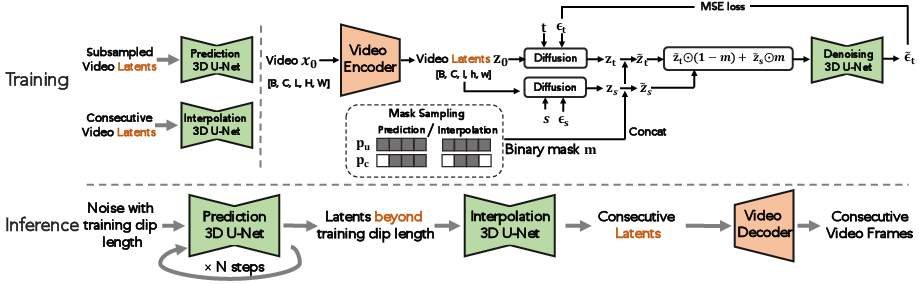
- The paper presents a novel hierarchical latent video diffusion model that leverages a 3D video autoencoder and diffusion processes to generate high-fidelity, long-duration videos.
- The model reduces computational load by operating in a low-dimensional latent space and uses hierarchical generation to mitigate error accumulation over extended sequences.
- Experimental results show significant improvements over previous approaches, with robust performance in both short and long video generation and applicability to text-to-video synthesis.
Latent Video Diffusion Models for High-Fidelity Long Video Generation
Introduction
The research paper "Latent Video Diffusion Models for High-Fidelity Long Video Generation" addresses the persistent challenge of generating high-quality and lengthy videos—a significant need within AI-generated content, gaming, and film production domains. Traditional GANs and autoregressive models have fallen short, unable to deliver the requisite fidelity and temporal scope due to limitations such as instability and mode collapse. The paper introduces a latent-video-diffusion-model framework (LVDM) that leverages low-dimensional 3D latent spaces and hierarchical diffusion processes to achieve extended video generation without prohibitive computational costs.
Methodology
Hierarchical Latent Video Diffusion Model (LVDM)
The LVDM framework introduces a novel hierarchical generative architecture to overcome the constraints of existing diffusion models.
Experimental Results
This section highlights the empirical validation of LVDM against state-of-the-art video generation techniques on datasets such as UCF-101, Sky Timelapse, and Taichi.
- Short Video Generation: The paper notes significant improvements over prior models, exhibiting a marked reduction in metrics like Fréchet Video Distance (FVD) and Kernel Video Discrepancy (KVD) across different benchmarks and resolutions.
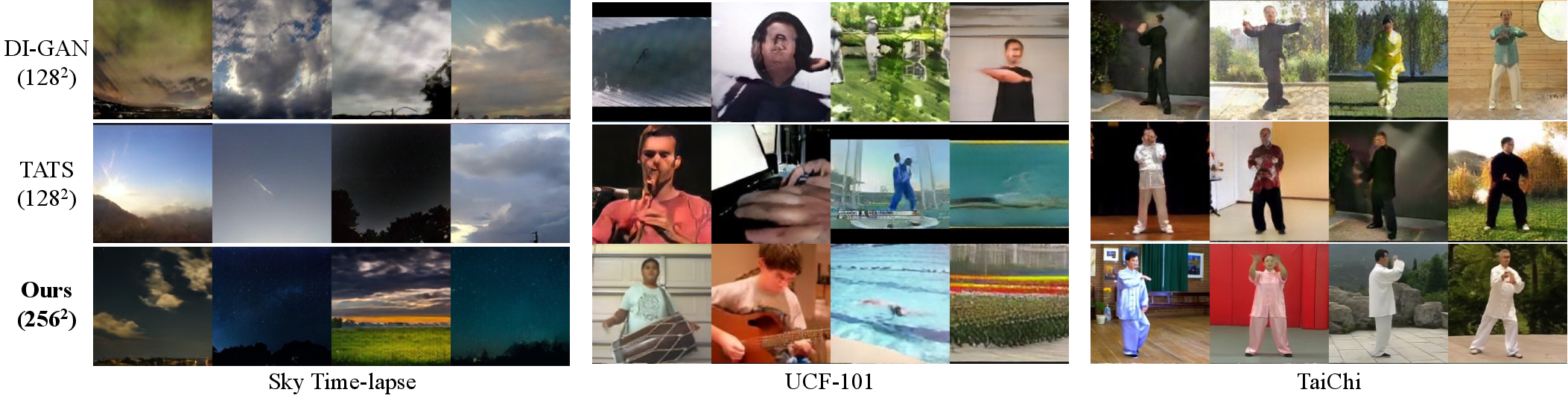

Figure 2: Qualitative comparison highlighting LVDM's superior spatiotemporal consistency versus state-of-the-art models in short video synthesis.
- Long Video Generation: LVDM prevails over TATS in generating videos extending beyond 1000 frames, with negligible degradation in metric evaluations over time (Figure 3, Figure 4).

Figure 3: LVDM's long video generation showing improved quality retention compared to TATS.
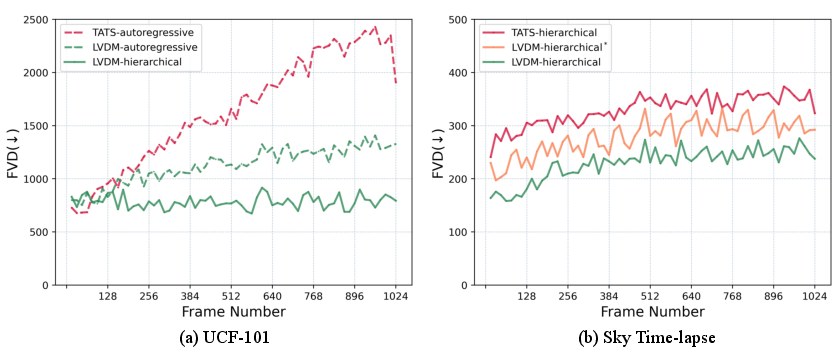
Figure 4: Quantitative analysis illustrating LVDM's performance over TATS on extended video generation tasks.
Extension to Text-to-Video
An extension to LVDM accommodates text-to-video synthesis, upgrading the model with pre-trained text-to-image systems to adeptly generate coherent video sequences from textual descriptions. The framework's versatility is validated on subsets from datasets like WebVid, demonstrating its applicability in multimodal settings (Figure 5).

Figure 5: Results of LVDM's extension to text-guided video generation.
Conclusion
The LVDM framework introduces an efficient and scalable approach for generating high-fidelity, long-duration videos. By optimizing latent space dynamics and employing hierarchical strategies, LVDM efficiently broadens video generation capabilities beyond prevailing models. This approach's robust applicability extends to text-to-video domains, setting a benchmark for future explorations in video synthesis, promising further enhancements in training efficiency and architectural evolution.