- The paper identifies three distinct user groups with varying needs from AI mixing tools, revealing key differences in acceptance and expectations.
- It utilizes interviews, questionnaires, and online discussions to evaluate the practical integration of AI in streamlining music mixing workflows.
- Findings emphasize the need for AI systems with adjustable automation and context-awareness to balance efficiency and creative control.
Adoption of AI Technology in the Music Mixing Workflow
Introduction
The paper "Adoption of AI Technology in the Music Mixing Workflow: An Investigation" explores the integration of AI technologies into the music mixing process. Through a combination of interviews, questionnaires, and analysis of online discussions, the authors identify three primary user groups—amateurs, professional-amateurs (pro-ams), and professionals—each with distinct requirements and expectations from AI mixing tools. These insights are expected to guide the development of AI mixing tools tailored to these user segments.
User Group Segmentation
The research identifies three categories of users who engage with smart mixing tools: amateurs, pro-ams, and professionals.
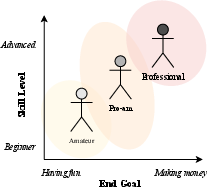
Figure 1: Categories of users for smart tools.
- Amateurs: This group primarily seeks tools that enable them to produce a "decent" mix with minimal effort. They are characterized by their limited technical skills and budget constraints, favoring fully automatic mixing solutions.
- Pro-Ams: Positioned between amateurs and professionals, pro-ams use smart tools as a learning aid and for stylistic experimentation. They require more precision and control compared to amateurs but remain resource-conscious.
- Professionals: Professionals view AI tools as assistive, focusing on enhancing workflow efficiency by automating repetitive tasks. They demand high precision, customizability, and seamless integration into established workflows.
The study reveals varied acceptance of AI technology across user groups.
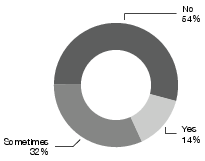
Figure 2: Responses to the use of AI-powered tools in mixing workflow as reported by pro-ams and pros.
- Amateurs are generally enthusiastic about adopting AI tools due to their ease of use and cost-effectiveness, although they are more forgiving of lower quality results.
- Pro-Ams exhibit cautious optimism, aware of the limitations yet optimistic about leveraging AI for educational purposes and creative inspiration.
- Professionals exhibit mixed reactions. While some appreciate the potential for efficiency gains in non-creative aspects, others criticize AI tools for lacking the creativity and nuanced understanding required in professional mixing.
Professionals specifically view AI tools as beneficial for standardizing and speeding up repetitive processes. However, skepticism remains due to the perception of AI as "black boxes" that may compromise creative control and precision in audio production.
Future Directions
The future development of AI mixing tools hinges on addressing three main factors: precision and quality of output, seamless workflow integration, and enhanced interaction models that build trust and allow for artist collaboration.
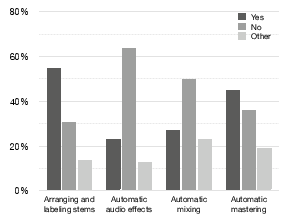
Figure 3: Preference for the use of different AI tools in mixing workflow as reported by pro-ams and pros.
- Control vs. Automation: There is potential in developing AI tools with adjustable levels of control and automation to cater to different user expertise levels. This flexibility can allow the same tool to serve as an automatic solution for amateurs or a nuanced assistive tool for professionals.
- Seamless Integration: Integration into existing workflows is crucial, particularly for professionals. AI tools must offer familiar interfaces and functionality to be effectively adopted into traditional mixing setups.
- Context-Awareness: Enhancing AI tools with the capacity to understand the contextual nuances of audio works could bridge the gap between automatic processing and creative audio production, making AI tools more acceptable to creative professionals. Developing systems capable of context-aware processing based on a mix's intended emotional effect is considered essential.
Conclusion
The paper concludes by emphasizing the importance of user-specific insights in the development of AI tools for music mixing. Customizing solutions to meet specific user needs across different skill levels will enhance the acceptance and efficacy of these technologies. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into music production workflows requires careful consideration of user expectations and seamless adaptability to existing practices.


