- The paper presents a novel dataset capturing mixed-initiative interactions in multi-turn information-seeking dialogues.
- It details a rigorous annotation pipeline that leverages Wikipedia to ground diverse agent strategies including clarifications and partial answers.
- Evaluation shows baseline models underperform human-level benchmarks, highlighting challenges in passage retrieval and adaptive response generation.
Introduction
The paper "INSCIT: Information-Seeking Conversations with Mixed-Initiative Interactions" (2207.00746) introduces the INSCIT dataset, developed to support the advancement of conversational agents in multi-turn information-seeking contexts. Unlike prior corpora which primarily focus on user-driven dialogue where the agent merely responds or abstains, INSCIT captures mixed-initiative dynamics — where agents are empowered to proactively steer interactions by providing direct answers, requesting clarifications, or sharing relevant but non-definitive information, all grounded in a large-scale knowledge source (Wikipedia). This design increases ecological validity for both dialogue modeling and response generation benchmarks.
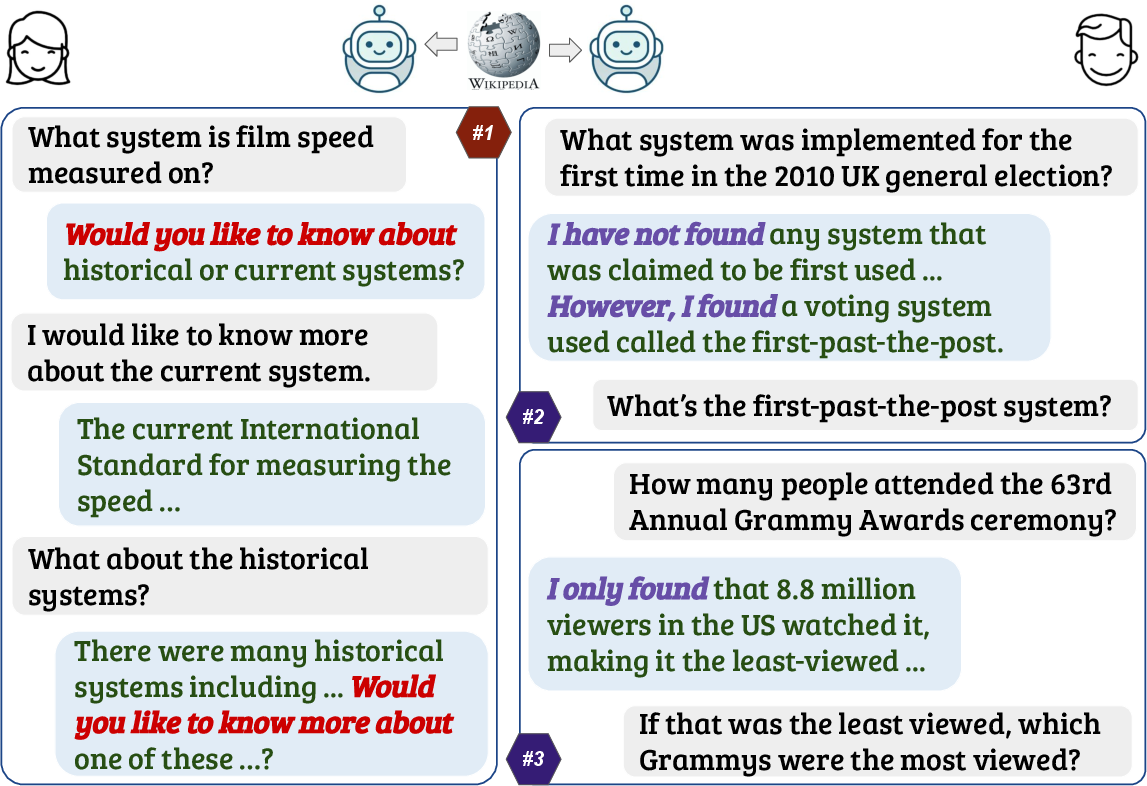
Figure 1: Typical dialogue flows in INSCIT illustrate agent behaviors: clarifying underspecified queries (left) and providing partial/relevant information when no direct answer exists (right).
Corpus Design and Annotation Pipeline
INSCIT comprises 805 natural human-human conversations, totaling 4,712 user-agent turns across diverse domains. The annotation pipeline is meticulously constructed to ensure dialogue coherence, high-quality grounding, and comprehensive coverage of information-seeking strategies:
- User turn design minimizes constraints, encouraging genuinely underspecified or ambiguous queries typical of real user behavior.
- Agent annotation leverages an integrated search tool scoped to Wikipedia and collects up to four relevant evidence passages per turn. Agents select one of four response strategies: direct answer, clarification, relevant answer, or no information.
- Validator review confirms that evidence passages are used correctly, that responses are both factually consistent and coherent, and that the chosen interaction strategy is appropriate.
This controlled crowdsourcing, augmented by incentive structures rewarding comprehensiveness, yields enriched agent behavior diversity and robust validation.
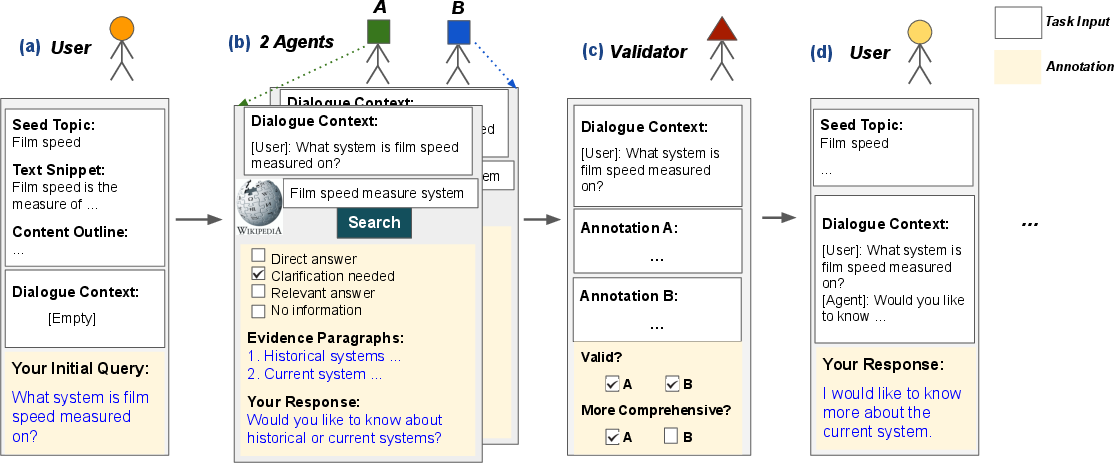
Figure 2: Annotation pipeline diagram. Parallel annotation and validation steps produce multiple reference agent responses and facilitate extensive quality control.
Dialogue and Strategy Diversity
The dataset departs from prior work by embedding substantial agent-side initiative. Quantitatively, 28.5% of agent utterances are either clarifications (12.7%) or relevant information when no direct answer is available (13.1%), with multi-passage grounding and open-endedness prevalent.
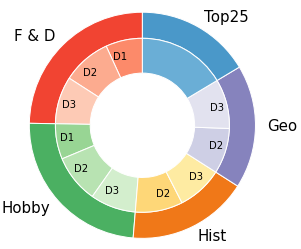
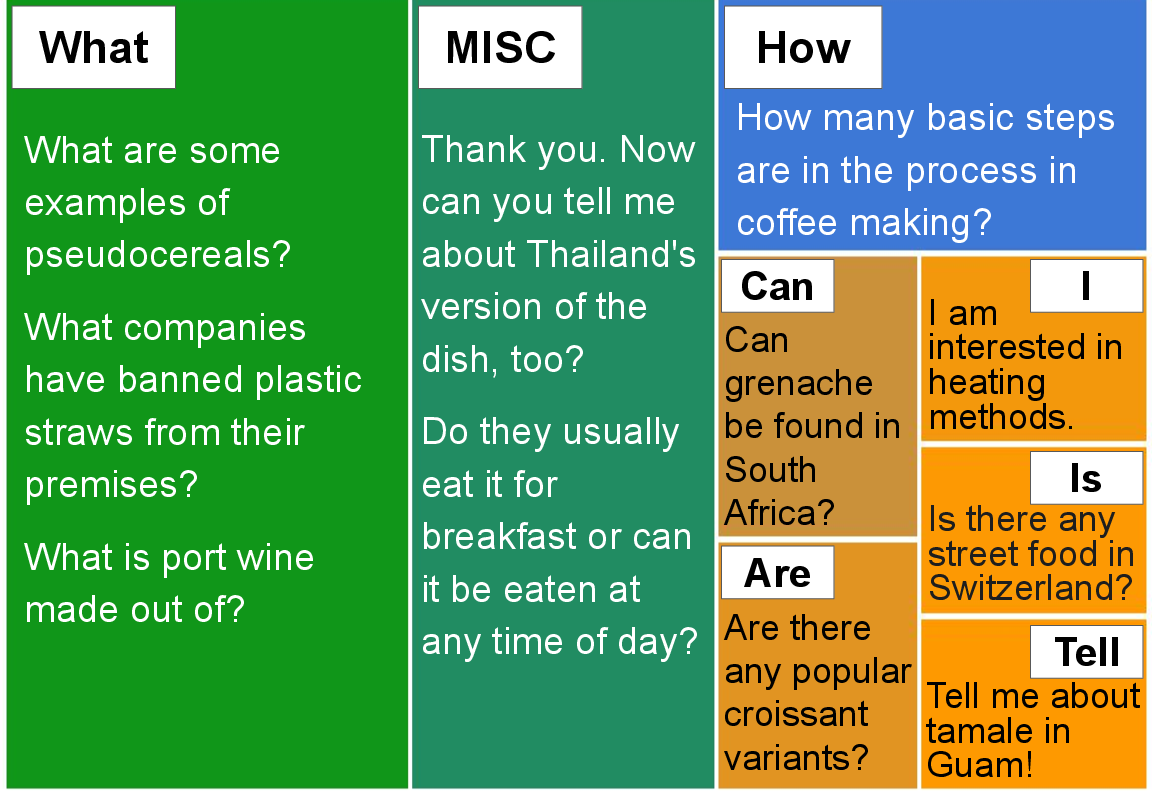
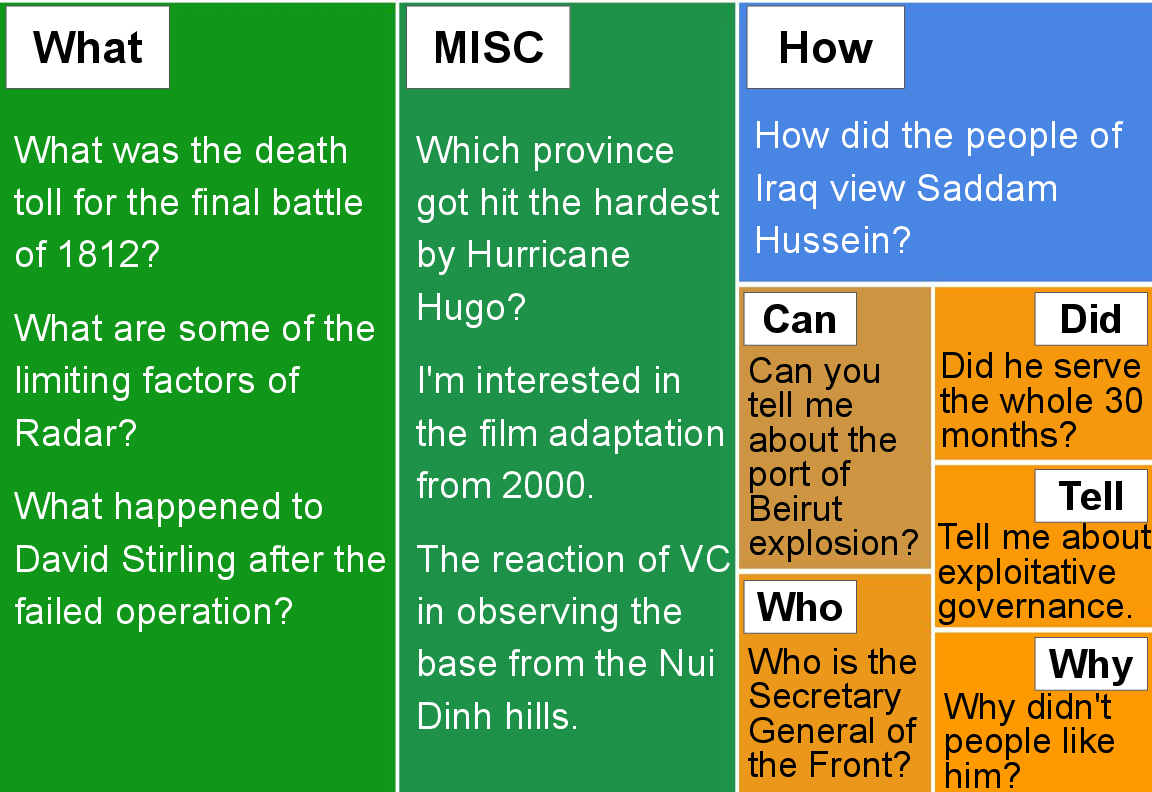
Figure 3: Analysis of user and agent turn diversity. Category breakdowns and token distributions demonstrate coverage across open questions and agent strategies.
Clarification-type responses are most frequent at dialog onset or after ambiguous turns, reflecting authentic conversational ambiguity and iterative intent refinement. The agent's use of diverse strategies is grounded in distinct evidence sets and often contingent on the nature of available knowledge — as shown by high variability in agent responses even within comparable contexts.
INSCIT is structured for two subtasks essential to conversational information-seeking agents:
- Passage Identification: Model must select a comprehensive set of evidence passages from Wikipedia relevant to the current user request and context, in contrast to simple ranking or single-passage selection.
- Response Generation: Given the chosen passages and the dialogue history, the model must produce a coherent, factually consistent, and comprehensive agent reply tailored to the interaction type.
These formulations require joint optimization of knowledge selection and strategy adaptation — especially for multi-passage and open-ended contexts.
Baseline Systems and Evaluation Protocol
Two advanced baseline models are trained:
- Fusion-in-Decoder (FiD): A generative reader encoding all retrieved passages independently and attending to them during response generation.
- DIALKI + FiD (Pipelined): DIALKI provides knowledge identification, followed by FiD response generation using selected passages.
Retrievers (BM25, DPR) gather candidate passages; models are trained with limited INSCIT data, sometimes leveraging prior conversational QA corpora for initialization.
Evaluation employs both automatic metrics (passage identification F1, response generation sacreBLEU and token F1) and a comprehensive human protocol focused on evidence utility, factual consistency, dialogue coherence, and information comprehensiveness. Notably, baselines significantly underperform relative to human annotators — especially for non-direct-answer settings.
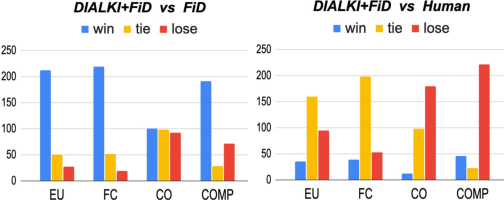
Figure 4: Comparative human evaluation of principal dimensions: evidence utility, factuality, coherence, and comprehensiveness. DIALKI+FiD scores below humans, with greatest gap in agent initiative scenarios.
Experimental Results and System Analysis
DIALKI+FiD outperforms FiD on most metrics, with best automatic scores for passage identification (23.7 F1), response BLEU (16.0), and RG-F1 (27.8), but both lag far behind human-level benchmarks (52.5, 33.8, 43.5 respectively). Error analysis highlights several failure modes:
- Passage retrieval remains the bottleneck: The retrieval component's performance constrains downstream generation quality, especially for ambiguous or open-ended cases and multi-passage contexts.
- Strategy inference and response adaptation challenges: Models frequently fail to fuse information from multiple passages or default to simplistic direct-answer modes, rarely producing nuanced clarifications or partial answers as humans do.
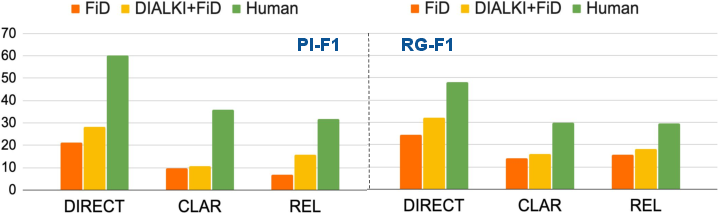
Figure 5: System performance breakdown by response strategy (direct, clarification, relevant answer). Marked degradation for clarifications and multi-passage cases, consistent across systems.
Implications and Future Directions
INSCIT’s establishment of mixed-agent initiative and multi-passage, open-domain grounding sets a rigorous benchmark for future conversational QA advances. The dataset exposes critical gaps in current neural agents’ ability to:
- Jointly infer user intent, retrieve relevant evidence, and adapt response strategy.
- Handle implicit ambiguity, constraint relaxation, and iterative query refinement in information-seeking scenarios.
- Achieve factual consistency and response comprehensiveness in multi-turn, multi-passage contexts.
Research on improved retrieval, knowledge fusion, adaptive strategy modeling, and transfer learning from larger corpora is essential. The authors highlight opportunities for more user-side initiative modeling, trustworthiness assessment of knowledge sources, and development of robust interactive evaluation metrics.
Conclusion
INSCIT advances the study of conversational agents by foregrounding mixed-initiative interactions, response strategy diversity, and multi-evidence grounding. Both practical and theoretical findings indicate significant gaps between state-of-the-art models and human performance, especially in handling ambiguous, multi-passage, and open-ended queries. Future work should prioritize robust passage identification, sophisticated information fusion, and agent initiative modeling; these directions are likely to inform the next generation of interactive information-seeking systems in open domains.








