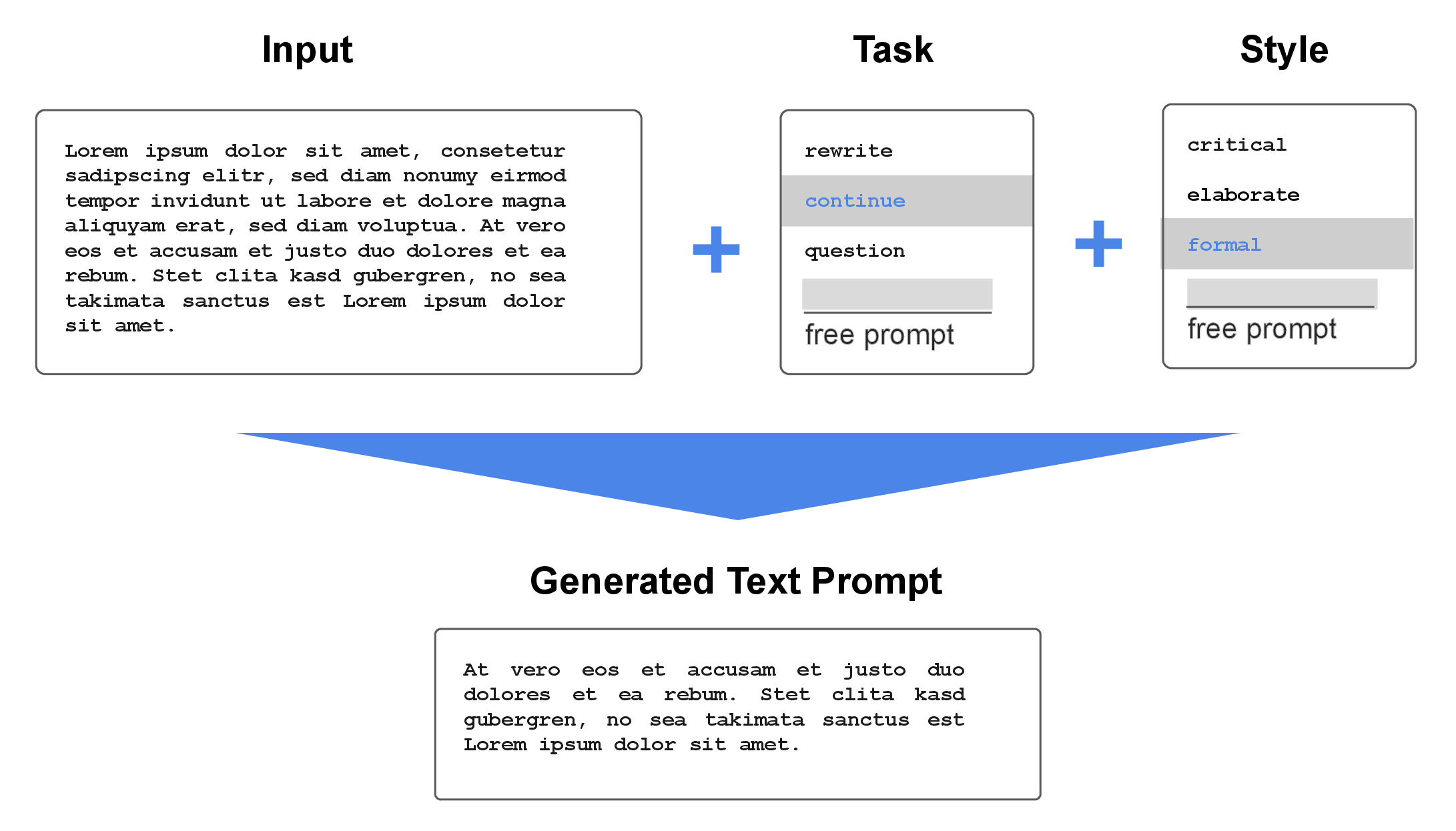
- The paper demonstrates that prompt engineering with zero- and few-shot techniques can democratize access to creative AI for non-expert users.
- It shows that interactive, modular prompt interfaces significantly enhance task-specific outcomes and user collaboration in generative models.
- The study identifies challenges such as iterative trial-and-error, computational delays, and ethical issues that must be tackled for optimal human-AI interaction.
How to Prompt? Opportunities and Challenges of Zero- and Few-Shot Learning for Human-AI Interaction in Creative Applications of Generative Models
Introduction
The study titled "How to Prompt? Opportunities and Challenges of Zero- and Few-Shot Learning for Human-AI Interaction in Creative Applications of Generative Models" explores how deep generative models can be repurposed for creative tasks through prompting. The prominence of zero-shot and few-shot learning has markedly shifted how task-specific AI models are utilized, emphasizing user-written prompts without the need for conventional retraining processes. This paper explores the interaction paradigms, especially in creative writing, and evaluates the potential and hurdles associated with leveraging prompts for human-AI co-creation.
Interactive Applications and Prompt Engineering
Recent interactive systems, such as AI Chains, demonstrate the necessity for sequential and modular use of LLMs to solve complex tasks, moving beyond individual one-shot interactions. Projects like Story Centaur demonstrate graphical interfaces that help users construct effective prompts by providing structural guidance and pre-defined phrases. Such platforms underscore the evolving landscape where few-shot learning can be applied in user-facing applications without requiring profound technical expertise.
Prompt engineering, a systematic method for optimizing prompt efficacy, continues to evolve with strategies like modifying word order for improved outcomes or using automatic prompt generation tools like AutoPrompt. These advancements suggest that even non-expert users can significantly harness LLM capabilities with correct interfacing.
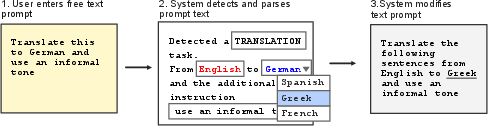
Figure 1: In this GUI example, users enter a prompt in natural language and the system automatically parses this input. Key parameters such as detected task and task parameters can thus be edited directly. Then, the system automatically creates the (refined) text prompt for the generative model.
Opportunities in Prompting for Creative Applications
Prompting allows users, particularly those without technical backgrounds, to define, refine, and operate AI-driven tools through natural language. This both democratizes access to generative systems and enhances real-time user collaboration in creative processes. The paper identifies several opportunities arising from this paradigm shift:
Challenges and Systematic Prompting Support
Despite the potential, the trial-and-error nature of current prompting systems creates challenges. Most users struggle with lack of systematic guidance, and prompts often require iterative, exploratory approaches without guaranteed outcomes. This necessitates interfaces that can abstract commonly effective prompt patterns for everyday users.
Moreover, the interaction might be hindered by computational latency and resource-intensive requirements. As users rely on prompts to drive creative outcomes, time delays can disrupt user experience and workflow continuity. Ethical concerns relating to bias in model outputs and accessibility gaps also represent pivotal areas for ongoing research and interface design adjustments.
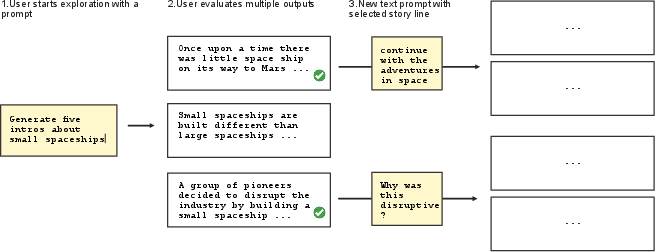
Figure 3: This example GUI focuses on prompt exploration and combination: Users write prompts to direct a ``narrative tree'' showing multiple possible responses to each prompt. Users select some of them as context for the next prompt(s), which direct the narrative further.
Designing Supportive UIs for Creative Prompting
The authors propose several design goals for creating user interfaces that effectively support prompting in creative applications:
Conclusion
Prompts represent a significant shift in enabling real-time, versatile user interaction with generative AI models, particularly in creative domains. By addressing the outlined challenges and capitalizing on emergent opportunities, prompting can bolster human creativity, enabling dynamic interaction with AI. Future work should focus on refining user interfaces to ensure they are conducive to effective prompting while maintaining accessibility and ethical integrity. Through collaborative and interactive design strategies, the potential of generative models as user-driven creative agents can be further realized.