- The paper proposes HERO, which decomposes cooperative tasks into hierarchical sub-tasks using high-level and low-level policy layers.
- It integrates opponent modeling in the high-level layer to predict other agents' behaviors, enhancing training stability in non-stationary environments.
- Experimental evaluations show that HERO outperforms state-of-the-art MARL methods in real-world scenarios like cooperative lane change.
Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning with Opponent Modeling for Distributed Multi-agent Cooperation
The paper explores enhancing multi-agent cooperation through a hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) approach with an opponent modeling mechanism. This framework is applied to distributed systems, primarily focusing on continuous action spaces. The methodology decomposes the cooperative task into hierarchical sub-tasks, enabling efficient policy learning in complex multi-agent environments.
Introduction
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) offers promising solutions for multi-agent systems, but faces challenges such as high-dimensional action spaces and non-stationarity induced by dynamic agent policies. Traditional approaches like Centralized Reinforcement Learning (CRL) and Centralized Training with Decentralized Execution (CTDE) encounter scalability issues and inefficiencies in communication-heavy scenarios. The proposed approach, Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning with Opponent Modeling (HERO), addresses these challenges by structuring decision-making into high-level cooperative policy layers and low-level individual control policies.
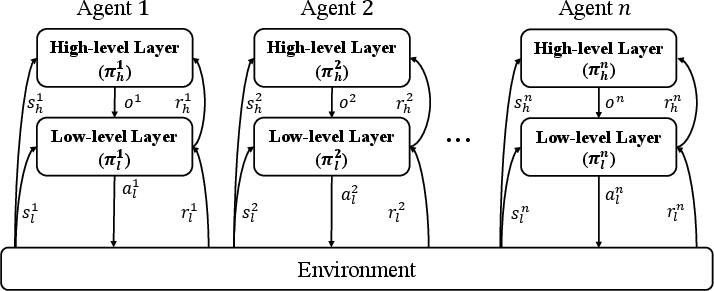
Figure 1: Illustration of hierarchical reinforcement learning for distributed multi-agent cooperation. Each agent maintains a high-level cooperation layer and a low-level individual control layer.
HERO Framework
Hierarchical Model Structure
The proposed HRL model consists of a high-level layer, which efficiently learns cooperative strategies in a discrete action space, and a low-level layer that manages individual control policies. This separation reduces overall task complexity by allowing each layer to focus on more manageable sub-components of the task.
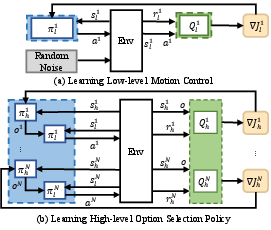
Figure 2: Two-stage training structure of HERO. (a) Each individual agent learns different individual control policy with random noise in the first stage. (b) Multiple agents learn to select options in the second stage.
Opponent Modeling
An opponent modeling mechanism is integrated into the high-level layer to predict other agents' behaviors, thereby promoting cooperation. This model learns opponent strategies without requiring direct policy access, improving stability and training efficiency in non-stationary environments.
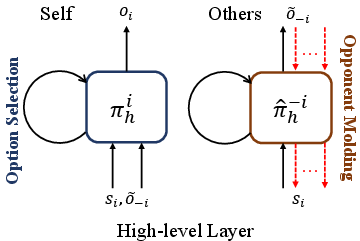
Figure 3: Illustration of the high-level opponent modeling in high-level layer. Each agent maintain a self policy network for its option selection and an opponent modeling network for other agents' option prediction.
Case Study: Cooperative Lane Change
A real-world cooperative driving scenario is used to validate HERO. In this scenario, vehicles must coordinate during lane changes to avoid collisions, improve traffic flow, and enhance safety. The hierarchical structure allows each vehicle to select between lane-keeping, acceleration, and lane change options, while the low-level control policies handle vehicle dynamics.
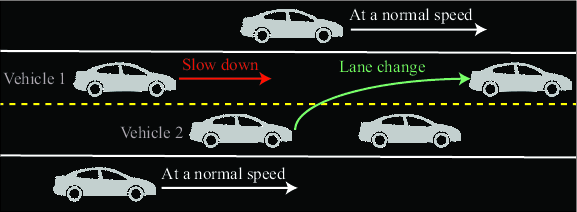
Figure 4: Illustration of the cooperative lane change scenario, where the vehicle 1 should coordinate with vehicle 2 to avoid the collision when vehicle 2 is performing the lane change.
Experimental Evaluation
HERO was tested in both simulation environments and real-world setups. The experiments demonstrate HERO's ability to achieve lower collision rates and higher task completion speeds compared to state-of-the-art MARL baselines such as Independent DQN, COMA, MADDPG, and MAAC.
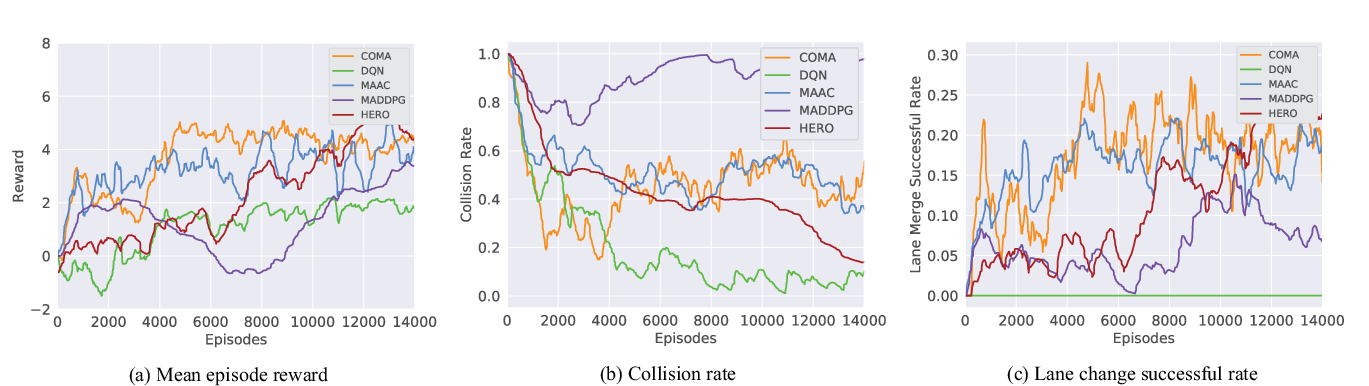
Figure 5: Comparison of the learning curve of different approaches in the cooperative lane change scenarios.
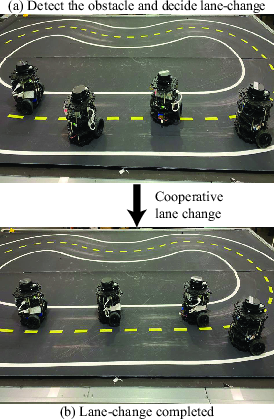
Figure 6: Real-world evaluation.
Conclusion
HERO presents a structured method for improving multi-agent cooperation in distributed systems, combining hierarchical task decomposition with opponent modeling. It effectively manages complex coordination tasks and has practical applications in autonomous systems, offering improved safety and efficiency. Future investigations will focus on automatic discovery of task hierarchies and bridging the gap between simulated and real-world implementations.







