, showing promising results. For instance, it achieved Hits@1 scores of 72.6% in WebQuestionsSP using ChatGPT, reflecting substantial improvement when compared to baseline LLM performance without structured data integration.
KGQA: The framework demonstrated competence in reasoning over multi-hop questions that exceed the zero-shot capabilities of conventional LLMs.
TableQA: Here, StructGPT helped LLMs surpass baseline accuracies in answering questions requiring deep table comprehension by effectively narrowing down the search space to relevant sub-tables.
Text-to-SQL: The framework significantly improved LLM performance in generating accurate SQL queries by facilitating better schema and relation extraction from databases.
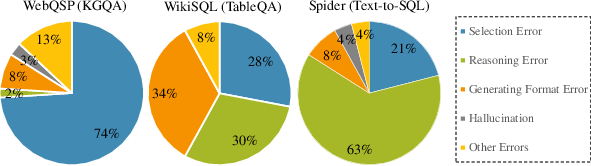
Figure 2: Proportions of different error types in three datasets over different types of structured data.
Error Analysis and Case Studies
The paper identifies common error types such as selection errors and reasoning errors, which helped in understanding the limitations of the proposed approach. The error analysis suggested targeted improvements in prompt design and iteration mechanisms to potentially enhance LLM accuracy further.
Case studies demonstrated how the framework isolates relevant relations and data points to yield more precise outputs. For example, correctly identifying and leveraging the "education" relation in KGQA scenarios shows StructGPT's ability to pinpoint pertinent information for complex question answering tasks.
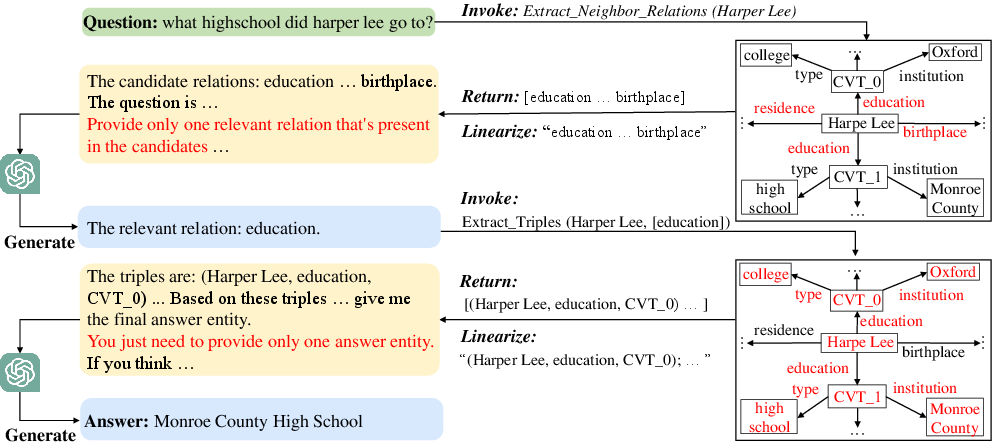
Figure 3: Case paper of our method on WebQSP.
Implications and Future Directions
StructGPT not only advances the cognitive boundaries of LLMs with structured data, but also sets a precedent for future research on tool-augmented LLMs. By integrating clear interfaces with LLMs, larger and more intricate forms of structured data can be more efficiently managed, hinting at broader applications in automated data analysis and decision-making systems.
Future research could focus on refining error-handling mechanisms and exploring interfaces for other structured data types. Additionally, scalability and efficiency of the approach can be improved to handle ultra-large datasets seamlessly, paving the way for applications in real-time intelligent systems.
Conclusion
The paper presents StructGPT as a cohesive framework that strategically enhances LLMs' interaction with structured data through a series of iterative data-reading and reasoning steps. This approach, validated by rigorous experiments and analysis, offers a promising avenue for expanding the utility and accuracy of LLMs in structured-data scenarios, bridging the gap toward more robust and intelligent natural language processing systems.




