- The paper introduces S2IR-GAN, a GAN-based model using energy decay relief loss for improved blind RIR estimation in reverberant environments.
- The methodology employs an encoder-decoder architecture combined with EDR, CGAN, and MSE losses to accurately capture key RIR features.
- Evaluations demonstrate a 22% improvement in early reflection energy capture and a 6.9% reduction in ASR word error rate compared to baselines.
Towards Improved Room Impulse Response Estimation for Speech Recognition
Introduction
The paper "Towards Improved Room Impulse Response Estimation for Speech Recognition" proposes an innovative method for blind Room Impulse Response (RIR) estimation aimed at enhancing Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) performance. RIR estimation is crucial in understanding the reverberation effects that occur due to the acoustic properties of environments like room geometry and materials. These reverberations significantly affect various audio applications, including ASR, speech dereverberation, and augmented/virtual reality.
The primary challenge in RIR estimation lies in the accurate measurement and simulation of the acoustic characteristics of environments without requiring extensive resources or a 3D scene representation. Traditional signal processing and recent deep learning approaches have attempted to tackle RIR estimation with varying success. This paper introduces a generative adversarial network (GAN)-based model, S2IR-GAN, utilizing an energy decay relief loss, which exhibits superior performance both in acoustic evaluation metrics and ASR tasks.
Methodology
S2IR-GAN Architecture
The S2IR-GAN incorporates an encoder-decoder architecture designed to estimate the RIR from reverberant speech. The encoder extracts RIR features, while the decoder reconstructs the RIR from these features. Key components include convolutional layers that adjust dimensions and channels to capture and construct RIR patterns.
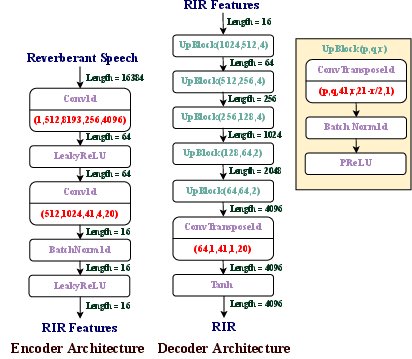
Figure 1: The encoder-decoder architecture of our S2IR-GAN. Our encoder network extracts the RIR features, and our decoder network constructs an RIR from the extracted features. For Conv1d layers and ConvTranspose1d layers, the parameters are input channels, output channels, kernel size, stride, and padding. The last parameter of ConvTranspose1d is output padding. We use a negative slope of 0.2 for the Leaky ReLU layers.
Training Objective
The training of S2IR-GAN involves optimizing an RIR estimation network with a discriminator network, using reverberant speech and corresponding RIR data. The objective function comprises three main losses: Energy Decay Relief (EDR) loss, Conditional GAN (CGAN) error, and Mean Square Error (MSE).
- EDR Loss: Captures the energy properties of the RIR.
- CGAN Error: Ensures accurate RIR estimation from reverberant speech by making estimations hard for the discriminator to differentiate from ground truth.
- MSE: Measures the difference between the estimated and actual RIRs.
Acoustic Evaluation
The approach was tested using synthetic reverberant speech from the LibriSpeech dataset and RIRs from the Meta RIR dataset. Evaluations measured EDR loss, Early Reflection Energy (ERE) loss, DRR error, and MSE.
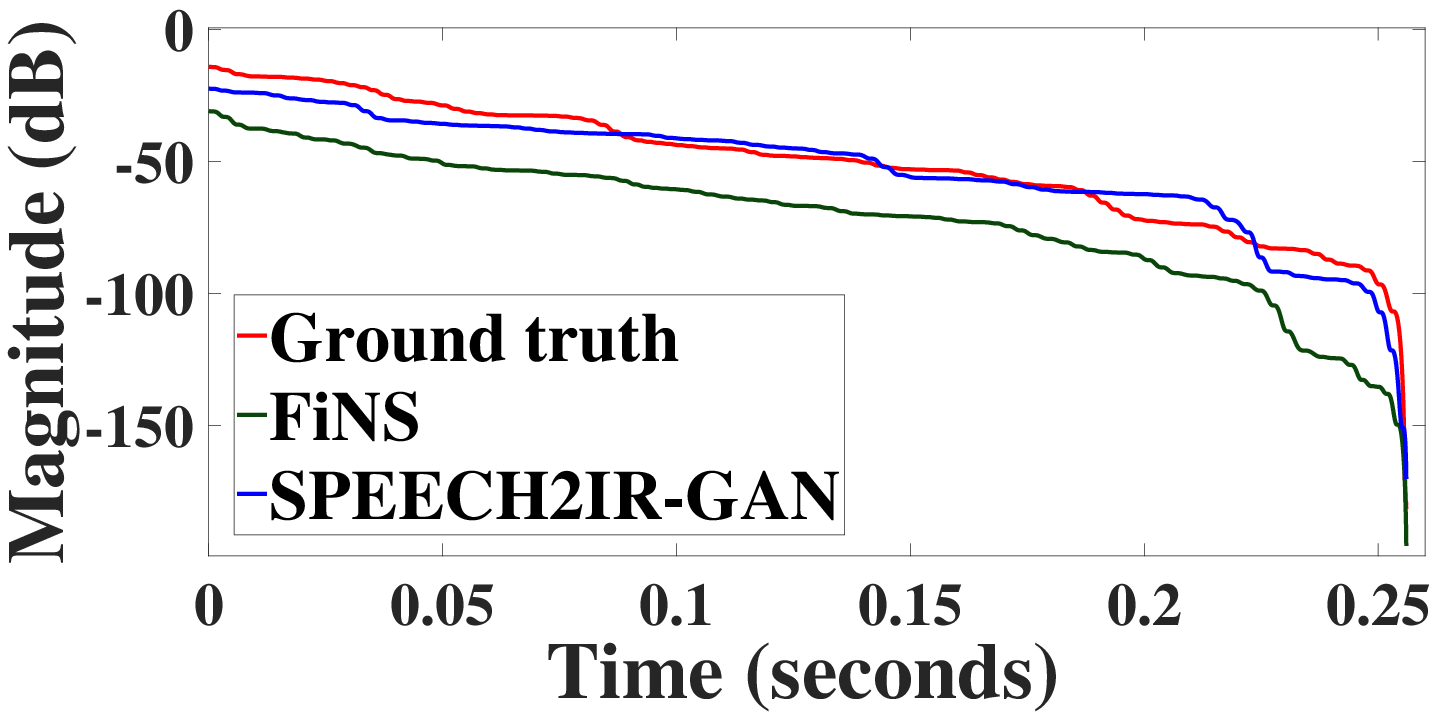
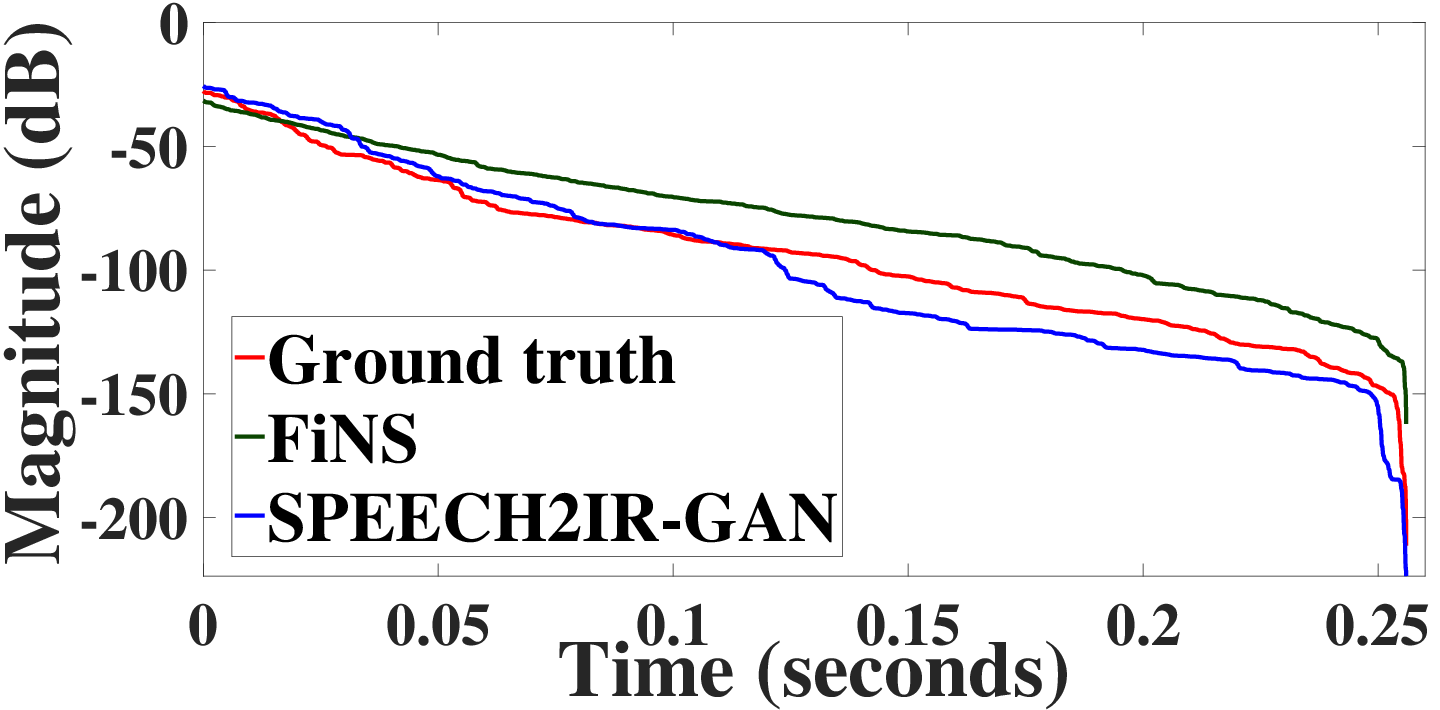
Figure 2: Time domain plot of the ground truth RIR and the estimated RIR from our S2IR-GAN. The estimated RIR has similar macroscopic structure as the ground truth RIR while the fine structure differs from the ground truth RIR.
S2IR-GAN demonstrated a 22% improvement in capturing ERE and a 17% improvement in energy metrics compared to baselines. Figure 2 depicts the time-domain similarity between estimated and actual RIRs, confirming the model effectively captures macroscopic RIR structures despite discrepancies in finer details.
Automatic Speech Recognition Evaluation
For ASR evaluation, the model was tested using the AMI corpus with close-talk and far-field speech data. The ASR system was trained with synthetic speech data augmented using estimated RIRs from S2IR-GAN and FiNS models. S2IR-GAN achieved a 6.9% reduction in Word Error Rate (WER) compared to existing models, underlining its capability to better align training and testing data reverberations.
Conclusion
The S2IR-GAN model excels in blind RIR estimation, significantly enhancing performance in ASR applications. The paper presents a robust framework leveraging GANs and energy-centric losses, surpassing state-of-the-art models in acoustic fidelity and practical ASR efficacy. While challenges remain in capturing fine temporal RIR structures, the perceptual impacts appear minimal, paving the way for future research exploring multi-modal data and broader application contexts.




